Published: August 2, 2017
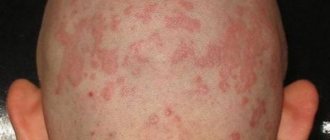
Human eyes are one of the most important and vulnerable organs; they are protected from the external environment for centuries; their skin is very thin and sensitive. Itching, redness or peeling of the upper eyelids occur quite often; about 10% of patients come to the ophthalmologist with this problem.
Many people ignore this symptom; of course, this is unacceptable. Redness and peeling of the eyelids may be a sign of a disease that leads to decreased visual acuity or complete loss.
Possible reasons why the upper eyelid may peel, itch, turn red, and even swell
Peeling of the upper eyelid is a rather unpleasant process, because flaking skin particles spoil the appearance, reduce self-esteem and performance. Very often peeling is accompanied by other symptoms:
- pain in the eyes;
- redness of the mucous membrane;
- swelling;
- pain;
- formation of pustules on the eyelid.
Such signs cannot be ignored; in a neglected state, this can affect visual acuity.
Before you do anything, you need to find out the cause of the skin change. You should not engage in self-diagnosis; you should urgently visit an ophthalmologist. The cause of peeling eyelids may be:
- allergic reaction to food, cosmetics, plants, animals or dust. In this case, peeling is preceded (or accompanied by) a red spot, swelling, and copious release of tear fluid;
- dry eye syndrome, which usually occurs in older people;
- respiratory viral infections;
- using low-quality, inappropriate eye cosmetics or expired products;
- dry and naturally sensitive skin;
- chronic fatigue, lack of sleep and prolonged work at the computer;
- washing with hard tap water using aggressive agents, such as regular soap;
- long stay in a room with dry warm air;
- using contact lenses for longer than the recommended time or being allergic to the solution for storing them.
These factors do not pose a serious threat to health and are easily eliminated.
Peeling can also occur when sand, insects or other small objects get into the eyes. At first there is severe itching and tearing. Peeling in this case is a reaction to constant skin irritation.
Peeling of the skin near the eyes can be one of the manifestations of certain pathologies:
- Demodecosis.
A dermatological disease that occurs when infected with hair mites. The pathology is accompanied by severe discomfort, redness of the whites and severe itching. In severe cases, foaming fluid is released from the eyes and eyelashes fall out. Every person has microscopic mites; pathological changes occur when the immune system is weakened.
- Fungal infections.
They manifest themselves as itching and peeling on the scalp and eyelids. Infection occurs through contact with infected people, animals, or after prolonged use of antibiotics.
- Viral diseases (most often herpes).
Very often they affect only one eye, but are easily transferred to the healthy one by touching. Viral infections are manifested by redness and dryness of the eyelid, subsequently small blisters filled with liquid form on the skin.
- Conjunctivitis.
Viral or bacterial infections of the eyes, the symptoms of which are redness of the whites, photophobia, tearing. In advanced cases, pus is released, sometimes in large quantities.
- Barley.
A painful bacterial lump on the eyelid caused by inflammation of the sebaceous ducts. The disease develops acutely, initially there is discomfort, itching and lacrimation, headaches, and a foreign body is felt in the eye. Gradually the size of the stye increases, after some time it ripens and pus comes out.
- Blepharitis.
A pathological condition of the eyes that occurs in people with weak immunity or gastrointestinal disorders. The eyes are constantly itchy, watery, and may become red and swollen. At the last stage, severe peeling of the eyelids and loss of eyelashes are observed.
Sometimes peeling of the eyes appears due to serious human diseases: cirrhosis, ulcers, diabetes mellitus, tuberculosis.
How to get rid of peeling eyelid skin
Any eye disease, even minor, requires proper treatment. Such a seemingly harmless symptom as peeling on the eyelids should not be ignored.
If, apart from dry eyelids, there are no other symptoms (pain, photophobia), or there is no opportunity to get to an ophthalmologist, you can try to alleviate the condition yourself:
- Provide rest to your eyes - limit watching TV, do not use the computer. Wear sunglasses when going out into the sun.
- Apply brewed and squeezed tea bags to your eyes, make compresses with natural rose water and herbal infusions.
- Do not use decorative cosmetics.
- Do not eat possible allergens.
- Relax and get a good night's sleep.
- Do not use contact lenses
If the cause of peeling of the eyelids is minor (overwork, allergies to cosmetics), your health will improve after eliminating the irritant, and after a few days the skin condition will normalize.
If peeling is accompanied by severe pain and unresponsiveness to bright light, a visit to the ophthalmologist cannot be postponed.
Possible complications
The crusts that appear on the skin around the eyes can partially or completely peel off, and pathogenic microflora - from the environment, from the surface of the hands - enter small wounds. This causes the development of a secondary inflammatory process, after which, among other things, scars may remain.
Demodectic mange causes eyelash loss (rejection of hair follicles). Even after the disease is eliminated, their growth is not always restored.
Lacrimation, which is accompanied by blepharitis and allergies, creates favorable conditions for the proliferation of pathogenic microflora and intensification of the inflammatory process.
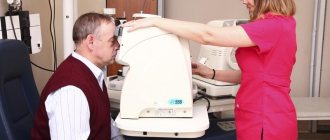
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of the cause that caused pathological changes in the eyelids and eyes is usually carried out on the basis of external signs. The ophthalmologist examines the patient, asks about concomitant symptoms and previous diseases.
In some cases, it is necessary to conduct a laboratory study of discharge from the eyes, tear fluid; if demodicosis is suspected, the subject of the study is the eyelashes (several pieces from the lower and upper eyelids).
After diagnosis, treatment is prescribed; the principle of therapy is selected individually in each case.
Here are the basic rules:
- Allergies can be treated with antihistamines in the form of tablets or ointments.
- For keratitis and conjunctivitis, antibacterial drops and ointments are used; in severe cases, oral administration is recommended.
- Treatment of demodicosis is carried out comprehensively - the patient is recommended to undergo antiparasitic treatment of the eyelids, take immunomodulators and vitamins, and associated symptoms are eliminated with antihistamines.
- Treatment of stye requires caution. Before ripening, it is not recommended to warm it up at home, but it is permissible to speed up the process with physical procedures. If its size is large or the patient experiences severe discomfort, the stye is opened in the hospital. To speed up healing and prevent the spread of infection, use antibacterial ointments and lotions.
- To eliminate eye fatigue, special moisturizing drops, vitamins, and eye exercises are prescribed.
The duration of treatment, list of medications and dosage are selected individually.
Medicines
Treatment of many eye diseases is carried out comprehensively and is prescribed by a doctor, based on the severity of the disease, age and health of the patient. The list of medications varies in each specific case. The most available drugs:
- Antibiotics are drugs of synthetic and biological origin with an antimicrobial effect.
Okomistin, Levomycytin, Albucid, Torbex, Tsipromed are prescribed in the form of drops. When the mucous membranes and membrane of the eyeball are affected, it is more effective to use ointments: tetracycline, Torbex.
- Antiseptics to prevent the spread of infections.
For eye diseases, use the most gentle, non-irritating mucous agents: Vitabact, boric acid solution or preparations with silver.
- Antihistamines are drugs to relieve itching and swelling.
These can be traditional Claritin, Loratidine tablets or topical preparations: Alergodil drops, Opatonol, hormonal ointments with hydrocortisone or dexamethasone.
- Antiviral agents: Anaferon, Acyclovir (ointment), Solcoseryl.
- Antifungal drugs: Levorin, Nystatin.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs are used if eye damage and peeling are non-infectious: Dexamethasone drops, Sofradex, Maxitrol.
- Vasoconstrictor drops, for example, the well-known Visine, help eliminate eye fatigue.
To increase the body's resistance to infections, immunostimulants (Echinacea tincture, Ergoferon) and vitamin complexes are prescribed. In the treatment of eye diseases, biological supplements with blueberries and eye vitamins are effective: Vitrum Vision, Complivit Oftalmo.
To eliminate the cause of peeling eyes, local remedies are usually used: drops and ointments. Such drugs act directly on the pathogen and practically do not penetrate into the blood.
If treatment involves the use of several types of drops, they are applied at intervals of at least 15 minutes. Ointments intended to act on the eyeball are usually placed under the eyelid at night.
Traditional therapy
You can get rid of peeling eyelids and other signs of eye disease using alternative medicine. They can be used if a symptom occurs as a result of allergies, fatigue, dry air, or as an auxiliary method in the treatment of serious diseases (usually after recovery).
To moisturize the skin, you need to wash your face with boiled, melt water, herbal decoctions or natural tar soap. The latter has unique properties: along with a pronounced antibacterial effect, it softens and moisturizes the skin.
Herbal decoctions can be used for rinsing and lotions. To prepare healing liquids, chamomile, St. John's wort, calendula, string, and celandine are used. The last two are used if it is necessary to eliminate the inflammatory process. They are not suitable for healing or dry skin, as they are very drying. Celandine is a poisonous plant, so you must be careful when using it.
The preparation of the medicine is very simple: a tablespoon of any herb (or a mixture of several) is poured with a glass of boiling water and kept in a closed container until it cools or boiled in a water bath for 5-10 minutes. The liquid is filtered through thick cloth and used:
- As lotions (compresses). Cotton pads or a piece of cloth are moistened in liquid and applied to closed eyelids for 15-30 minutes.
- For washing eyes. Moisten a cotton pad generously and wipe the eye from the nose to the temple. If both eyes are affected, use separate discs.
- For rinsing the face after washing. The infusion is diluted with boiled water (1 to 5) and irrigated on the face.
For the same purposes, you can use black tea, preferably large leaf tea without additives. It is necessary to prepare a very strong brew and use it as described above.
Softening masks made from available products will help eliminate peeling.
Recipe one:
- grate raw large carrots on a fine grater;
- add the yolk of a chicken egg to the vegetable mass, mix;
- add 1.5-2 tablespoons of flour to the mixture and beat well;
- apply the mixture in a thick layer to the eyelid;
- leave for 20 minutes and rinse.
Recipe two:
- mash a ripe banana with a fork;
- melt 2 tablespoons of honey and the same amount of butter in a water bath;
- connect all components;
- Apply on eyelids and wash off after a quarter of an hour.
Recipe three:
- Boil large potatoes in their skins, cool and mash;
- soak a piece of white bread in cream;
- connect both components;
- Apply on eyelid for 20 minutes.
Fresh parsley juice, a mixture of carrot and apple juice, cosmetic oils (cocoa, peach, wheat germ, shea) or regular olive oil will soften delicate skin.
During treatment, you need to pay great attention to hygiene procedures, stop wearing contact lenses and follow all the doctor’s recommendations.
Treatment
Conservative therapy
Treatment tactics are determined by the cause of itching in the eye area:
- Conjunctivitis.
Rinsing, instillation of medications, eye ointments, and subconjunctival injections are indicated. Depending on the etiology of the pathological process, antibacterial, antifungal or antimycotic topical drugs are used. - Blepharitis.
Eliminate factors that cause weakening of the body (carry out immunocorrection, sanitize chronic foci of infection). They carry out careful hygiene, use ointments with antibiotics, topical hormonal preparations, perform eyelid massage, ultraviolet irradiation, darsonvalization, electrophoresis, magnetic therapy, UHF. - Barley.
Before an abscess forms, the affected area is carefully treated with brilliant green, iodine or 70% ethyl alcohol. Antibiotics are instilled into the conjunctival cavity. At the maturation stage, dry heat, UHF, and quartz tube are prescribed. After spontaneous opening, topical antibacterial agents continue to be used. - Demodecosis.
It is necessary to strictly observe the rules of personal hygiene. Warm compresses with chamomile extract and eyelid massage are recommended. When a bacterial infection occurs, antibiotics are instilled. In case of complicated course, local glucocorticosteroids are prescribed. - Dirofilariasis.
Drug treatment is carried out against the background of surgical interventions. Antihelminthic drugs are used. To prevent allergic reactions and reduce intoxication caused by the decay of worms, antihistamines, glucocorticoids and NSAIDs are used. - Allergic diseases.
Avoid contact with the allergen, carry out local and systemic desensitizing therapy, immunotherapy, and symptomatic treatment. Antiallergic eye drops and general antihistamines are indicated. In severe cases, topical NSAIDs and corticosteroids may be required.
Prevention
Often, peeling and many ophthalmological disorders are easier to prevent than to eliminate later. To do this, you need to follow the following recommendations:
- exclude possible allergens;
- replace contact lenses on time (after any infectious diseases, be sure to purchase a new pair);
- use high-quality decorative cosmetics, cleansers and care products;
- remove makeup every evening;
- spend less time at the computer, take regular breaks from work;
- humidify the air in the room;
- do not touch your eyes with dirty hands.
Peeling skin can occur due to frequent stress or lack of vitamins. To prevent the problem, you need to eat foods that contain substances beneficial to the skin:
- dairy products;
- fish;
- liver;
- nuts;
- fresh seasonal fruits and vegetables;
- lean meat;
- liquid (pure water, herbal teas) in an amount of 2 liters per day.
To normalize your emotional state and sleep, it is recommended to drink tea with chamomile and mint, boiled milk with honey at night.
Excessive dryness and flaking of the skin on the upper eyelid is one of the signs of dysfunction of the body or visual system. This symptom cannot be ignored; if it occurs, it is necessary to change your diet, lifestyle and consult a specialist.