Skin hyperpigmentation
Thyrotoxicosis
18335 May 21
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Skin hyperpigmentation: causes of appearance, what diseases it occurs with, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
Skin hyperpigmentation is an excess deposition of melanin pigment of varying location, shape and size, leading to changes in skin color of varying intensity.
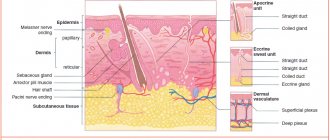
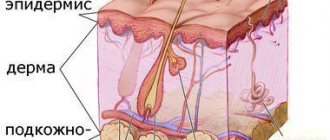
The surface layer of the skin (epidermis) is a multilayered (five layers) epithelium. The largest number of melanocytes, the main function of which is the production of melanin, are located in the basal layer of the skin (basal membrane)
Thanks to melanin, the skin protects a person from ultraviolet and infrared radiation.
The formation of age spots largely depends on the condition of the basement membrane.
Types of skin hyperpigmentation
Based on
the mechanism of occurrence,
the following types of skin hyperpigmentation are distinguished:
- melanocytic - pigmentation occurs due to an increase in the number of melanocyte cells;
- melanin - pigmentation is caused by an increase in the production and accumulation of melanin or a decrease in the rate of renewal of the stratum corneum of the epidermis.
The accumulation of pigment can be limited
or
widespread
, caused by
physiological
or
pathological
reasons, the process can be primary or secondary.
Possible causes of skin hyperpigmentation
Scientists identify several main causes of skin hyperpigmentation:
- genetic predisposition;
- exposure to ultraviolet radiation (in isolation or in combination with other reasons);
- burns (thermal, chemical, electrical);
- inflammatory processes;
- infectious diseases, including parasitic ones;
- endocrine disorders;
- metabolic disorders;
- use of herbal substances and drugs with photosensitizing effects
freckles for people
(ephelides) are a striking example of a realized genetic predisposition, which is based on an increase in the formation of melanin.
What diseases cause skin hyperpigmentation?
The group of melanocytic pigmentations includes various types of lentigines
.
Simple lentigo occurs at any age as a single (or multiple) formation up to 5 mm in size, brown in color. Doesn't change over time.
For xeroderma pigmentosum
Lentigo occurs before the age of 2 years on areas of the skin exposed to the sun (face, neck, back of the hands), then spreads throughout the body. Often combined with keratosis - thickening and peeling of the skin.
Solar lentigo
Appears, as a rule, after 40 years of age on areas of the skin previously exposed to sunburn. They appear as spots ranging in size from 1 to 3 cm, their color can vary from light yellow to dark brown.
Lentigo reticularis
resembles a black blot and is considered a type of solar lentigo. Most often occurs in individuals with skin phototypes I and II who have a history of severe sunburn with blistering.
Less common are other types of lentigo, occurring in isolation under the influence of solarium lamps, drug therapy (PUVA lentigo) or as part of syndromes affecting other internal organs (for example, with Peutz-Jeghers syndrome, lentigo of the oral mucosa is combined with intestinal polyps).
Skin hyperpigmentation can occur due to hormonal imbalance.
For example, during pregnancy the level of estrogen increases, and against the background of exposure to ultraviolet radiation, chloasma can form - round spots of different sizes and colors on the face.
In the later stages of pregnancy, existing moles, freckles, nipples and areolas of the mammary glands, the white line of the abdomen, and the skin around the navel may darken. Chloasma is often observed in women taking hormonal contraceptives, as well as with inflammatory or tumor pathologies of the ovaries. Chloasma is rarely recorded in men - as a rule, they have an increased level of luteinizing hormone and a decreased level of testosterone.
Hyperpigmentation of the skin throughout the body with darker areas exposed to sunlight is seen in primary or secondary chronic adrenal insufficiency (Addison's disease or syndrome) due to low levels of the hormone cortisol.
As a result of excessive thyroid function (thyrotoxicosis), secondary adrenal insufficiency occurs, and pigmentation can be diffuse or limited in the form of chloasma.
In diseases accompanied by extreme exhaustion (cachexia), the skin of the neck, abdomen, and genitals turns dirty brown.
The pigment can accumulate in places of thermal, chemical or electrical burns, injuries with damage to the skin. The pigment often remains after resolved boils, carbuncles, urticaria, lichen planus, psoriasis, as well as after scabies and lice.
In Riehl's melanosis, a bluish-brown reticulate pigmentation appears on the back of the hands and forearms, and the same occurs when in contact with synthetic clothing, rubber products or hydrocarbons, enhanced by ultraviolet exposure.
Some plants (legumes, figs, parsley, citrus fruits) contain photosensitizing substances - psoralens.
When present in food, they increase the photosensitivity of the skin. Such plants can be included in cosmetics; if you apply them to the skin and then go out into the sun, hyperpigmentation will occur at the site of application. Some medications also have a photosensitizing effect: sulfonamides, tetracyclines, antipsychotics, etc. Taking cytostatics slows down the rate of epidermal renewal, so the pigment is removed more slowly.
Which doctors should I contact for hyperpigmentation?
If hyperpigmentation occurs, you should consult a dermatologist. If the examination reveals pathologies of internal organs, you may need to consult an endocrinologist, therapist, gynecologist, urologist and other specialists, and if there is a risk of malignancy of the process, an oncologist.
Diagnosis and examinations for skin hyperpigmentation
Diagnosis of hyperpigmentation is based on clinical examination and patient interviews.
If necessary, the doctor can remove a pigmented formation (for example, lentigo reticularis) followed by histological examination to confirm its benignity.
Table of contents
- Etiology and pathogenesis
- Clinical manifestations
- Principles of treatment
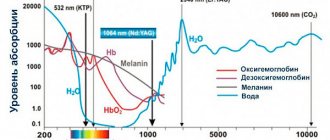
Deep pigmentation is a congenital or acquired hypermelanosis, in which the bulk of excess pigment lies in the dermal layer of the skin.
In our company you can purchase the following equipment for removing deep pigmentation:
- M22 (Lumenis)
- Fraxel (Solta Medical)
Face and body
There are a huge number of different reasons why skin hyperpigmentation appears. It can occur not only on the surface of the face, but also on the arms, back, legs, and abdomen. This may be due to genetics, various autoimmune disorders, excessive uncontrolled exposure to ultraviolet rays, insurmountable external circumstances, for example, the climatic characteristics of the region of residence, the environmental component, smoke or dust in cities.
Darkening on the stomach or back, on the arms or legs can appear after an inflammatory process in the epidermis. For some, insect bites cause light or dark areas of varying sizes that last a long time. Why is this happening? There are many prerequisites, they are worth discussing separately.
Diagnostics
Basically, pigmentation disorders do not pose a particular danger to the health and life of patients and only cause psychological discomfort from a cosmetic defect. However, if the affected areas are injured or exposed to ultraviolet radiation, melanomas can develop into malignant tumors.
Therefore, when age spots appear, it is necessary to undergo a comprehensive examination and determine the cause of their occurrence.
Diagnostics consists of:
- In external visual examination of the skin.
- In collecting anamnesis, which is often not limited to interviewing the patient, but also concerns his immediate family.
- In a dermoscopic examination, in which a device is used to repeatedly magnify and detail the pathological area of the skin.
- In computer diagnostics, which provides the study of affected areas and their comparison with reference samples.
- In histological analysis of tissue sections.
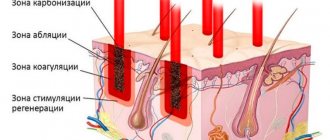
Based on the data obtained, treatment tactics are selected and internal medications are prescribed, as well as external means, for example, the use of photoprotective ointments, peelings, laser resurfacing and other methods of hardware therapy.
RESULT OF TREATMENT OF PIGMENTATION
An individually selected treatment regimen allows you to eliminate hyperpigmentation or make it less pronounced. To achieve an optimal aesthetic result, as a rule, a course of procedures is required. After several sessions of mesotherapy, laser therapy, peeling or plasma lifting, the skin tone is evened out, it becomes more elastic, and a rejuvenating effect is observed.
Complications
Hyperpigmentation of the skin causes discomfort more because it noticeably spoils the appearance. Typically, the appearance of spots does not indicate any serious health problems that are life-threatening. But this does not mean that hyperpigmentation can be completely ignored.
Age-related rashes, progressing, can eventually turn into malignant formations. Therefore, it is better to play it safe and consult a doctor for advice.
Among the complications, it is worth highlighting the following:
- spots may begin to peel off;
- sometimes itching and intense keratinization of the epidermis appear;
- Some patients experience decreased immunity;
- the latter often leads to the development of dermatitis, infections, and inflammations.
Prevention or how to prevent the appearance of new spots
After getting rid of the disease, it is important to avoid direct contact with UV rays on the skin or to reduce the time spent in the sun to a minimum. You should not sunbathe or visit solariums. Wear hats and clothing that covers your arms and legs.
It is worth using protective products with SPF and creams to prevent the appearance of tumors. Maintaining the result involves the use of whitening agents such as salicylic acid, hydrogen peroxide, hydroquinone, arbutin, kojic acid, as well as folk remedies.