From this article you will learn:
- The first signs of facial skin aging
- Photoaging as the main cause of skin changes
- 2 main types of protection against photoaging
- 10 Tips to Prevent Skin Aging
The skin is a full-fledged organ, the condition of which speaks volumes about a person’s health and appearance. If the outer covering of the body is dry and wrinkled, it means it is deteriorating. And most likely it's a matter of age. In this case, 10 steps to prevent skin aging is a path that will come in handy for you!
Rules for healthy skin and products that will help maintain youth - all this awaits you further. Read with pleasure and become beautiful!
Facial anatomy
The face, like many other tissues, undergoes sagging processes under the influence of gravity. This process is called gravitational ptosis. I propose to consider the anatomy of the face layer by layer. It is a layer-by-layer description of facial anatomy from the perspective of the concept of Australian surgeon Brian Mendelson that will help to understand the mechanisms of aging.
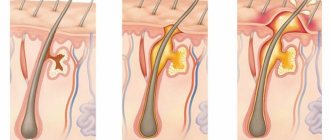
Essentially, the face consists of 5 layers: skin, fatty tissue, muscles, ligaments, periosteum and facial skeleton.
- The skin is the outermost layer. Traditionally, facial aging is associated with skin changes, so most treatments begin with skin care. Many people use creams, masks, etc. It really has a positive effect. However, up to a certain age. According to various authors, facial aging begins at the molecular level on average at the age of 30. This process occurs deep in the structures of the skin, so all rejuvenation procedures are essentially care and do not have a long-lasting effect.
- Subcutaneous tissue. Lies under the skin and consists of adipose tissue. The thickness of the fat layer varies in different parts of the face. With age, fat sinks and accumulates in certain places, forming bags under the eyes, jowls, etc.
- Muscles . There are 21 facial muscles on the face. With age, muscles weaken and sag, like a hammock in which fat accumulates. In this regard, working exclusively with the skin will not help achieve aesthetic rejuvenation. After all, even after performing a skin tightening, an array of muscles and adipose tissue will stretch the face and the result of skin procedures will disappear in no more than 1 year.
- Ligaments . With the help of ligaments, the soft tissues of the face are attached to the facial skeleton and are located in certain places. Time and gravity have virtually no effect on the ligaments, so weakened muscles and hanging fat are thrown over the ligaments, forming pronounced age-related contours of the face.
- Periosteum and facial skeleton. The bony skeleton determines the shape of the face and the very uniqueness and individuality of our faces. However, over time, the bone tissue slowly collapses, which creates the preconditions for the heavy mass of the face to slide down.
Rice. 1. Layers of the face according to Mendelssohn
Rice. 2 Mendelssohn's ligaments
Rice. 3 Young and old face
SKIN NUTRITION - PREPARATIONS FOR INTERNAL USE
VITAMIN C
Vitamin C stimulates the production of collagen, thereby helping to maintain the strength and density of the skin. Strengthens the attachment points of collagen fibers between the dermis and epidermis.
ISOFLAVONES
These substances of plant origin belong to the group of phytoestrogens, imitate female estrogen, but are less active. Their help with menopause during hot flashes, night sweats, and osteoporosis is widely known. Isoflavones are effective not only for climatic symptoms, they help improve metabolism in the body, have anti-carcinogenic properties (reduce the risk of cancer), and have a positive effect on the cardiac system and skin.
- Isoflavones are found in foods of plant origin: soy, red clover.
- The most famous isoflavone complexes (BAA): Genistein, Daidzein, Glycitein, Biochanin A.
LACTO-LYCOPINE
Lycopene stimulates cell renewal, promotes skin hydration, protects collagen and supporting fibers in the dermis. Lycopene is the most powerful keratonoid antioxidant:
- suppresses painful microflora in the body;
- normalizes cholesterol metabolism;
- supports the cardiovascular system (prevention of atherosclerosis);
- helps with weight loss;
- provides DNA protection (can prevent the emergence and development of cancer cells).
This antioxidant is not produced by the body at all and comes only from food. After a single dose, the maximum lipin is detected in the blood after 24 hours; it appears in the body tissues much later (at least after a month of regular use). Consume lycopene about 5 mg per day, maximum 10 mg. There are known cases of overdose.
The most famous food with a lot of lycopene is tomato. Depending on the color (the redder the better), it contains from 5-50 mg/kg. The most interesting thing is that during heat treatment the amount of lipin in the product does not change, but with strong evaporation and frying it becomes very large, for example, ketchup contains 60-140 mg/kg, tomato paste - from 50 to 1500 mg/kg.
But tomato is not a champion in the amount of lycopene:
- 6800 mcg – rose hips;
- 5204 mcg – guava;
- 4532 mcg – watermelon;
- 2573 mcg – tomato;
- 1828 mcg – papaya;
- 1419 mcg – grapefruit;
- 159 mcg – persimmon.
Two glasses of tomato juice contain the daily requirement of lycopene.
Correction of age-related changes
With age, multifactorial processes occur that determine the aging process of the face. These processes affect the facial skeleton and integumentary tissues. After 30 years, the beginning changes in the face are already visually noticeable. Changes in all tissue layers lead to their displacement and downward movement. More pronounced processes occur in the middle third of the face. The decisive factor in the drooping of the integumentary tissues of the face is a change in the bone surface.
- Forehead
Flattening of the frontal bone, combined with constant tension of the frontal muscle, leads to drooping of the integumentary tissues of the upper area of the face and the formation of transverse grooves in the forehead. The sliding mass of soft tissues of the forehead forms excess tissue in the area of the upper eyelids, the tails of the eyebrows droop and a “heavy” look is formed.
- Middle face area
Atrophy of bone tissue and fat packets in the midface area, combined with weakening of the muscles, leads to contusion of the ligaments and grooves. Pronounced bags under the eyes and eye bags form.
- Neck
The framework that holds the tissues of the lower zone of the face is the platysma - the subcutaneous muscle of the neck. Atrophy of the jaw bone, prolapse of the submandibular salivary gland, together with weakening and divergence of the platysma fibers, form an obtuse cervical-mental angle and a “double chin.” Thus, with age we observe: a reduced lower jaw; a stretched space at the bottom of which fat has accumulated; atrophied neck muscles that can no longer hold soft tissue and sag under gravity; the resulting jowls.
Fig.1 Aging according to Mendelssohn
Rice. 2 Bone atrophy according to Mendelssohn
Rice. 3 Facial aging: pronounced folds, jowls, “fat packets”
Photoaging
When the sun's ultraviolet rays (or UV rays from a tanning bed) are regularly exposed to unprotected skin, gradual damage occurs. Moreover, all changes in skin cells and their genetic material that occur under the influence of UV exposure tend to accumulate. This means that the consequences of excessive tanning in youth can affect the skin later. This type of skin damage is clinically known as photoaging and can lead to age spots, facial spider veins, fine lines and wrinkles, and in some cases even skin cancer.
To protect your skin from photoaging, be sure to use creams with ultraviolet protection before going outside.
How to slow down facial aging?
Facial aging is a multifactorial process manifested in bone resorption, changes and sagging of the soft tissues of the face. Procedures for external influence on facial skin are essentially care products that do not bring the proper rejuvenating effect.
- Superficial treatments: creams, ointments, gels and other procedures moisturize and maintain skin condition.
- Injection techniques: fillers and botulinum toxin. Fillers based on hyaluronic acid help fill the volume of tissue that has undergone atrophy, and botulinum toxin relaxes the muscles that form wrinkles. The absolute advantage of these techniques is their reversibility of action. Typically, fillers and botulinum toxin preparations dissolve within 6 months.
- Surgical facial rejuvenation: the most effective method. There are different types of face lifting. It is necessary to approach the choice of face lifting method from the standpoint of existing facial changes, their severity, the patient’s wishes and the surgeon’s capabilities.
Fundamentally, the following types are distinguished: skin lifting; SMAS lifting; MACS-lifting; spacelifting.
- Skin lifting
In the mid-20th century, it was believed that it was skin changes that led to facial aging. However, the era of skin tightening showed its ineffectiveness due to the short-term results - the result lasted no more than 1 year. Modern cosmetology is again resorting to skin tightening using threads. Thread lifting gives short-term results and makes sense for initial facial changes. Pronounced age-related changes are not properly corrected with the help of threads, so their use must be strictly dosed.
- SMAS lifting
SMAS is a complex acronym that stands for the entire muscular aponeurotic complex of the face. After separating the skin layer from the muscle layer, an incision is made and the facial muscles are tightened and fixed in a new position. At the same time, the neck is lifted and jowls are eliminated. After the muscles are moved to the new position, excess skin is created, which is removed and the skin is sutured along the incision around the auricle. Therefore, this type of lifting is suitable for pronounced changes in the middle zone of the face, the presence of jowls and a flabby neck.
- MACS-lifting
It is considered a low-traumatic technique. Through a small incision near the auricle, the skin is peeled off and the muscles are tightened using purse-string sutures. The difference from SMAS is that the muscles do not move and are fixed, but are stretched like a drum, which will soon lead to drooping of the face. However, the commercial attractiveness of this method is very high. It is worth remembering that this method can only be good for initial changes - just like thread lifting.
- Spacelifting
The essence of the operation developed by Dr. Mendelson is to eliminate the facial spaces that stretch under the influence of gravity. Since these spaces exist only in certain areas of the face, spacelifting does not provide a comprehensive lift and does not allow for significant rejuvenation of the neck area. Therefore, spacelifting gives a good rejuvenating effect in the middle zone of the face with unexpressed changes in the neck.
What are the reasons for premature skin aging?
Age-related decline of the body occurs due to natural physical processes. This type of aging is considered natural and is called “chronological.” In some cases, the skin fades ahead of schedule, but this process can be corrected and slowed down, unlike the natural process.
There are several reasons for premature aging:
- Environment. Sudden changes in weather conditions, exposure to ultraviolet radiation, rain, cold and heat. Air pollution and so on.
- Stress. It has long been proven that the health of all organs, especially the skin, depends on the health of the nervous system. People who wisely protect themselves from stress age later.
- Activity. Sedentary work and an inactive lifestyle lead to excess weight, stagnation in the body, and deterioration of metabolism. Without regular physical activity, the aging process accelerates.
- Nutrition. Fast foods, sweet soda, junk food, snacks, unbalanced diet are the causes of premature skin aging. The diet should be dominated by vegetables and fruits, natural fiber, and foods rich in vitamins and minerals.
- Alcohol abuse and smoking. These factors rapidly accelerate skin aging and worsen the condition of hair and nails.
- Diseases. Any disease carries consequences that need to be prevented in time. Chronic pathologies, including hormonal disorders, are one of the most important factors in rapid skin aging.
- Photoaging. This term applies to those who indulge in excessive tanning. Sun and solarium – in moderation. The skin must be carefully protected from the harmful effects of UV at any time of the year.
- Dream. You should get full rest at night, at least 7-8 hours. If circadian rhythms go wrong, the problem can develop into chronic insomnia, and this will definitely have a negative impact on the skin.
- Drinking regime. There is no need to get hung up on the obligation to drink 1.5 - 2 liters of water per day. The body itself will tell you when and how much it wants to drink. But the main thing is to avoid dehydration and drink only purified water.
And another reason is heredity. Although with current technologies even this factor is not considered decisive.