Redermalization is a non-surgical rejuvenation method carried out by intradermal injection of the drug Hyalual. The serum has a unique composition. The action of the components is aimed at activating intercellular metabolism, leading to enhanced regeneration of fading tissue.
The technology provides a pronounced and sustainable improvement in skin quality. Experienced cosmetologists at the TRINITY clinic will help restore your youth and beauty with the help of the innovative Hyalual product.
Why does the body age?
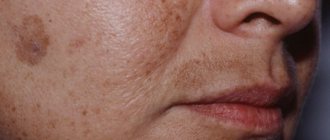
Aging is an inevitable biological process. The first signs of skin changes appear after 25 years, when thin, barely noticeable lines begin to appear on the surface. Wrinkles gradually form and deepen over time. The layers of the dermis become looser, density and elasticity decrease, and volume is lost.
The main reasons are a decrease in metabolic rate, a decrease in the production of active substances (enzymes, hormones, hyaluronic acid, fibrillar proteins, etc.). Poor ecology leads to dehydration and the accumulation of free radicals that damage cells. The causes of early aging can be active facial expressions, fluctuations in body weight, and smoking.
Methods of modern aesthetic cosmetology will help stop the process and start the clock in the opposite direction. One of these techniques is hyalual redermalization.
Biorevitalization Hyalual
Hyalual is a biorevitalizant that contains not only hyaluronic acid. Its feature is succinic acid, which is not found in other biorevitalization preparations. It eliminates puffiness, fights free radicals and improves energy exchange in tissues.
25% discount all January on mesotherapy and biorevitalization with any drugs in stock
Save 25%
Save 25%
Promotion until 31.01
More details
Peculiarities
Injections with Hyalual are aimed not only at moisturizing the skin. Succinic acid is needed in it in order to block the action of free radicals. A free radical is a molecule without a pair of electrons. But she needs a pair, so she begins to take electrons from healthy cells. When this happens, an oxidation reaction begins, and the tissues are irreversibly destroyed. This is how our skin loses elasticity and wrinkles appear on it. It turns out that biorevitalization with Hyalual helps us fight the very cause of aging.
Result of the procedure
At the body level this is the procedure:
- improves lymph flow and eliminates swelling
- protects cells from damage
- stimulates nutrient intake
- accelerates protein synthesis.
But visually the result will be like this:
- the skin will become moisturized and dense, and wrinkles will be reduced
- the severity of inflammatory processes (acne) will decrease
- tissue tone will moderately improve.
The concentration of the drug at 2.2% provides not only the effect of hydration and general rejuvenation. If you introduce it at special points, you can achieve a good lifting effect!
Typically, patients are recommended a course of 3-4 sessions, with a break of three weeks between procedures. Ideally, 2 courses per year are required, but the doctor can change the recommendations according to the indications of a particular patient.
Contraindications and rehabilitation
The doctor may refuse the procedure if the patient has inflammation or problems with blood clotting. If you have a cold or are in the acute stage of a chronic disease, it is better not to undergo the procedure. Biorevitalization is not yet performed for pregnant and nursing mothers.
Biorevitalization with Hyalual has several side effects that are considered normal and expected: swelling, papules, hematomas. They will go away on their own within a few days. Then you can observe the skin and evaluate the changes that occur in it. But the final effect should be assessed after completing the course prescribed by the doctor.
Redermalization of facial skin: what is it?
Redermalization is a method that affects all key components of aging: it stimulates cellular metabolism, initiates rehydration, and has an antioxidant effect. By accelerating biochemical reactions, it helps restore tissue metabolism.
Activation of processes leads to normalization of the production of collagen, elastin, and other components necessary for rejuvenation. Cell respiration improves and the dermis is deeply hydrated. The result of skin redermalization with Hyalual is: a smooth, elastic surface without wrinkles, a beautiful healthy color of the epidermis.
Hyalual: composition of the drug.
Hyalual is a famous Swiss brand that produces redermalization products, as well as skin care cosmetics for the face and body. The institute has its own research laboratories, in which unique formulas for future products are created. Production bases are located in different countries of the world, but due to careful control from the center, the high quality of products does not suffer from this.
The restorative effect of skin redermalization products is achieved thanks to the highly effective components included in their composition.
Succinic acid.
The injections contain carboxylic acid in the form of a sodium salt (succinate). This is a natural substance for the body. It is formed during the breakdown of nutrients supplied with food.
Colorless crystals are excellent nutrition for mitochondria (“energy intracellular stations”). By absorbing succinate, the organelle enhances the energy production necessary for cellular biological processes.
Under the influence of sodium succinate, the following processes occur:
• gas exchange is activated (the flow of oxygen into the cell is normalized);
• local blood circulation improves;
• local immunity is established;
• stimulates the production of fibrillar proteins;
• new capillaries begin to form;
• free radicals are inactivated;
• the process of regeneration of epithelial cells is accelerated.
When administered intradermally, sodium succinate increases the elasticity and firmness of the skin, evens out its texture and color.
Hyaluronic acid.
Hyaluronate is a biological polymer that is the main component of the intercellular matrix. The substance molecule is highly hydrophilic. It is able to attract large amounts of water, which provides an intense moisturizing effect.
The production of polysaccharide decreases significantly over the years. This leads to sagging, dry skin.
Hyaluronic acid takes part in cellular homeostasis and has anti-inflammatory properties. It activates the production of natural non-sulfonated glycosaminoglycan and fibrillar proteins. In combination with succinates, it helps strengthen vascular walls, reduce the severity of rosacea and pigmentation.
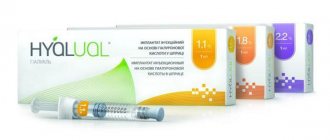
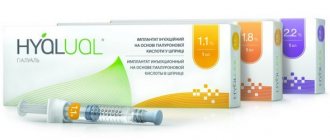
Varieties of the drug.
The cosmetic product Hyalual can be used to redermalize the face and different areas of the body: arms, abdomen, décolleté, neck, etc. The drug is available in three modifications. They differ in the concentration of hyaluronic acid.
| Variety | Sodium succinate, % | HA, mg/ml | Notes |
| Hyalual 1.1% | 1,6 | 11 | More often used as a prophylactic composition. Used for young skin (18–35 years old) with facial wrinkles. Prescribed at the preparatory stage before acid peeling, plastic surgery and after these interventions. Effective for correcting post-acne, oily skin, pigmentation. |
| Hyalual 1.8% | 1,6 | 18 | Used for skin redermalization in patients over 35 years of age. Purpose: prevention and elimination of aesthetic defects: • facial, gravitational wrinkles of varying severity; • age-related tissue ptosis; • violation of the oval, etc. |
| Hyalual 2.2% | 1,6 | 22 | The highly concentrated composition is used for deep age-related changes (< 45 years) for the purpose of: • rehydration; • correction of chrono-, photoaging; • lifting. |
In addition to cosmetology, branded drugs have found application in medicine. The drug Hyalual Artro
used in traumatology and orthopedics for degenerative lesions of articular cartilage as a replacement for lost synovial fluid.
Buy Hyalual Arthro synovial fluid prosthesis 1.8% 2ml No. 1 in pharmacies
Dosage forms implant synovial fluid 1.8% 2ml
International nonproprietary name: Synovial fluid prosthesis
Composition Hyalual Artro synovial fluid implant 1.8% 2ml 1.8% synovial fluid implant adjusted with succinate buffer solution to pH 5-8
Group: Means that replace synovial and tear fluid
ManufacturersYuria-Pharm (Ukraine)
Indications for use
Hyalual Artro synovial fluid implant 1.8% 2ml Hyalual Artro synovial fluid implants are used for traumatic and degenerative joint lesions, and pathological changes in synovial fluid or to reduce it.
Directions for use and dosage
Hyalual Artro synovial fluid implant 1.8% 2ml Hyalual Artro synovial fluid implant is injected into the damaged joint in adults at intervals of 1 ml or 2 ml depending on the size of the joint. The course of therapy is 3-5 injections into one joint, depending on the severity of the disease. The interval between administrations is 7-10 days. Simultaneous treatment of 2 joints is allowed. If necessary, repeated courses of injections may be prescribed.
Contraindications Hyalual Artro implant synovial fluid 1.8% 2ml - active inflammatory processes in the places of intended injection and adjacent areas; - tendency to form hypertrophic scars; - tendency to bleeding; - thrombolytic or anticoagulant therapy during the last 2 weeks; - increased sensitivity to hyaluronic acid; - acute viral or bacterial infections or related conditions; - pregnancy and breastfeeding.
pharmachologic effect
The uniqueness of the mechanism of action is due to the specific action of the components of the drug. Hyaluronic acid in Hyalual Artro normalizes the visco-elastic, shock-absorbing and lubricating properties of synovial fluid, stimulates the natural formation of hyaluronic acid and the synthesis of components of the extracellular matrix of cartilage. Succinate normalizes intracellular metabolism of joint tissue and a number of physiological indicators within cells. Taken together, Hyalual Artro reduces the degenerative processes of cartilage, exhibits anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects, improves the functional state of joints and the patient’s overall quality of life.
Side effect
Hyalual Artro implant synovial fluid 1.8% 2ml - reactions characteristic of injection sites: redness, swelling, pain, induration, itching, bruising, and soreness at the implantation site. Usually these phenomena disappear within a few days after injection into the skin. - swelling of the joints and/or pain at the site of intra-articular injection. These symptoms are temporary and disappear within a few hours after injection of the drug.
Overdose
No data.
Interaction
Hyalual Artro implant synovial fluid 1.8% 2ml No data.
special instructions
Follow the rules of asepsis and antisepsis when performing procedures. The use of local or regional anesthesia is allowed. Connect the needle and syringe tightly. Before starting the procedure, gently press the plunger until a small drop forms at the end of the needle. — the product is intended for intradermal injections. Synovial fluid implants are administered intra-articularly; — do not use if the primary packaging is damaged; — the product is intended for single use only; — do not subject Hyalual Artro to repeated sterilization; - avoid unintentional injection into blood vessels; — do not insert into areas where a permanent implant of a different composition was previously implanted; - strictly adhere to the technique of intra-articular injections under sterile conditions and take care not to damage the joint capsule during the injection. Hyalual Artro should be inserted exactly into the joint cavity; - synovial fluid implants should not be prescribed to children, since there are no clinical trials regarding the effectiveness and safety of Hyalual in children under 18 years of age. Other Safety Precautions: Regular safety precautions associated with injections should be followed. The injection site should not be subjected to intense heating or strong cooling until the primary swelling and redness disappears. Until the normal state of the skin is completely restored after implantation, do not use laser irradiation, chemical peeling or other procedures that may contribute to the development of inflammatory reactions at the implantation site. Any side effects should be reported to your doctor immediately and the manufacturer informed. The syringe, needles and all remnants of unused drug must be disposed of immediately after the procedure.
Storage conditions
Store in a dry place, protected from light, out of reach of children, at a temperature not exceeding +25C. Freezing is not allowed.
Differences between redermalization and biorevitalization.
Patients of beauty clinics do not always understand the difference between Hyalual redermalization and biorevitalization. Both procedures are very similar in technique. The difference lies in the composition of the drugs, and accordingly in the effect they provide.
Widespread biorevitalization involves saturating the skin layers with hyaluronic acid. The main goal of the manipulation is intensive hydration, which achieves a rejuvenating effect.
Redermalization is carried out with a complex preparation that, in addition to hyaluronate, contains succinates. Due to the additional ingredient, the tissues are not only saturated with moisture, but also important biochemical intracellular cycles are stimulated. As a result, the dermal layers are restored from the inside.
Algorithm for the procedure.
Hyalual redermalization does not require special preparation. If the patient is taking blood thinning medications, then the medications must be discontinued a few days before the session (only in consultation with the doctor who prescribed them).
Before the procedure, a consultation with a cosmetologist-dermatologist is carried out. The doctor collects anamnesis, identifies the presence of contraindications, and examines the skin. During the inspection, pay attention to the following points:
• nature of changes in the dermis (age-related, photoaging, hormonal aging);
• degree of sensitivity and dehydration of the integument;
• the presence of inflammation in the area of intended treatment with Hyalual;
• skin type (oily, dry, mixed), etc.
The duration of the session depends on the amount of work (20 – 45 minutes). The drug is injected into the middle layer of the dermis, where there is the highest level of proliferation and sufficient activity of fibroblast cells. The injection technique is determined by the type of drug, the age of the patient, and the area of the redermalization zone.
The number of sessions required to obtain maximum effect is determined by the cosmetologist. For minor defects, 1–2 procedures may be sufficient. For deeper disorders, you will need to visit the clinic at least 3-4 times. The interval between visits is from 14 to 28 days.
Sequence of manipulations
Hyalual rejuvenation consists of several successive stages:
1. Cleansing the cover. Using products selected according to the client’s skin type, the doctor cleanses the skin of cosmetics and dust.
2. Antiseptic treatment (Miramistin, Chlorhexidine, other antiseptics).
3. Pain relief with local anesthetics. Use creams, gels, sprays containing lidocaine.
4. Carrying out injections with Hyalual. The tip of the needle is inserted to a depth of 0.2 cm. After several injections, the cosmetologist gives a light massage to the treated area. This tactic allows you to evenly distribute the product inside the skin.
5. Redermalization ends with repeated disinfection.
After the Hyalual procedure, slight hyperemia and swelling of the skin is observed. Small hematomas are possible. Within about a day, the dots left by the needle puncture are visible. Such consequences are not complications, do not require treatment, and go away on their own.
Osteoarthritis of the knee joint
Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common disease of synovial joints, caused by the action of biological and mechanical factors that upset the balance between the processes of degradation and synthesis of chodrocytes, extracellular matrix of articular cartilage and subchondral bone, which are the main cause of chronic pain syndrome, causing gait disturbances, disability and significant deterioration in the quality of life of patients. Osteoarthritis occurs predominantly in 65-85% of people in the older age group (over 65-65 years old). The general trend towards an increase in the proportion of older people in the population is accompanied by an increase in the prevalence of osteoarthritis, significant financial costs for its treatment and disability of patients, which determines the high socio-economic significance of this problem.
There are predispositions to the development of OA, which can be divided into modifiable and non-modifiable. Modifiable factors include: obesity, injury, disruption of the biomechanics of movements in a particular joint, habitual overload of the joints. Non-modifiable risk factors for development include: age, gender, heredity, race, congenital diseases, endocrine and metabolic disorders.
There are two forms of OA: idiopathic (when the exact cause of the disease is unknown) and secondary (when the cause is known).
The development of osteoarthritis always begins with pathological microscopic changes in cartilage tissues, which are not clinically manifested, while the period of subclinical manifestations can vary in duration - from 2 to 6 years. Cartilage tissue is damaged under the influence of mechanical or metabolic changes, it becomes thinner, with the formation of ulcers. Subsequently, the meniscus, ligamentous apparatus, periarticular bursa and proliferation of adjacent bone structures occur in the process. The narrowing of the joint space is accompanied by a decrease in the production of synovial fluid, friction of the articular surfaces and additional secondary destruction of cartilage tissue.
Inflammatory markers (cytokines, tumor necrosis factor) contribute to the appearance of pain. At the early stage of OA, interleukins 1.6 (IL-1.6), tumor necrosis factor-a (TNF-a) increase the synthesis of serum CRP and amyloid A. In the later stages of OA, the presence of synovitis correlates with both plasma CRP and the level of IL-6 in synovial fluid. In addition, the intensity of pain in gonarthrosis increases with increasing levels of serum CRP, TNF-a and IL-6.
In addition, blood circulation in the joint and adjacent tissues is simultaneously impaired, which leads to the development of secondary osteoporosis. Reflex muscle disorders occur around the joint, which create an additional mechanism for the formation of pain and limitation of mobility.
In turn, a decrease in motor activity in the joint leads to a decrease in the production of synovial fluid in it, which provides nutrition to the cartilage tissue and the removal of metabolic products from the joint cavity. A “vicious circle of osteoarthritis” is formed - a decrease in the production of synovial fluid increases the degree of damage to cartilage tissue.
Treatment of patients with OA includes a complex of measures consisting of a physical rehabilitation program (load limitation, correction of orthopedic disorders, physical therapy regimens), drugs with anti-inflammatory activity and drugs aimed at reducing pain and slowing down structural damage in joint tissues (SYSADOA - Symptomatic slow acting drugs for osteoarthritis). Of great importance is the impact on the metabolism of cartilage tissue in order to restore the balance between the load and the reparative capabilities of chondrocytes. For this purpose, slow-acting symptom-modifying or neuroprotective drugs are used. Currently, a large number of international and national recommendations for the treatment of OA have been proposed. According to these recommendations, in addition to the general principles of managing patients with OA, which include educational programs for weight loss and aerobic exercise, the prescription of not only paracetamol, NSAIDs, glucosamine sulfate and chondroitin sulfate, but also intra-articular administration of hyaluronic acid and topical glucocorticoids is indicated. In recent years, hyaluronic acid (HA) preparations, having a minimal risk of systemic side effects, have found widespread use in OA of the knee joints. Intra-articular therapy using GLA derivatives is approved by the world's professional rheumatology and orthopedic organizations as a symptomatic treatment for patients under 65 years of age who have not responded to non-pharmacologic treatments and simple analgesics or who have contraindications to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) therapy (ACR, 2000, 2012 ; OARSI, 2010; EULAR 2003, ESCEO 2014).
So what is hyaluronic acid and through what mechanisms does it act on the disease?
Hyaluronan is a biological fluid that occurs in synovial fluid and is quite ubiquitous throughout the body. Hyaluronan is a polyanionic (negatively charged) polysaccharide, also known as glycosaminoglycan, which consists of alternating units of N-acetylglucosamine and sodium glucuronate molecules. The length of such a polysaccharide chain can reach 12 thousand disaccharide units, and the molecular weight is 4-6 million daltons. Biosynthesis of hyaluronan occurs on the inner surface of the cell membrane of fibroblastic differential cells with the participation of hyaluronan synthase (HAS). As the concentration of polysaccharides increases (above the saturation point), the long chains begin to overlap and become entangled, forming a cross-linked network or matrix.
In synovial joints, hyaluronan is produced by hyalocytes (mononuclear phagocytic cells) and released into the synovial fluid. Constant movement in the joint promotes the passage of hyaluronan into the acellular superficial layer of articular cartilage, where it is present in a concentration 5 times higher than in the deep layers of cartilage. Hyaluronan also penetrates into the extracellular matrix of the extracellular synovial tissue and capsule, filling the collagen matrix of the extracellular substance, where proteoglycans attach to it. The concentration of hyaluronan in normal synovial fluid is 2-4 mg/ml, which is 10 times higher than required for saturation. At such a high concentration, hyaluronan forms a continuous network of polysaccharide molecules surrounding collagen fibers. The primary function of haluronan in a healthy joint is to coat and protect the synovium and superficial collagen structure of cartilage from mechanical damage caused by friction due to flexion or body weight loading of the joint. The elastic-viscous nature of the network formed by hyaluronan allows it to adapt to applied mechanical load (both low-energy (flexion), where the hyaluronan molecules align in the direction of flow and behave like a viscous fluid, dissipating mechanical energy in the form of heat; and high-energy (impact) , exhibiting elastic properties, being absorbed to such a level that the energy is dissipated in a viscous flow.)
In addition to its rheological and mechanical functions, hyaluronan is able to physically inhibit the passage of large molecules such as fibrinogen into the joint space.
Currently, the pharmaceutical market offers more than twenty types of GLA preparations for intra-articular administration, differing in molecular weight (from 5 to 10,000 kDa), origin (natural, biosynthetic), molecular structure (linear or cross-linked), concentration (from 1 to 2%), the volume of the administered drug (from 1 to 3 ml), the number of injections per course (from one to five).
By origin they distinguish: 1) preparations obtained from cockscombs: Gialgan, Gialux, Atri Inzh, Rusvisk, Giruan Plus. 2) biosynthetic, obtained by bacterial fermentation: Ostenil, Fermatron, Sinokrom, Visco Plus, Suplazin. Preparations obtained from rooster combs can cause allergic reactions because they contain protein fragments and other pyrogens.
According to the structure of the molecule, hyaluronates are divided into: 1) native (from the word - nature-natural) long molecules obtained by bacterial synthesis: Fermatron, Ostenil, Sinokrom, Fermatron Plus, Suplasin. 2) so-called modified, cross-linked molecules: Duralan, Fermatron S, Synvisc. (Cross-linking of HA molecules is provided by two mechanisms: physical, due to electrostatic interaction, and chemical, due to the formation of covalent bonds. Since chemical stabilization is more resistant to temperature changes, it is preferable .
Hyaluronic acid preparations, which can be divided into 3 groups, depending on molecular weight. Molecular weight is one of the main characteristics that ensures the duration of the therapeutic effect of medications for intra-articular injections.
The rate of polymer degradation depends on the molecular weight. At low molecular weight, the polymer will quickly undergo separation until the molecular weight is reduced to critical values and the drug is excreted from the body in the form of monomers and short linear polymers.
In the case of a high molecular weight, the degradation of the polymer will occur slowly, and accordingly the therapeutic effect will be prolonged.
| Low molecular weight | 500,000 – 800,000 Yes | well tolerated by patients, require a large number of injections per course and minimal duration of action due to rapid removal from the joint |
| Average molecular weight | 800,000 – 2,500,000 Yes | are the most common for use, require about 5 injections per course and have a short duration of action. |
| High molecular weight | from 2,500,000 Yes | are removed from the joint more slowly, have a long-lasting effect and require a minimum number of injections per course. |
The main preparations of HA depending on the molecular weight, structure of the molecules and accompanying additives.
| Drug name | Molecular mass |
| Low molecular weight Hyalgan Fidia (Hyalgan Fidia) | 500 000-730 000 |
| Suplasyn (Suplasin)/Suplasyn 1-shot (Suplasin 1-Shot) | 500 000-1000 000 |
| Average molecular weight of Jointex (Jointex)/Jointex Starter (Jointex Starter) | 800 000-1200 000 |
| Intragel (Intragel) | 800 000-1 200 000 |
| Fermathron (Fermatron)/Fermathron Plus (Fermatron Plus) | 1000 000 |
| Ortholure (Ortolur) | 1200 000 |
| Viscoseal (Viskosil) | 1200 000 |
| GO-ON (Go-On) | 1400 000 |
| Ostenil (Ostenil)/Ostenil mini (Ostenil mini) | 1400 000-1700 000 |
| Synocrom/Synocrom mini | 1600 000 |
| ViscoPlus (ViskoPlus) | 2 000 000 |
| Synocrom forte (Sinokrom Forte) | 2 100 000 |
| Hyruan Plus (Giruan Plus), Hialux (Hyalux) | 3 000 000 |
| VERSAN FLUID(Switzerland) | 1 200 000 |
| Giastat | 3 000 000 |
| RusVisk | 3 500 000 |
| High molecular weight Synvisc (Hylan GF 20) (Synvisc (Hylan GF 20)) | 6,000,000-7,000,000 (cross-linked) |
| Preparations with the presence of cross-linked molecules Durolane (Duralan)/Durolane SJ (Duralan SJ) | 1000 000 (cross-linked) |
| Synvisc (Hylan GF 20) | 6,000,000-7,000,000 (cross-linked) |
| Fermathron S | No data (cross-linked) |
| Hyruan ONE ( Korea) | No data ( cross-linked) |
| Preparations with active accompanying additives Ostenil Plus (Ostenil Plus) | 1400 000-1700 000 (mannitol) |
| Hyalual Artro (Hialual Artro) | 3,000,000 (sodium succinate) |
Molecular weights are based on data published by the manufacturer or in the scientific press.
Low molecular weight HA drugs are quite well tolerated by patients when administered intra-articularly. Low molecular weight causes rapid breakdown of HA molecules in the joint and tissues. Literature data provide grounds for intentionally using low molecular weight HA preparations (500-750 kDa) of animal origin for extra-articular injections. We are talking about localizations where there is synovial tissue and HA is naturally produced to carry out metabolic processes, in particular the synovial sheaths and synovial membranes of tendons during chronic inflammation in this area (tendinitis, tenosynovitis, bursitis).
Medium molecular weight HA preparations represent the largest group. All of them are products of bacterial fermentation and in most cases are well tolerated by patients, but just like drugs with low molecular weight, they require 3 to 5 injections per course. A distinctive feature of some drugs from this group is the possibility of their use for injection into the joint cavity immediately after arthroscopic intervention for the speedy restoration of intra-articular metabolism.
HA preparations with active accompanying additives form a separate group, since along with the described properties they acquire new qualities.
A special group consists of GC preparations with the presence of cross-linked molecules. The presence of a significant number of intermolecular cross-links makes it possible to achieve a more pronounced analgesic effect by improving the shock-absorbing properties of the synovial fluid. Innovative technologies used in the production of this group of drugs have provided unique properties. The large number of cross-links and molecular structure allow for a single injection into the joint. The half-life can approach 4 weeks, which creates the preconditions for long-term catabolism. The transition from 3-5 injections to a single injection is a significant clinical benefit.
Let's consider the evidence for a broader role for NA in the treatment of OA beyond joint shock absorption and lubrication. Exogenous HA may reduce pain transmission and blunt the inflammatory cascade through the CD44 receptor, which is associated with OA, as well as stimulate the synthesis and deposition of extracellular matrix molecules, which are suppressed and degraded in the osteoarthritic joint. The effect of HA depends on the fragment size. In particular, long-chain high molecular weight HA is anti-inflammatory and can stimulate endogenous HA production, whereas shorter chain HA fragments are pro-inflammatory and can inhibit HA production at high concentrations.
The role of GC on disease progression.
Decreased HA synthesis, increased HA degradation, and increased oxidative stress lead to a decrease in both the concentration and average molecular weight of HA present in the synovium. Several studies have shown that exposure of chondrocytes and fibroblasts to HM HA fragments (<400 kDa) can cause increased activity of proinflammatory cytokines. In addition, it has been shown that the levels of IL-18 and IL-33 increase in mouse synovial fibroblasts after exposure to HA fragments, and that HA fragments enhance the inflammatory activity of macrophages. In contrast, high molecular weight hyaluronic acid has the opposite effect on some of these systems, inhibiting mediators such as TNF-α and IL-1β. HA receptor activity may be responsible for the long-lasting pain-relieving effect of intra-articular HA therapy, although the residence time of the exogenous molecule in the joint is quite short.
Hyaluronan products have certain rheological properties that inhibit nociceptors, acting as an elastic filter. There is also a reaction to chemical sensitization of nociceptors in inflamed joint tissues, possibly related to HA concentrations. Results from a study in cats with experimental arthritis showed that intra-articular injection of high molecular weight GC reduced the activity of nociceptive primary afferents at the onset and during movement, suggesting that joint lubrication is not solely responsible for the antinociceptive effects of NA.
Recently, single intra-articular injections of NA were shown to reduce pain by more than 50% compared with saline in the bradykinin/prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) model. Use of an anti-CD44 antibody abolished the inhibitory effects of NA on LPS-mediated increase in PGE2 production and COX-2 induction , indicating that the anti-inflammatory effect of GC was CD44 receptor mediated. Additional mechanisms that may contribute to the antinociceptive effects of GCs include inhibition of arachidonic acid release from fibroblasts and activation of opioid receptors. Exposure to GCs has been shown to reduce the secretion of arachidonic acid from fibroblasts taken from patients with knee OA and is stimulated by bradykinin. The results of one study showed that, in contrast to anti-inflammatory drugs, pain reduction resulting from GC administration was associated with stimulation of cartilage regeneration. The effects of NA and loxoprofen in the joint were experimentally compared. Both HA and loxoprofen significantly reduced pain in the rabbit OA model (partial menisectomy) and also reduced PGE2 production. Hyaluronic therapy also significantly inhibited cartilage degeneration, whereas loxoprofen did not.
Inflammatory effects.
High molecular weight HA may inhibit the inflammatory processes involved in OA by interfering with the effects of HM HA fragments on CD44, RHAMM, and TLR-2 and TLR-4. Results from in vitro and in vivo studies indicate that administration of high molecular weight GC has significant anti-inflammatory effects that are mediated, at least in part, by CD44 blockade. Administration of high molecular weight hyaluronic acid leads to suppression of IL-8 and NO synthase gene expression in cells that were not stimulated by IL-1. In cells that were stimulated with IL-1, TNF-α gene expression was also suppressed. Blocking CD44 with a specific antibody inhibited the effects of high molecular weight HA on proinflammatory gene expression. Recently, high molecular weight hyaluronic acid has also been shown to suppress IL-1β production in monocyte/macrophage cultures under various inflammatory conditions. Provision of IL-1β and TNF-α by GCs has important downstream effects on the expression of proinflammatory and catabolic molecules. IL-1β induces ADAMTS through p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and NH2-terminal kinase phosphorylation in human fibroblast-like synovocytes. ADAMTS degrade aggrecan in cartilage; High molecular weight hyaluronic acid also suppresses ADAMTS expression. IL-1β suppresses peroxime proliferation-activating receptors. (PPARγ) . ( Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs), ligand-activated nuclear transcription factors (NTFs) from the hormonal receptor family, regulate the metabolism of fats and carbohydrates, cholesterol and bile acids, inflammation, regeneration and differentiation/proliferation of liver cells. All PPAR isoforms ( PARα, PPARβ/δ, PPARγ) are present in the liver, Activation of PPARs receptors most effectively reduces chronic inflammatory processes and has a lesser effect on acute inflammation. PPARα not only affects lipid metabolism and transport, FA oxidation and glucose homeostasis, but also exhibits anti-inflammatory effects effects. These effects are associated with inhibition of proinflammatory cytokines, adhesion molecules and extracellular matrix proteins or stimulation of the production of anti-inflammatory molecules. In general, PPARα reduces the production of proinflammatory cytokines, which limits inflammatory reactions and atherogenesis). PPAR activity is regulated by products of lipid metabolism and other natural and synthetic activators and increases the expression of MMPs. Results from a study examining the expression of inflammatory genes in human chondrosarcoma cells induced by IL-1β show that high molecular weight hyaluronic acid increases the expression of PPARγ and decreases that of COX-2, MMP-1 and MMP-13. Additional anti-inflammatory effects of GC are achieved through the suppression of mitogen-activated protein kinases and nuclear factor signaling. In a rabbit model that induced OA through injection of sterile papain into the knee, intra-articular injection of HA resulted in a significant decrease in IL-1β and TNF-α expression and an increase in TIMP-1 expression compared with intra-articular saline controls. GC treatment also resulted in chondrocyte proliferation in this model. Exogenous HA also reduces levels of inflammatory cytokines and MMPs in tissues collected from patients with OA and other conditions associated with joint damage. In one study, subacromial synovial fibroblasts were taken from patients with rotator cuff disease and stimulated with IL-1β. The addition of GC resulted in a dose-dependent decrease in the expression of IL-1β, TNF-α and IL-6. These effects of GC were lost when CD44 was blocked by anti-CD44 antibody. Incubation with GC has also been shown to inhibit IL-1β-induced MMP activity in synovial tissue from patients.
Changes in the extracellular matrix alter the biomechanical environment of chondrocytes and lead to disease progression. The ECM is integrally involved in the development and progression of OA, and its preservation and restoration have become the focus of treatment. The results of several studies have shown that exogenous NA can increase the synthesis of ESM molecules. Exogenous HA stimulates synovial fibroblasts to produce new HA. When synovial fibroblasts from the knees of osteoarthritis rabbits were cultured with HA formulations of varying molecular weights, the amount of newly synthesized HA depended on both the concentration and molecular weight of exogenous HA. Higher molecular weight agents stimulated GA synthesis more strongly, while low molecular weight GAs suppressed GA synthesis when used in high concentrations. Two additional studies showed that intra-articular injection of HA in patients with OA increased endogenous NA production. In in vitro experiments, treatment of bovine articular chondrocytes with HA caused a significant increase in the synthesis of sulfated glycosaminoglycan and hydroxyproline, which coincided with an increase in matrix deposition of chondroitin-6-sulfate and type II collagen. Mechanical stress leading to injury has been shown to result in the loss of proteoglycans from cartilage and may play a role in the development and progression of OA, whereas administration of HA has been shown to increase proteoglycan synthesis in cartilage exposed to mechanical stress. In 2007, a review of disease-modifying drugs for OA devoted only one paragraph to HA, stating that there was no evidence that HA provided a disease-modifying effect. This conclusion was based on the observation that intra-articular injection of HA into the knee had no significant effect on radiographic progression versus intra-articular saline over 1 year of follow-up.
A 2006 Cochrane review of randomized trials concluded that viscofilling with HA (or hylan derivatives) was superior to placebo in improving pain and function over several weeks. In addition, viscosupplementation has generally demonstrated benefits over a longer period of time compared with intra-articular corticosteroid injections. Systematic reviews have also shown the safety and effectiveness of GC over non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and other non-surgical treatments. It is becoming increasingly clear that NA influences a wide range of biological processes through multiple molecular pathways.
In October 2022, J Arthroplasty published one interesting study that compared injections of low, moderate, and high molecular weight hyaluronic acid during surgical delay. The study included 30,417 patients. The effectiveness of low molecular weight (MW) hyaluronic acid injections, moderate molecular weight HA (MMWHA) injections, and high molecular weight HA (HMWHA) injections for preventing or delaying knee surgery in patients with knee osteoarthritis was compared. According to the study results, there was no significant difference in the likelihood of surgery between LMWHA, MMWHA, and HMWHA users after controlling for empirically based factors.
Another study (double-blind, randomized, multicenter) (BMC Musculoskelet Disord, 2022 May 26) tested the efficacy and safety of a single injection of cross-linked sodium hyaluronate versus three injections of high molecular weight sodium hyaluronate for knee osteoarthritis.
Two hundred eighty-seven patients with osteoarthritis (Kellgren-Lawrence grades I-III) were randomized to each group. Three weeks of injections were given in both groups, but two physiological injections were preceded by cross-linked hyulronate injections to maintain double blindness. The primary endpoint was change in severe weight-bearing pain (WBP) 12 weeks after the last injection. Secondary endpoints included the Western Ontario and McMaster Osteoarthritis Index; global patient and investigator assessment; pain at rest, at night or with movement. This study showed that a single injection of cross-linked hyaluronan was as effective as three injections of high molecular weight sodium hyaluronate in reducing WBP.
In a review and analysis of 68 studies, products with an average molecular weight ≥3000 kDa provided favorable efficacy results compared with products with an average molecular weight <3000 kDa. Products with molecular weights ≥3000 kDa demonstrated significantly lower rates of discontinuation due to treatment-related side effects than their counterparts ≤1500 kDa. In addition, biological fermentation HA had a significantly lower incidence of effusion than HA obtained from poultry. Biological fermentation HA demonstrated fewer inflammatory responses at the injection site than avian-derived HA products. In the available literature, IA-GCs products with molecular weight ≥ 3000 kDa and those derived from biological fermentation show excellent clinical observations and minimal side effects.
Another interesting study was published in the journal Int J Mol Sci 2022 Mar 17, which compared the effectiveness and cost of treatment with stabilized hyaluronic acid (Durolane) in one injection with standard hyaluronic acid (HA) preparations in five injections for osteoarthritis (OA) of the knee. Patients were randomized into two groups: group I with intra-articular injection of NANA (Durolane®) and group II with HA (Go-ON®). Control examinations of patients were at the 1st, 2nd, 4th, 8th, 12th and 26th week after treatment. A statistically significant improvement in WOMAC score was observed in patients receiving NAHA compared to those receiving GC at week 26. In addition, the need for analgesia was significantly reduced at week 26 in the NANA-treated group. Finally, economic analysis showed an increased cost of overall treatment with HA injections. Our data supports the use of the ANAS class of products for the treatment of the knee joint
A systematic review and meta-analysis of electronic database data, including PubMed and Embase, conducted from January 1980 to November 2015 evaluated the effectiveness of 3 injections of sodium hyaluronate (Hyalgan) compared with 5 injections into the knee joint. The review included studies that assessed the effectiveness of a course of 3 or 5 weeks of intra-articular injections of Hyalgan for the treatment of OA knee pain. Clinical studies evaluating the effectiveness of a 3-week course of other US-approved hyaluronic acid products were also included. 24 studies were identified, including 2168 study participants in 30 cohorts processed. Meta-analysis results indicated that knee pain relief with a 3-week course of Gialgan was similar to a 5-week course of Gialgan (P = 0.916). The level of pain reduction from baseline pain with a 3-week course of Hyalgan is similar to a 3-week course of other HA products. There was no statistical difference between the reduction in knee pain with a 3-week course of Hyalgan compared to the reduction in OA knee pain with a 5-week course of Hyalgan or a three-week course of other HA products.
Groups of scientists conducted a meta-analysis of 20 studies with 3034 patients that compared the effectiveness of Synvisc with low molecular weight hyaluronic acids. According to the results, limited data showed a superior effect for hylan GF 20 compared to low molecular weight hyaluronic acid at 2 to 3 months after injection (assessed by VAS and WOMAC scores). There was no evidence of an increased risk of treatment-related side effects for hylan GF 20 injections.
Hylan GF 20 is a product of animal origin and consists of two fractions. Their molecular weight is 6 million Da, which is very close to healthy synovial fluid. This makes it possible to restore the viscoelastic properties of the synovial fluid to a greater extent and improve the functional state of the joint. The clinical effect of the drug has been demonstrated in numerous clinical studies: the analgesic effect of hylan GF 20 was longer lasting compared to standard NSAID therapy. - persisted in 28% of patients versus 6% of patients who took only NSAIDs and compared with intra-articular corticosteroids. — 56% of patients versus 37% of patients; this effect lasted significantly longer and also made it possible to delay endoprosthetics of the affected joint by 3.8 years. The use of hylan GF 20 for the treatment of OA has allowed patients to reduce the need for other medications. The design of the studies conducted with hylan GF 20 underscores their high degree of reliability. The clinical effectiveness of the drug is confirmed by the dynamics of laboratory parameters both in vitro and in vivo. In vitro, in a rabbit model of osteoarthritis, not only the chondroprotective effect of hylan GF 20 was shown, but also a decrease in the formation of osteophytes. It has also been found that hylan GF 20 can stimulate cartilage repair by increasing Col II and inhibits IL-1p-mediated cartilage matrix degradation by decreasing metalloproteinase activity. The chondroprotective effect of hylan GF 20 was also confirmed by the dynamics of serum levels of Coll2-1 and Coll2-1 NO2, which are biomarkers of OA. Three intra-articular injections of 2 ml of Synvisc led to a statistically significant decrease in their levels, while their dynamics were more pronounced in patients with stages III-IV of OA according to Kellgren.
Side effects with intra-articular administration of GC drugs rarely develop - on average in 1-13% of patients and are, as a rule, local in nature. Most often, pain occurs at the injection site. Any intra-articular injections may be accompanied by an inflammatory response, but the literature describes cases of the development of a clinically isolated reaction, known as a spontaneous acute inflammatory reaction (SAIR), during intra-articular administration of GC drugs to patients with OA. It is not yet clear, however, whether these pseudoseptic reactions are directly related to GC.
The technique of intra-articular administration of the drug is important: when using an anterior approach to the knee joint, the frequency of side effects is usually higher than when introducing GC into the joint through a lateral approach. This can be explained by the fact that in the first case the drug is sometimes administered not into the joint cavity, but paraarticularly.
The analysis of the literature on the role and properties of HA, the use of synovial fluid replacement agents based on it, indicates the high significance of this segment of therapy in the relief of articular and periarticular pain syndrome, and high efficiency in the complex treatment of OA. Drugs with high molecular weight demonstrate the longest analgesic effect up to 8-12 months and a more pronounced improvement in functional activity. Recent data and observations have made it possible to better understand the mechanisms of GC metabolism and determine the features of the use of GC preparations depending on the characteristics of production, molecular weight and other pharmacological and pharmacodynamic properties.
Skin care after redermalization with Hyalual.
The rehabilitation period after redermalization with Hyalual does not exceed 3–5 days. During this period, a number of rules must be observed:
• 24 hours after injection, do not touch the injection area with your hands;
• do not apply decorative and skincare cosmetics until the wounds are completely healed;
• on the recommendation of a cosmetologist, it is necessary to treat the skin with an antiseptic, use regenerating pharmaceutical products (Bepanten, Panthenol);
• exclude visiting the sauna, swimming pool, solarium;
• refuse to play sports;
• scrub and peeling can be carried out no earlier than 14 days after redermalization with Hyalual;
• protect covers from UV rays with high SPF.
It is not advisable for the patient to drink alcohol before and after redermalization. Ethanol reduces the activity of the drug Hyalual, which affects the final effect. After the procedure, it is recommended to drink more water. If signs of inflammation, allergies, or other undesirable reactions appear, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Skin redermalization Hyalual® (Hyalual)
- Description
- Sign up for the procedure
The new generation injection drug Hyalual ® acid , which affects all mechanisms of skin aging and achieves a powerful comprehensive anti-age effect.
What is redermalization:
- this is skin rejuvenation by restoring it
- this is a scientifically proven result
- this is a new life for your skin
Translated from Latin, the prefix “Re” means “restoration”; “derma” is the main layer of the skin, which is responsible for youth.
To implement the redermalization technique, a new generation injection drug Hyalual® , which affects all mechanisms of skin aging and provides a powerful comprehensive anti-age effect.
Why REDERMALIZATION?
- The technique is used to prevent chrono- and photoaging
- A technique that effectively combats already existing signs of aging
- A technique that protects skin from premature aging
Indications for the procedure:
Prevention of chrono- and photoaging;
- Prevention of early skin aging caused by stress (smoking, long-term use of chemicals, living in a metropolis, rehabilitation after serious illnesses);
- Correction of involutional changes in the skin (deep dehydration, wrinkles, hypotonia and atony of the skin, gravitational ptosis - changes in facial oval);
- Skin after acne (post-acne) - prevention and correction of scar changes;
- Physiological preparation of the skin for the correction of wrinkles and folds, atrophic scars and other skin defects (ensures improvement of the structure of the dermis before filling difficult-to-correct wrinkles);
- Correction and temporary filling of wrinkles;
- Preparing the skin for dermatoplastic surgeries, deep and medium peels in order to optimize the final result and reduce the rehabilitation period;
- Rehabilitation after peelings (chemical, mechanical) and plastic surgeries.
- Treatment of the scalp.
Redermalization effect:
What happens to skin cells during and after redermalization?
- powerful restorative effect;
- powerful antioxidant effect;
- powerful activation of metabolic (metabolic) processes in the skin: increased cellular and tissue respiration, ion transport, etc.;
- direct effect on the main cell of the skin - fibroblast, which stimulates its division and increased synthesis of two structural proteins - collagen and elastin, as well as the synthesis of its own hyaluronic acid, which maintains the water balance of the skin;
- increased microcirculation;
- powerful stimulation of energy production (ATP);
Result:
- Improved skin color;
- Improving skin texture and relief;
- Reducing the depth of wrinkles and their size;
- Skin lifting (tightening);
- Young and healthy skin;
- Lightening of age spots until they completely disappear;
- Prevention of neoplasms.
RE rejuvenation effect:
- As a result of a course of redermalization procedures, a comprehensive effective approach is implemented not only to eliminating the external manifestations of aging, but also to rejuvenation in general, slowing down the aging process of the skin through maximum restorative action, antioxidant action and blocking free radicals, activating metabolic processes in the skin, and moisturizing it. Small wrinkles are smoothed out, large ones become less noticeable, and the texture of your skin changes. Redermalization eliminates signs of fatigue by increasing microcirculation. The skin regains its youth and health, restores tone (turgor and elasticity), tightening occurs without the help of a surgical scalpel.
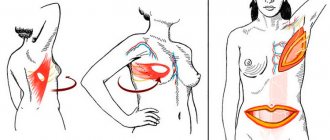
- Facial correction areas: periorbital zone, face lifting, restoration of the perioral zone and red border of the lips, treatment of wrinkles (glabellar and horizontal forehead wrinkles, nasolabial, crow's feet), neck, décolleté, ear skin correction (pretragal zone, earlobe).
- Body correction areas: legs (inner thighs, knees), arms (inner shoulders, elbows), abdomen, buttocks, mammary glands.
Hyalual ® is:
- the world's first ready-to-use preparations that act on all pathogenetic mechanisms of skin aging and provide a powerful comprehensive anti-age effect;
- a new generation of injectable anti-age drugs;
- innovation in anti-age therapy for men and women;
- basic preparation for redermalization;
- proven effectiveness and safety by preclinical and clinical studies;
- products registered in Russia;
- high biocompatibility and hypoallergenic drugs;
- products manufactured according to European quality standards (ISO 9001:2001, GMP)
Sign up now!, 211-08-66
The cost of the service can be found in the price list of the Belle Allure Beauty Institute.
Up…
Sign up for the procedure
Undesirable consequences.
Hyalual redermalization, like any injection technique, is associated with a primary violation of the epidermis. Most complications that appear after cosmetic surgery occur due to a nonspecific reaction to damage to the integrity of the skin and the development of inflammation.
After redermalization the following complications are possible:
• hyperemia, hematomas, edema;
• papules, noticeable puncture sites;
• short-term loss of sensitivity in certain areas of the skin;
• itchy skin rashes;
• hypersensitivity reaction;
• addition of a bacterial infection;
• ptosis of the upper eyelid;
• appearance of scars.
The likelihood of serious consequences after redermalization of Gilaul is very small (about 0.5%). The reasons may be incorrect technique for administering the drug, incorrectly selected injection points, etc. Correct preparation of the skin, compliance with rehabilitation rules, and choosing a clinic with a good reputation will help to avoid adverse effects.
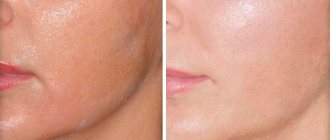
Efficiency of the method.
The effectiveness of hyalual redermalization is visually noticeable if you compare the appearance of patients before and after the procedure. The pronounced anti-age effect is clear evidence of the high efficiency of the Swiss brand. Positive changes are visible after the first session. The maximum effect is observed after a full course of procedures:
• the elasticity and firmness of the dermis increases;
• the relief is leveled;
• sagging areas disappear;
• fine wrinkles are smoothed out, deep folds are significantly reduced;
• the skin becomes velvety, a pleasant shade appears;
• pigmentation fades;
• pores become narrower;
• oily shine disappears;
• the consequences of acne are eliminated;
• scars, stretch marks become less intense or disappear completely, etc.