Published: 11/03/2021 10:00:00 Updated: 11/03/2021
Urticaria is an allergic disease, the causes of which in children and adults can be very different. The main symptom of the disease is the appearance of blistering rashes on the skin, which are very itchy and resemble a nettle burn.
According to statistics, 25% of the entire population of the planet has encountered this pathology at least once in their lives, mainly children and women under the age of 40. With constant contact with the allergen, the disease becomes chronic, and in half of all cases it is accompanied by Quincke's edema.
Reasons for the development of urticaria
Hives never develop on their own; there is always a reason for this.
In some cases, identifying it is not difficult, but sometimes it is difficult to do. Most often, urticaria in children appears after using certain medications or eating certain foods. The most allergenic foods for babies are honey, nuts, fish, food additives, spices, sausages, and processed foods. Therefore, they are not recommended for children under 3 years of age.
Also, provoking factors include:
- insect bites;
- the presence of parasites in the body;
- plant pollen;
- mold;
- chemicals, including household chemicals;
- latex;
- ultraviolet radiation;
- vibration.
However, it is not always possible to find out what exactly the patient developed allergic urticaria to. In about a third of all patients with this diagnosis, the causes of the disease, even after numerous tests and analyses, remain unknown.
Symptoms of urticaria
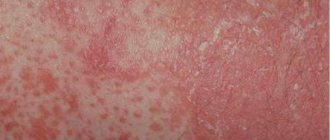
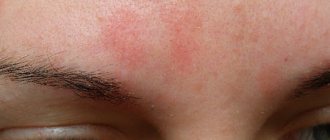
The main manifestation is the appearance on the skin of red or pink spots of various shapes, and blisters, the size of which can reach several centimeters.
A slight swelling may appear, which gradually disappears over the course of a day, rarely two. If the swelling affects the deeper layers of the skin or mucous membranes, angioedema may result - a life-threatening condition that requires immediate medical intervention.
The rash of allergic urticaria is always accompanied by unbearable itching, and some patients describe it as an unbearable burning sensation. Violent scratching of such areas can lead to infection of the epidermis with further complications in the form of pustules and wounds.
Minor manifestations of urticaria include:
- headache;
- elevated temperature;
- sleep disorder;
- anxiety;
- loss of appetite.
According to the nature of the course, allergic diseases are divided into two types.
Acute urticaria is diagnosed most often. Blisters and swelling of the skin in this form appear completely suddenly, sometimes against the background of a person’s excellent health. Most often caused by some external reasons, food. It also happens after using medications, especially when self-medicating. Symptoms go away on their own within a few days to several weeks.
Chronic urticaria is a condition in which symptoms continue to persist for more than 6 weeks after the first rash on the skin. This variant is characterized by a wave-like course, when periods of complete absence of symptoms (recovery) are abruptly replaced by exacerbations with the appearance of a new portion of spots and blisters. This is accompanied by unbearable itching and rapid development of Quincke's edema. The emerging elements of the rash can merge with each other, covering more and more new areas of the skin.
Sometimes periods of complete well-being without symptoms can last for a long time - up to 10 years.
Children's urticaria is an allergic skin disease, which most often develops against the background of an existing exudative diathesis and appears due to food products introduced as complementary foods.
It has been noticed that this type of allergy mainly develops in babies who are bottle-fed or eat foods that are not appropriate for their age.
Causes of ring-shaped spots on the skin
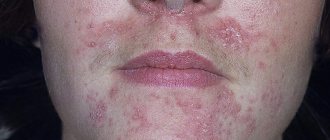
Ring-shaped spots on the skin may be erythema annulare, which is also called persistent or anular erythema. This disease can be caused by various factors and is prone to relapse. It is most often diagnosed in children, adolescents and young men.
To date, the exact reasons for the development of erythema annulare are not yet known to scientists. However, experts make some assumptions about the connection between its occurrence and the impact of certain factors - viruses, infections and other health problems.
Darrieus centrifugal spot
The origin of Daria's annular erythema raises especially many questions among scientists, since it has not yet been possible to identify the causes of the appearance of such a malaise.
Some experts suggest that the development of this type of disease may be associated with fungal infections of the skin. There is also a theory that skin symptoms are based on autoimmune processes or genetic predisposition. Darier's erythema can also occur under the influence of certain medications.
What diseases is it typical for?
The development of annular erythema can be provoked by a number of ailments, including:
- Pathologies of the digestive tract.
- Various types of intoxication of the body.
- Bacterial and viral lesions.
- Focal infections represented by tonsillitis, cholecystitis, osteomyelitis, sinusitis, etc.
- Disturbances in the functioning of the immune system.
- Fungal skin diseases.
- Endocrine diseases.
- Oncological processes. Erythema may be part of the paraneoplastic syndrome (complex of symptoms of cancer).
- Parasitic infections.
- Dysproteinemia (with this condition the ratio of proteins in the body is disturbed).
Since today the mechanism of development of annular erythema remains not fully understood, it is not yet possible to find out what factors can trigger its progression. This makes therapy somewhat more difficult and reduces its effectiveness.
Annular redness due to rheumatism
The appearance of ring-shaped erythema can sometimes be a specific manifestation of rheumatism in the active phase. This pathology is most often diagnosed in childhood and adolescence, as well as in adult patients under 30 years of age. Red spots on the skin can appear in various phases of the rheumatic process; they can be observed with polyarthritis or rheumatic carditis, and sometimes become apparent before other symptoms of rheumatism appear. With the current rheumatic process, erythema can warn of another attack of the disease or its exacerbation.
Ring spot for viral infections
Some viral infections can lead to changes in the body's functioning and trigger the appearance of erythema migrans. This is a chronic disease, which is similar in its characteristics to dermatosis. Most often it is diagnosed in middle-aged men, and doctors assure that this form of the disease is easier to treat than other types of annular erythema. Erythema migrans may appear after bites from ticks and other insects.
Complications of urticaria
It is important to know what hives look like and to be able to provide first aid correctly.
This will help prevent the development of severe complications that can lead to death. Often urticaria is accompanied by Quincke's edema, which is also called angioedema. Its development in the larynx area is especially dangerous, as it can compress the trachea and impair breathing.
Another serious complication is anaphylactic shock. This is a life-threatening immediate allergic reaction that occurs when the human body is hypersensitive to a particular allergen. Usually develops upon repeated contact with the allergen and requires immediate medical attention.
Diagnosis of urticaria
Before starting treatment, it is important to understand what exactly a person has such a strong allergic reaction to.
Only by removing this provoking factor from your usual life can you not be afraid that the symptoms of urticaria will appear again, and this is possible even after proper therapy. Most often, this type of allergy appears to food. It is possible to determine what exactly caused the rash by a blood test: the level of IgE antibodies to a mixture of food allergens is detected. First of all, you need to diagnose the presence of an allergic reaction to:
- nuts;
- vegetables and legumes;
- citrus fruits and fruits;
- seafood;
- cereal and sesame flour;
- fruits and melons;
- baby formula;
- fish;
- meat;
- mushrooms;
- loose leaf tea;
- goat milk.
In addition to food, allergic manifestations can also occur to other substances that surround us almost everywhere in life:
- mold fungi;
- pollen from early flowering trees;
- pollen of late-flowering trees;
- weed pollen;
- epithelium of domestic animals;
- house dust;
- house dust mite;
- poultry feather.
To identify the exact type of allergen, allergy tests are performed on certain foods.
It often happens that rashes appear due to seasonings and herbs used in cooking: paprika, cumin, cloves, basil, ginger, tarragon, thyme, marjoram, dill, bay leaf, black pepper, vanilla. Some types of fish may also be allergenic: cod, halibut, mackerel, and squid meat. But sometimes an allergic reaction in the form of urticaria develops to such familiar products as:
- cucumber;
- apricot;
- cherry;
- tomato;
- plum;
- grape;
- persimmon;
- carrot;
- beet;
- watermelon.
All tests are carried out only by a specialist laboratory technician. You cannot independently determine the presence of an allergy in the form of urticaria to a particular food product or substance. This can be life-threatening, since it is possible to develop not only Quincke's edema, but also anaphylactic shock.
Diagnostics
Even experienced doctors may encounter some difficulties when diagnosing ring-shaped erythema, because its manifestations resemble many dermatological ailments, ranging from seborrheic eczema and lichen to syphilis. Therefore, to make an accurate diagnosis you may need:
- Microscopic examination of skin scrapings.
- Performing various blood tests.
- Histology of biopsy (material from the affected area).
- Carrying out a complex of mycological tests.
To find out the exact reasons for the appearance of erythema, sometimes consultation with other specialists is required, for example, a rheumatologist, gastroenterologist, endocrinologist and oncologist.
First aid for hives
It is important that you always have allergy medications in your home medicine cabinet, since urticaria in adults, and in children too, can appear at any time.
Allergy medications can be in the form of drops or tablets. Modern remedies do not cause drowsiness and have virtually no side effects. Doctors recommend having in your home medicine cabinet to eliminate urticaria and itching, Fenistil drops, which can be used from childhood, Erius tablets, which have a long-lasting antihistamine effect after administration, Loratadine, which helps cope with Quincke's edema, which often accompanies urticaria.
It is important to take the medicine at the first symptoms, without waiting for the general condition to worsen. If after 20 minutes from the moment of administration there is no improvement, you should call an ambulance.
Folk remedies and recipes
In parallel with traditional remedies, herbal treatment methods can be used. Proven recipes:
- pour 2 tablespoons of dry arnica into a heated thermos, pour in 2 cups of boiling water. Close the container and, wrapped in a blanket, leave for a day. Drink the strained infusion 5 times a day, 1 teaspoon. Store the product in the refrigerator;
- Grind 100 g of dry arnica root into powder. Add an equal amount of melted pork or goose fat. Keep the mixture in a water bath for 3 hours, stirring from time to time. Place the product in a porcelain or glass container and seal tightly. Treat erythema 3 times a day;
- 10 g of dry white mistletoe pour 0.5 liters of alcohol. Leave for a month, shaking the bottle periodically. Filter means. Take 25-30 drops every day in the evening before meals with water. Drink it for a month, take a break, and after 30 days you can take a second course. Mistletoe is poisonous, so it is very important to control the dosage.
For more successful treatment, it is important to normalize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. It is necessary to regularly make mint, lemon balm or lingonberry tea. Take the product before meals or in between meals. You need to drink at least 1 glass per day.
Find out interesting details about the treatment of herpes on the lips during pregnancy.
Read about the treatment of neurodermatitis in adults at home at this address.
If you go here you can find out how and how to treat psoriasis of the scalp.
Treatment of urticaria
The only way to get rid of the disease is to avoid contact with the allergen, which is previously detected by laboratory tests.
If testing does not reveal a provoking factor, and the urticaria is episodic, then taking antihistamines will quickly eliminate the symptoms. During treatment, it is recommended to follow a diet that, in case of urticaria, will help prevent the recurrence of the disease. The menu should include only hypoallergenic products: lean boiled meat, soups with recycled meat broth or vegetarian. It is better to choose rice, buckwheat, and oatmeal from cereals. Low-fat cottage cheese, natural yogurt, apples, dried fruit compote, excluding raisins, and whole grain bread are recommended.
Citrus fruits, nuts, fish and all seafood, chocolate products, smoked meats, coffee, eggs, honey, and store-bought baked goods should be excluded from the menu during treatment.
Treatment is carried out by a dermatologist and an allergist-immunologist. For topical application, ointments for urticaria are effective; they not only relieve itching, but also eliminate swelling, redness and a burning sensation on the skin. One of the most effective is Dimetinden gel, which must be applied in a thin layer to the affected area of the skin up to 4 times a day.
A course of antihistamines is prescribed in the form of tablets. Your doctor may also prescribe calcium gluconate or calcium chloride for urticaria. They help reduce the symptoms of allergies, but they should only be administered under the supervision of a doctor in the treatment room.
If antihistamines do not provide the desired effect quickly, or for severe forms of hives, corticosteroids are used, which can be applied to the skin or taken in the form of tablets or injections.
Archives
Short Wiklad
Sylvia Hsu, Elaine H. Le, Mohamad R. Khoshevis Am Fam Physician 2001;64:289-96
Ring-like lesions of the skin appear frequently and occur quickly, sometimes making them difficult to diagnose. The smell appears as ring-shaped or oval macules or spots with an erythematous peripheral part and clear spots at the center. Their most common etiology in the adult population is dermatophytosis, which can be successfully diagnosed without a biopsy. Other illnesses may manifest themselves in the same way (Table 1). The doctor tries to turn off other illnesses, especially if anterior treatment for dermatophytosis was unsuccessful.
Table 1. Diseases that manifest themselves as ring-like lesions on the skin
| Diagnosis | Clinic | Likuvannya |
| Dermatophytosis tuba | Ring-like, erythematous plaques or papules on the skin without hair, covered with patches | Local and systemic stagnation of antifungal drugs |
| Ringworm | Small oval patches of a yellowish-brown color with small patches along the edges of the Langer lines on the skin | Local or systemic stasis of corticosteroids; UVA, UVB |
| Ring-like granuloma | Thick ring-shaped plaques and papules in the color of the skin without peeling, especially located on the ends | Local stasis of corticosteroids or their administration at the site of depression |
| Sarcoidosis | Severe, erythematous plaques | Local and systemic stasis of corticosteroids or their administration at the site of depression; antimalarial drugs; thalidomide |
| Leprosy | Erythematous annular plaques, with or without crusty skin | Dapsone; rifampicin |
| Kropyvnytsia | Ring-like erythematous plaques without scaling of the skin, which appear for a short hour | Oral antihistamines |
| Pre-hide red shepherd | Ring-like or psoriasiform plaques, with or without crusted skin, on areas of the body where sleepy tissues fall | Local and systemic stasis of corticosteroids or their administration at the site of depression; antimalarial drugs |
| Circular subcentral erythema | Ring-like patches with erythematous edges and vein-like lesions at the center | Local or systemic stasis of corticosteroids; oral antihistamines; feast of the primary illness |
Notes. UVA - ultraviolet light type A (wavelength 320–400 nm), UVB - ultraviolet light type B (wavelength 290–320 nm).
DERMATOPHYTIA TULUBA
Dermatophytosis tuba is a superficial fungal infection of the skin (with localization on the hands, feet, scalp, face and crotch). The most frequent events lie before the birth of Trichophyton, Microsporum
ta
Epidermophyton
.
In the USA, Trichophyton rubrum, Trichophyton tonsurans, Trichophyton mentagrophytes
and
Microsporum canis
. All dermatophytes have aerobes and are capable of acquiring keratin, which can therefore penetrate the corneal skin.
| The most common cause of ring-like skin lesions in adults is dermatophytosis |
People become infected with pathogens of dermatophytosis through close contact with infected individuals, creatures or the earth. Sometimes self-infection occurs through infected nails, scalp or feet. The risk of illness should be avoided in the post-pubertal age, although patients from the pre-teen age should be treated. Representatives of both articles fall ill with the same frequency. The main factors of the risk are the peculiarities of the climate and the environment of people. Fungal infections are caused by warm environmental conditions (huge showers, swimming pools) and the use of other people's towels, clothes and toilet items. Trival depletion of systemic corticosteroids promotes the risk of such fungal infections.
Patients have clearly demarcated, erythematous plaques or papules on the skin, which can progressively increase in size over time. At their edges there is an active process of fermentation; they may be slightly raised or covered with wedges (Fig. 1).
Rice. 1.
Clearly demarcated, erythematous plaques with raised edges, covered with flakes, with dermatophytosis of the tubes.
Fastening for additional care KOH
To establish a diagnosis, it is necessary to microscopically detect the fungus in a preparation doped with KOH. Using a scalpel, lightly (so as not to cause bleeding or pain) pluck the small pieces from the active edge of the element. They are transferred to a slide and covered with a curved slide. Add 10–15% drops of KOH with dimexide or without it. Afterwards, carefully heat the mixture (preparations with dimexide do not require heating). Superheated or boiled liquid will lead to crystallization of KOH, creating crazy artifacts.
The eye is quilted at low magnification of the microscope. Under the action of KOH, the heated cellular membrane of keratinocytes breaks down, so that long-term, direct or fragile hyphys of the fungus can be easily damaged. These structures can also become loose, but have a different diameter. If repeated treatment for additional KOH causes negative results, and the patient is clinically suspected of having a dermatophytic infection, it is necessary to take a culture (the result can be seen after 2–4 days).
Treatment of dermatophytosis tuba
If you want to treat dermatophytosis tubules with the help of numerous local and systemic antifungal drugs, it is quite simple, without the risk of re-infection. After treatment there is no contact with infected people, creatures or the earth. In case of localized infections, it is better to try local treatment with topical imidazoles (clotrimazole and miconazole) or allylamines (naftifine, terbunafine and butenafine).
Systemic antifungal drugs (griseofulvin, terbinafine or itraconazole) are indicated for lichen annularis, resistant to local treatment, or with its intolerance; an important interruption or a massive storm; chronic infection; primary or secondary immunodeficiency; affected by dermatophytosis of the skin with hyperkeratosis (the loins and feet). Although ketoconazole is also effective, it is characterized by potentially dangerous side effects: weakening of the liver and suppression of sterol metabolism. The severity of the initial course of oral therapy becomes 2 years old. Unfortunately, systemic antifungal drugs are expensive and may interact with other drugs.
Ringworm
Lichen erysipelas is a widened, self-circumscribed, psoriasimorphic viscus, which may indicate dermatophytosis of the tuberculosis. Although its etiology is not entirely clear, current data indicate that it may be a viral exanthema. Tinea erysipelas often occurs in sick people from 20 to 40 years of age, while sickness is avoided in young and mature adults. Women get sick more often; spring and summer seasonality is typical.
If you want more elements of visipa in patients with lichen erysipelas, represented by macules, papules and plaques, the primary cavity (“maternal plaque”), you can have the appearance of a ring-like skin with hyperemia, some raised edges, dribbling They have little strips and light spots at the center (Fig. 2). The primary cavity is primarily represented by one oval-shaped macula on a tube with a diameter of 2–10 cm. Although the majority of patients who suffer from viscera are asymptomatic, in 5% of patients it appears before the appearance of the primary cavity. headache, weakness, arthalgia, groves, vomiting , diarrhea and nervousness. Over the course of 7–14 days, a viscous appearance appears, which suggests the primary rot: small oval macules of a yellowish-brown color with “commercial” patches on the periphery. These elements are placed very symmetrically on both sides and can be localized on any part of the body, especially on the neck, trunk and proximal part of the ends. The shards of visipka appear along Langer's lines on the skin, giving the characteristic appearance of a “new-growing yalinka”.
Rice. 2.
Yellowish-stormy patches with tiny flecks along the edges in patients with erysipelas.
There is no effective treatment for lichen erysipelas; only the disease with the manifestation of itching can be relieved due to local depletion of corticosteroids and oral antihistamines. In important cases, treatment with ultraviolet light type A and B or systemic corticosteroids is indicated. Over the course of 6–8 years, spontaneous development of the viscosity is possible, during which time new elements of the viscosity continue to appear, just as the old ones gradually emerge. Less than 3% of patients suffer from relapses. In patients with lichen erysipelas, turn off syphilis, and in these illnesses the visipa is similar.
CIRCULAR GRANULOMA
Ring-like granuloma is an idiopathic, self-limiting skin disease with a good history, which often occurs in children and adults and is characterized by the appearance of smooth ring-like plaques and papules in the color of the skin. The visipka usually appears on the hands, feet, wrists and ankles, although it can appear on any part of the body. Although illness is generally asymptomatic, such illness may result in mild itching. Ring-like granuloma often develops in women; in most patients, the disease develops before the age of 40.
Ring-like granules are divided into localized, generalized, perforated, subcutaneous and actinic (on the scalp, where the dormouse occurs).
localized with the widest clinical form
ring-shaped granuloma, which occurs in approximately 75% of cases. Patients usually exhibit one or a number of erythematous or color-colored skin papules that can be isolated from one or another plaque (Fig. 3). The elements of the vein have smooth, raised edges, their diameter becomes 1–5 cm. The legs are most often affected, and the ankles, scalp and feet are left intact. In addition to dermatophytosis tuba, the elements of viscera in annular granuloma are not accompanied by scaly skin, vesicles and pustules. Approximately half of the patients with localized ring-like granuloma of the two strands become spontaneously alert.
Rice. 3.
Plaques with slightly raised hyperemic edges without desquamation in patients with annular granuloma.
During generalization
The shape of the viscous is wider, there are 10 or more elements. In this form, spontaneous swelling is less comparable with the localized form, and the onset of remission in less than 3–4 days is also doubtful.
Perforated
Ring-shaped granuloma is characterized by fragmented papules with navel-like retractions at the center, which are especially localized on the hands and fingers.
With subcutaneous
CG, large nodes of the skin color appear, which can be located in the lower spheres of the dermis or subcutaneous fatty tissue.
Although the etiology of CG is not entirely known, it is believed that illness is associated with vasculitis, trauma, activation of monocytes, or a reaction of type IV hypersensitivity.
The diagnosis is based on clinical findings. Laboratory tests are not very informative; patients with generalized CG are more often diagnosed with impaired glucose tolerance.
The fragments of the CG are self-limited and therefore asymptomatically ill; treatment is not required. In patients with symptomatic symptoms and especially those who are concerned about a cosmetic defect, you can try the following treatment methods: injections of corticosteroids in the area of \u200b\u200bthe disease, local corticosteroids, electrical anemia, cramping Therapy, ultraviolet bathing and systemic drugs such as dapsone, colchicine or delagil. Although in some patients the symptoms change in some way, we do not want them to have superiority over others and do not provide clothing. It is important to judge the clinical variability of illness progression and the effectiveness of treatment methods.
SARCOIDOSIS
Sarcoidosis is an idiopathic polysystemic disease, which is characterized by the development of stationary granules in the skin system of body organs, most often in the legs, skin, liver, spleen, eyes, lymph nodes and lymph nodes (about soblyo in the mediastinum). Although sarcoidosis occurs in every age, the most common risk in adults is the young age (20–40 years of age).
The progression of the disease varies: from asymptomatic to severe. Typical changes on the skin - infiltrated papules and plaques, axillary nodes and infiltration of old scars - may appear and become known over time. The most common forms of infection are brown or purplish papules 1–3 cm in diameter with minimal changes to the epidermis on the face, especially the orbits and nasolabial folds, and on the mucous membranes. Large lesions can become angry, looming with the appearance of ring-like lesions on the skin or plaques (Fig. 4).
Rice. 4.
Increased hypertrophic plaques in sarcoidosis.
The diagnosis is based on clinical findings, histological and radiological findings. Bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy is practically pathognomonic for sarcoidosis. If you suspect sarcoidosis, it is important to carry out a survey to identify skin lesions from which a biopsy can be easily taken without the need for invasive diagnostic procedures. In 85–90% of patients, histological confirmation of the diagnosis can also be determined using additional specimens from the bronchoalveolar tree and transbronchial biopsy of the leg.
Although sarcoidosis is a mild illness, its symptoms can be effectively alleviated with the help of systemic corticosteroids. Indications before treatment: shortness of breath, cough and disabling illness. For patients who are resistant to corticosteroids or cannot tolerate them, hydroxydelagil, delagil, methotrexate or thalidomide are prescribed. For localized skin lesions, corticosteroids can be localized or injected at the site of the lesion.
LEPROSY
In the United States, the majority of leprosy outbreaks are caught in individuals who lived behind the border in Asia, Africa and Latin America. The disease is caused by acid-fast bacteria Mycobacterium leprae
, which are transmitted among humans by the wind-droplet route. The risk of transmission of the disease through everyday contacts is low. Although children are more susceptible to leprosy, as adults, 95% of people are immune to leprosy. The incubation period lasts 3–20 years.
M. leprae
growth is greatest at a temperature of 35.6°C, which is why the disease has tropism to the coldest areas of the body: the skin, peripheral nerves and eyes, the remaining intact area, axillary folds and the scalp. The clinical picture varies depending on the reaction of the host’s body to the infection. In patients with tuberculoid form of leprosy, a generally well-functioning cellulosus is present in the macular decal or erythematous or violet-colored plaques with a clear demarcation. Ine (Fig. 5). Especially with a dark color, the skins and elements may appear hypopigmented. Visipka can be accompanied by skin inflammation, alopecia and, most importantly, anesthesia. Nerves, infiltrated with bacteria, become aggravated by burning cells, as a result of which their sensory and motor function is impaired and the smell becomes noticeable on palpation. Patients with the lepromatous form of leprosy have a clear defect in the immune system; they have bilaterally symmetrical macules and papules of significant size, which can become angry or turn into nodes. These patients clearly have a large number of bacteria.
Rice. 5.
A plaque with edges that can be covered with tiny pieces, in patients with leprosy.
Clinical diagnosis is based on medical history and histological examination. If the skin is dry, lacks hair, and has hypoesthesia, it is easy to suspect leprosy, especially if the peripheral nerve is palpable. In case of tuberculous leprosy, the biopsy specimen reveals epithelioid granulomas with excess peripheral lymphocytes, and in case of lepromatous leprosy, a large number of macrophages with foamy cytoplasm. If you suspect leprosy, you should carry out a special preparation of the smear using the Veit method; the fragments, when prepared with Ziehl-Neelsen, bacteria may lose their acidity. In patients with tuberculoid leprosy, as opposed to the lepromatous form, there is obviously only a small number of waking hours.
Typical treatment with dapsone and rifampicin in patients with tuberculoid leprosy lasts 3–5 years, and in patients with lepromatous leprosy it lasts.
KROPIVNYTSIA
Urticaria is characterized by itchy, clearly marked erythematous fur with erythematous, slightly raised edges and clear spots at the center (Fig. 6). As a result of the presence of histamine and other mediators, penetration of the vessel wall advances, causing massive swelling of the superficial dermis.
Rice. 6.
Erythematous swelling with clearing in the center and the presence of irritation with urticaria.
It is important to distinguish between allergic, physical and idiopathic urticaria according to etiology. Allergic urticaria is caused by saws, hedgehogs, grass, fungi, mold, Hymenoptera venom
that parasites (reaction of non-gain hypersensitivity type I), it also occurs as a reaction to transfusion and in case of serum sickness (due to hypersensitivity of type II and type III with activation of systems and complement).
| Urticaria occurs in 10–20% of the population, although the actual incidence of this illness may be higher, as a result of a good journey, many patients do not seek medical care |
Before physical hives, get rid of hives from pressure (caused by wearing tight clothes, on the feet, when undergoing heavy wear), cold (usually on the hands, ears, nose and cold areas of the body from the undersides) For example, fatty fatty cells are found on the lateral surfaces of females. ), cholinergic (caused by fever, hot bath or physical exercise), sleepy and dermatographic. In most cases, the specific etiology becomes unknown.
| Symptoms that subside before 24 years may indicate urticarial vasculitis |
With hives, visipka usually lasts for 90 days up to 24 years. The symptoms of urticaria significantly change under the influence of the most powerful antihistamines, but, as a rule, they are completely unknown, indicating that histamine is not the only mediator of the allergic reaction. ї. Symptoms that subside before 24 years may indicate urticarial vasculitis. Urticarial vasculitis is actually not urticaria, but leukocytogenic vasculitis, which can clinically suggest urticaria, except that the symptoms can subside within 3–5 days. In such patients, histological confirmation of vasculitis is necessary followed by skin biopsy.
PIDGOSTRIY SHKIRNY CHERVONIY VOVCHAK (PSHCHV)
The pig-skinned sheepdog (PSHV) manifests itself as a ring-like (Fig. 7) or psoriasimorphic viscid. The important rice of PSHCHV is sensitive to light, so the liquid is especially placed on the exposed surfaces of the skin. Half of the patients met the American Rheumatology Association's criteria for systemic worm disease (ASD). Patients with SHF usually exhibit arthralgia or arthritis, low-grade fever, fatigue or myalgia. Overcoming systemic illness is mild or of moderate importance, problems are rarely encountered.
Rice. 7.
Pre-hide red shepherd dog. Ring-like erythematous plaques show clearing in the center, often when associated with swelling suggest annular psoriasis.
In 63% of patients with PSPV, antibodies to the Ro antigen/Schöngren's syndrome antigen (SSA/Ro) are detected; 5–10% of such patients have Sjöngren's syndrome. It has been established that SSA/Ro antigens, found in the nucleus and cytoplasm, move to the surface of keratinocytes under the infusion of type B ultraviolet light. Anti-SSA/Ro blood serum antibodies can bind to similar antigens that appear on the keratinocyte membrane under ultraviolet light, affecting the skin through a cytotoxic mechanism.
CIRCULAR VID-CENTRAL ERYTHEMA
Annular subcentral erythema (CVE) is characterized by non-strengthened annular-like lesions with desquamation between the erythematous edges. Histologically, perivascular lymphocytic infiltrates are grouped in the dermis, resembling a “cloak and sleeve” pattern, with associated swelling of the papillae, interclinary plaque and parakeratosis. Ring-like lesions most often appear on the torso, buttocks, quilts and forearm, as well as brushes, feet and other parts of the body are left intact. Sickness tends to recur, underlying symptoms rarely disappear. The etiology and pathogenesis are unknown.
The diagnosis is based on clinical and morphological criteria. The duration of the illness varies, fragments of CBE can last for several periods up to 30 years, although most episodes last for about 9 months.
In most cases, there is no need for treatment, except for the need for treatment of the initial illness (as you can see). For symptomatic relief of itching, local or systemic corticosteroids and antihistamines can be administered.
OTHER CIRCULAR-FOLDED SKIN INVASIONS
Chronic migratory erythema
— the skinny manifestation of Lyme disease. At any stage of the skin, one or more large erythematous patches may appear, which expand in the center, sometimes from the clearing at the center, creating ring-like patches.
Polymorphic exudative erythema
- a reaction mediated by cellulitis immunity, often associated with herpes infection. The skin of the palms, feet, legs and knees is characterized by papules or plaques that expand with erythematous edges, then the center is darkened or necrosis appears, a seemingly “target-like” lesion.
Psoriasis
It is most often accompanied by erythematous plaques, diffusely covered with thick white patches, or may appear as ring-like lesions with patches along the edges (Fig. 8).
Rice. 8.
Psoriasis. The plaques may be covered with little pieces around the edges.
Coin-like eczema
often knitted with dry skin, often caught on homilks. Obvious coin-like papules and plaques with mikhurts, which can widen with the appearance of enlightenment in the center, forming a ring-like appearance.
Prepared by Bogdan Boris
How long does it take to cure hives?
Within 4-6 weeks, acute urticaria resolves in almost all patients with this diagnosis.
However, sometimes the acute form can become chronic, and then the disease becomes incurable, with periods of exacerbation and complete remission with the absence of symptoms, which alternate with each other. To deal with this allergic reaction as quickly as possible, it is recommended:
- Immediately consult a doctor at the clinic or call an ambulance.
- Follow a hypoallergenic diet for several months.
- Follow all doctor's orders and recommendations regarding treatment. Do not stop taking allergy medications at the first signs of improvement, but complete the full course.
- Be sure to have modern antihistamines recommended by an allergist in your home medicine cabinet.
Author:
Pugonina Tatyana Alekseevna, Therapist
Symptoms
Classic ring-shaped erythema of Darier is characterized by an acute onset:
- The skin becomes covered with coin-shaped spots of red or pinkish-yellow color. They can grow up to 15 cm in diameter.
- The spots do not itch or itch, and there is no peeling. Sometimes the edging peels off or becomes covered with vesicles - superficial cavities filled with exudate.
- The patient may experience some malaise, an increase in temperature, and a headache.
- The skin may become swollen.
- The spots are localized mostly on the torso, in the chest area, on the skin of the abdomen and back, and also on the surface of the limbs. It is possible to place circles on the face and in the buttock area.
Rings with annular erythema often grow and merge, sometimes they form arcs or garlands. It is possible to form openwork elements. The central part of such spots is covered with smooth and pale skin, and the outer edge rises somewhat above the surrounding skin and has a bright red or purple-violet color. With rheumatic erythema, the color of the edging is most often not very pronounced - it appears pale pink.
The rings usually remain on the skin for a couple of weeks, then disappear, leaving behind areas with stagnant pigmentation.
Sometimes spots appear on the skin in just half an hour, for example, when exposed to the sun or cold, and then disappear just as quickly. It is possible to develop a chronic form of the disease, which worsens during the off-season, as well as in the summer.
Features in children
In children, ring-shaped erythema of rheumatic origin is most often diagnosed; it can occur with the development of polyarthritis, rheumatic carditis or rheumatism. Experts call this disease a special term - Leiner's annular erythema. The disease has a number of specific symptoms:
- Bright red spots, about the size of a five-kopeck coin, appear on the skin of the baby’s body. They tend to expand and merge with each other.
- They do not cause any discomfort to the child and do not cause the desire to scratch.
- The spots are present on the body for quite a long time and disappear after successful treatment of the underlying rheumatological disease.
If the underlying disease becomes chronic, erythema annulare in children often recurs. Doctors are confident that this development of events is associated with severe complications in the heart and blood vessels.