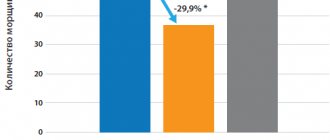
Beautiful skin is first and foremost healthy skin. In order for your face to shine, you need proper nutrition, care and immunity support, incl. local, at the proper level. If acne appears on the face, especially in adulthood, the immune system cannot cope, it needs support. One of the most effective means is autohemotherapy. These are injections of the patient’s own blood, which help activate metabolic processes, strengthen the immune system and reduce inflammation.
How does the procedure work?
Previously, cosmetologists did subcutaneous injections. This made it possible to achieve the desired result, but there was a side effect in the form of hematomas. Injections began to be given intramuscularly. After them, no traces remain on the face, and the effect remains.
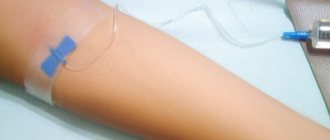
The procedure goes like this: blood is taken from a vein from the patient and injected into the muscles, usually the buttocks, on the opposite side. So, if blood was taken from the right arm, then an intramuscular injection is made to the left side. The course starts with 2 ml. and continue increasing with a factor of 2. The procedure is carried out every other day for 10 days, sometimes more.
What is autohemotherapy
The procedure is based on transfusion of the patient's own blood. The material is taken from a vein and injected intramuscularly, less often – subcutaneously. The method is not new: it began to be used in the 2000s, that is, more than a century ago. During the war period, when there were no antibiotics for inflammation from wounds or the consequences of surgical operations, complex colds were practically impossible to cure. People were dying. One of the “pioneers” of autohemotherapy, Voino-Yasenetsky, in his “Essays on Purulent Surgery” of 1900, notes the effectiveness of the treatment of inflammatory and indolent diseases.
Types of autohemotherapy
Fresh, unpurified blood is most often injected into the muscles, but this is not always the case. In some cases, various drugs are added to the plasma and injected into reflexogenic points or back into the vein. Types of autohemotherapy:
- Introduction of autologous blood. The molecular composition of plasma can be changed by exposure to X-ray waves, ultrasound, or freezing.
- Biopuncture. Blood mixed with oxygen, which enters it as a result of shaking, is injected into reflexogenic points. Sometimes homeopathic medicines are added to the composition.
- Ozone cleaning. To enhance the immunomodulatory, anti-inflammatory and antiviral effect, plasma is ozonated. This composition is injected into a vein, and not into the muscles.
- Stepwise technique. If the problem is infectious, antibiotics are added to the plasma.
Indications for use
Autohemotherapy, as has been repeatedly proven, has an extremely positive effect on the body, especially improvements are noticeable in the following diseases and disorders:
- Weak immunity
- Metabolic disorders in the body
- Problems of lymph flow and blood circulation in general
- Disorders and diseases of the endocrine system
- Purulent processes of soft tissues
- Slagging and intoxication of the body
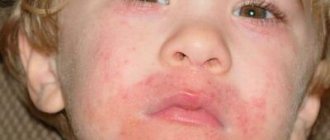
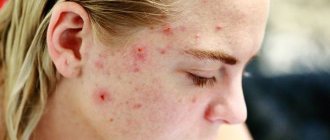
- Acne and pimples
- Decreased vitality and performance.
In addition, significant positive changes have been noted when using this technique in the treatment of chronic cytomegalovirus infection, chronic inflammatory process in the uterus, appendages, in the treatment of genital herpes, with adhesions in the pelvis, with severe menopausal syndrome, in the treatment of condylomatosis, papillomatosis, and infertility .
Contraindications to the procedure
There are few absolute contraindications, but there are certain restrictions. Autohemotherapy will have to be postponed during pregnancy and lactation, with a low level of hemoglobin, with a viral infection, menstruation, during menopause, inflammatory processes of the appendages, etc. The procedure is not recommended for severe forms of arrhythmia, the presence of neoplasms (malignant and benign). The final decision on the possibility of using the method in a particular case is made by the doctor.
Effective or dangerous: what evidence-based medicine says
Yes, today, in the era of development of the pharmaceutical business, it is unprofitable to prove the benefits of a virtually free “medicine”, because blood for transfusion does not even need to be processed. Therefore, there are enough opinions from opponents of the method, proving not only the ineffectiveness, but also the danger of therapy.
To believe it or not is a matter for the patient and his attending physician. However, the collected evidence base, including the results of studies by European scientists, shows that in some cases autohemotherapy cures faster and better than medications, and also does not cause mutations in the body.
Interesting fact! If some opponents consider the transfusion of unchanged blood dangerous, then outdated but still used “banks” and acupuncture, which is popular today, are treated with less mistrust. And the methods are very similar. In all cases, an artificial bruise is formed using physical pressure. It is a hematoma in a certain place that activates the necessary resources (program) of the body, setting it up for independent healing.
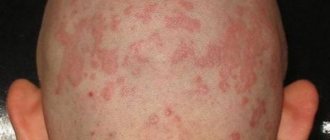
Types of psoriasis
There are a large number of classifications of psoriasis, which are based on the severity of the condition, the nature of the rash, the location of the lesion, etc. The most common types of disease are:
1. Plaque (vulgar) makes up the majority of all types of psoriasis. It is characterized by the appearance of traditional plaques covered with white-gray scales.
2. Guttate psoriasis ranks second in prevalence and is diagnosed in every tenth patient. In this case, numerous and rather small rashes appear with scales over the entire surface of the body.
3. The pustular variant is characterized by the formation of pustules.
4. In palmoplantar psoriasis, the elements are located on the corresponding areas of the skin.
5. The exudative version differs in that the scales are saturated with a yellowish liquid that seeps out of the body. Due to this, they look stuck together and change color.
6. Erythroderma is a severe form of the disease, since almost the entire surface of the skin is affected and systemic reactions occur (fever, enlarged lymph nodes, blood disorders).
7. Psoriatic arthritis is characterized by damage to the joints.
According to the stages of the pathological process, progressive , stable and regressive scaly lichen is distinguished.
Other symptoms
In addition to the skin, psoriasis affects nails, hair, as well as joints and internal organs. Changes on the nail plate begin at the base and are characterized by subungual hyperkeratosis. Subsequently, the surface becomes striated, and impressions form on it (thimble symptom). Psoriatic arthritis begins with damage to small joints and is accompanied by pain and inflammation. Also, scaly lichen is characterized by itchy skin. The result is scratching, superficial cracks and a tendency to bleed. In places of trauma, pathogenic microbes can multiply, which leads to secondary infection and the development of dermatitis.
Preparations and remedies for psoriasis
For this disease, the most popular means are for external use. They may contain several components that prevent excessive division of skin cells, as well as soften and reduce skin itching. The names of the drugs vary, but most often they contain the following substances:
- Glucocorticosteroid hormones that reduce inflammation and inhibit the reactivity of the immune system. When applied topically, hormones have a less pronounced systemic effect. They are part of Elokom, Advantana.
- Vitamin D is included in a large number of topical preparations. Its greatest effectiveness for the treatment of psoriasis is shown when combined with ultraviolet irradiation.
- Tar is used mainly for the treatment of lesions located in the scalp area.
- Activated zinc quickly eliminates redness and skin itching. This component is practically harmless to the body. Among the drugs for the systemic treatment of psoriasis are:
- corticosteroids, as they regulate metabolism and eliminate foci of inflammation, but they have a pronounced withdrawal syndrome;
- cytostatics inhibit the division of epidermal cells, but at the same time weaken the immune system and slow down the regeneration of other tissues;
- immunomodulators help normalize immune reactions, but their effectiveness has not been fully studied;
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs reduce only the severity of itching and inflammation, but do not affect the primary changes. Vitamins and antiallergic drugs are used in addition to the main therapy. Since there is no truly effective medicine to combat psoriasis, it is prescribed in conjunction with physiotherapeutic procedures.
Causes of psoriasis
The non-infectious nature of the disease was established back in the 19th century. Since then, numerous studies have been continuously conducted to study the causes of psoriasis. However, as with most systemic diseases, it is still not possible to find out a single cause.
There are several theories, each of which has scientific confirmation:
- Immune theory , according to which the disease is a consequence of a number of dysfunctions in the immune system. The development of an autoimmune response is expected, as a result of which a large number of T-lymphocytes accumulate in the thickness of the skin. This leads to chronic inflammation and thickening of the affected area. The theory is confirmed by the fact that a biopsy of a psoriatic plaque can detect a high concentration of immune cells, as well as the fact that the course of the disease is significantly influenced by the use of immune drugs.
- The hereditary factor is associated with congenital pathology of genetic material. Scientists have already identified several DNA sections whose mutations are observed in patients with lichen planus. These genes are mainly responsible for the maturation of immune cells (T lymphocytes). Therefore, if they break, the likelihood of psoriasis increases significantly. If parents suffer from this skin disease, then the risk of developing dermatosis in children is 50% higher.
- The genetic theory is similar to hereditary theory, however, in this case, genes are considered in which a mutation can occur at any age.
- The endocrine factor is confirmed by the fact that most patients with psoriasis have some changes in the endocrine organs (pituitary gland, pancreas and thyroid gland). In addition, this category of patients often has a disorder in the synthesis and release of melatonin. The course of the disease can also be influenced by the level of sex hormones.
- Stress and severe shock can lead to the manifestation of the disease or to an exacerbation of its symptoms. At the same time, due to the release of hormones into the blood, a number of biochemical reactions are triggered, which lead to the appearance of a scaly rash on the skin.
- The exchange theory is based on the fact that scientists have identified elevated lipid levels in patients with psoriasis. In addition, with exacerbation of the disease, nitrogen metabolism changes and the overall level of toxins in the body increases.
In fact, all the causes of psoriasis can be combined into two groups:
- violation of skin cell division;
- changes in the functioning of the immune system. All external factors (ecology, stress, trauma) only aggravate the course of the disease, but cannot act as a single cause.
Prices for services
| Intravenous infusion of ozone-saturated saline solution, 1 procedure | RUB 2,376 |
| Intravenous infusion of ozone-saturated saline solution, 5 procedures | 6,050 rub. |
| Intravenous infusion of ozone-saturated saline solution, 10 procedures | 11,000 rub. |
| ILBI (intravascular laser irradiation of blood), 1 procedure | RUB 3,459 |
| ILBI (intravascular laser irradiation of blood), 5 procedures | 6,050 rub. |
| ILBI (intravascular laser irradiation of blood), 10 procedures | RUB 11,385 |
| Autohemotherapy (without the cost of the drug), 1 procedure | RUB 1,185 |
The term “psoriasis” comes from the Greek word “psoriasis”, which means “pruritus” or “itchy skin”. It is these symptoms that most clearly characterize this non-infectious dermatological problem. With such dermatosis, skin cell division occurs almost thirty times faster. Since they do not have time to fully mature, intercellular contacts are lost. This leads to the formation of characteristic scales. The body’s immune system is also involved in the pathological process: protective elements are directed against its own cells, which causes chronic inflammation in the lesion. Let us describe in more detail the question of what psoriasis is and how to treat it.
Autohemotherapy regimens for acne
The following blood transfusion regimens are used to treat acne:
- Subcutaneously. Using a disposable syringe, venous blood is collected for subcutaneous administration. No other components are added to the blood.
- Intramuscularly. Typically, the regimen involves a course of 10 or 15 injections. The dosage is increased by 1 ml daily. During the first procedure, up to 2 ml of blood is injected intramuscularly.
- Intravenously. Ozone autohemotherapy has anti-inflammatory, antiviral, and immunomodulatory properties.
In most cases, blood transfusion is carried out according to the classical scheme. It is also possible to use stepwise autohemotherapy (according to Reckeweg). The procedure involves mixing biological material with homeopathic remedies for subsequent transfusion. The introduction of the resulting solution is carried out using several stages.
Blood transfusion for acne on the face is carried out using 2 methods:
- administering part of the blood to the patient and mixing the remaining biological material with a homeopathic medicine for subsequent injection;
- mixing 2-5 ml of blood with a homeopathic remedy, followed by administration after shaking.
When using the first method, detoxification properties appear that allow you to cope with acne. The course of treatment is performed once every six months.
Important! The course of therapy and method of blood transfusion are determined by the doctor on an individual basis.
Localization of rashes
As a rule, the skin that is located on the extensor surfaces (elbows, knees) of large joints changes. The favorite localization is the border of the scalp and places that are constantly exposed to injury or friction. However, this sign cannot be considered a diagnostic criterion, since in atypical forms of lichen planus, other surfaces of the skin are also affected.
Characteristics of plaques
The size of the rashes may vary. The primary elements are considered to be small papules of bright red or burgundy color. Over time, their size increases significantly, and they also tend to merge. In 90% of cases, signs of psoriasis include the formation of standard plaques, which are characterized by the triad:
1. A stearin stain is characterized by lightly scraping off gray-white scales that resemble candle shavings in appearance.
2. If you continue to scrape the surface of the plaque, then after removing all the scales, a thin white film will appear, called terminal.
3. The symptom of blood dew can be detected by removing the terminal film. If the skin papillae are damaged, there will be not heavy bleeding, but drip bleeding.
Side effects
After administering venous blood for acne, lumps may appear. This is due to the structure of the biological material. Poor absorption of blood in the muscle is due to its density. This is manifested by pain and the appearance of a characteristic lump at the injection site. It should be taken into account that the pain may gradually increase.
Often, seals appear when 4 ml of venous blood is injected. To avoid this unpleasant manifestation, you should make compresses and use an iodine mesh.
In rare cases, among the side discharge that appears, chills, weakness and a slight rise in temperature are observed. The likelihood of unwanted effects is influenced by the general condition of the body and well-being.
- Why is it necessary to transfuse blood from a vein into the buttock?
Quality of life of patients with psoriasis
Along with other chronic diseases, psoriasis can significantly worsen the quality of life of patients, who may experience both physical and psychological discomfort. Difficulties with labor and social adaptation often arise. Thus, severe itching sometimes interferes with normal rest, and plaques on the hands can limit performance. Scaly rashes on the scalp are especially difficult to tolerate. This is due to the fact that these plaques cause rejection in some, as a result of which patients become unsociable, and social phobia may even arise. Stress due to dissatisfaction with one's own appearance, constant pain or itching, as well as immune disorders quite often lead to the development of mental disorders (increased anxiety, depression, social isolation). Only a quarter of patients with psoriasis do not experience psychological discomfort; for the remaining patients, this disease is a serious obstacle to normal life. Among the symptoms of psoriasis that worsen the quality of life, the first place is occupied by itching of the skin, in second place is joint pain due to psoriatic arthritis.