Composition and dosage form
Ascorutin contains 2 active components:
- rutoside (rutin, vitamin P): necessary for normal microcirculation of substances in cells, fluid outflow, strengthening and maintaining the elasticity of vascular walls;
- ascorbic acid (vitamin C): important for general metabolism, absorption and conversion of nutrients into energy, tissue trophism, maintaining immunity, synthesis of collagen and muscle fibers.
Ascorutin is produced in the form of tablets containing 50 mg. ascorbic acid and rutoside of natural origin. An extract from black currant berries is often used as a starting material, so the taste of the pills is pronounced, sweet and sour. Uncoated pills have a yellowish or light green color with small inclusions. Among the formative and additional components of the drug: sugar, starch, magnesium stearate, MCC and other compounds.
The drug Ascorutin D of a similar composition and form contains sorbitol instead of sugar and is safe for patients with diabetes.
Classification
During the pathological process, certain patterns can be traced. Therefore, experts have identified separate types and stages of rosacea. It is important to identify them in order to develop treatment tactics and assess the prognosis, and prevent complications. Source: Molecular mechanisms of the pathogenesis of rosacea. Davydova A.V., Bakulev A.L., Morrison A.V., Leonova M.A. Saratov scientific and medical journal No. 3, 2013. p. 561-565.
Experts distinguish four types of rosacea, differing in clinical manifestations.
- Erythematotelangiectatic type : typically the presence of transient erythema, which gradually becomes persistent, the presence of swelling and spider veins.
- Papular-pustular type : in addition to redness, spider veins and edema, the formation of papules and vesicular rashes is typical.
- Phymatous type : typically thickening of the skin, the formation of a bumpy surface, growths in the form of bumps on the face, especially in the area of the nose, chin, forehead and ears, eyelids. Formations may have different structures and severity of changes.
- Ophthalmic rosacea can develop at any stage of the process, sometimes occurring even before skin lesions. Most often, inflammation of the eyelids (blepharitis), conjunctivitis, damage to the meibomian glands or barley occurs; less commonly, scleritis and keratitis may occur.
The typical course of the disease has five stages:
- transient erythema in the center of the face - episodes of redness occur spontaneously and briefly, disappear without a trace;
- persistent erythema with the development of telangiectasia - due to the constant dilation of blood vessels, the redness becomes persistent, spider veins appear under the skin.
- papular stage - the formation of tubercles and nodules under the skin (papules) is added to the elements described above;
- pustule stage - blisters appear on the affected skin, which can have both serous and purulent contents.
- infiltrative-productive stage - pronounced swelling develops on the skin, hypertrophic and fibrous skin changes are formed.
Separately, in dermatology, atypical forms of rosacea are distinguished, which require specific approaches to therapy. This:
- lupoid (the second name is granulomatous) form : very dense papules of a yellowish color are formed, after the resolution of which pronounced scars remain on the skin;
- conglobate form : large nodes form in the thickness of the skin, inside which an abscess and fistula tracts form. If these changes occur against the background of consuming bromine or iodine, the form is called halogen;
- the steroid form occurs against the background of irrational long-term use of corticosteroids;
- the gram-negative form is provoked by irrational use of antibiotics and the addition of drug-resistant flora;
- fulminant - symptoms suddenly, extremely quickly develop - swelling and redness of tissues, the formation of papules and pustules, which merge into a single mass with its suppuration.
How does Ascorutin work?
The vitamins contained in the drug quickly dissolve in the stomach and are absorbed through the mucous membrane into the blood. In the complex, ascorbic acid and rutoside complement and enhance each other’s effectiveness. Both compounds are active antioxidants. They help reduce intoxication of the body during inflammatory and infectious processes, increase resistance, regulate blood clotting and fluidity, preventing red blood cells from sticking together.
In the complex therapy of vascular diseases, Ascorutin helps restore peripheral blood supply, restore the integrity of capillaries, prevent and eliminate edema, trophic ulcers, improve the supply of nutrients to tissues and the removal of toxins.
Treatment methods for rosacea: recommendations
Success in treatment can only be achieved with complex effects and simultaneous correction of the functioning of all organs and systems. Source: Modern approach to the treatment of rosacea. Teplyuk N., Shurubey V. Doctor No. 12, 2015. p. 72-75. Therefore, the patient, in addition to the dermatologist, can be advised by other specialists - an endocrinologist, an ophthalmologist, a gastroenterologist, a psychologist.
Rosacea is a chronic disease, so it cannot be completely cured. Key goals of therapy:
- reduction of symptoms (redness, pustules, spider veins and papules);
- inhibition of disease progression;
- formation of the longest possible remissions;
- prevention of complications and exacerbations;
- elimination of possible cosmetic defects in the facial area;
- improving quality of life.
Key approaches to therapy include complete care for affected skin for rosacea and individual selection of cosmetics. Equally important is lifestyle changes and nutritional correction: the doctor develops a diet for rosacea and determines what is and is not possible.
The basis of therapy is drug treatment, additional methods of therapy, which are selected based on the form, severity of the pathology and existing complications. The list of medications for rosacea includes a variety of drugs: antibiotics from the tetracycline group, macrolide drugs, vitamins, metronidazole. Systemic isotretinoin preparations may be prescribed. Usually the drugs are administered orally; injections for rosacea are rarely used.
Various ointments and creams are used topically to treat rosacea with antibiotics, metronidazole, retinoids, benzyl benzoate and other components. Source: Innovations in external therapy for rosacea. Olisova O.Yu., Kochergin N.G., Smirnova E.A. Russian Journal of Skin and Venereal Diseases No. 5, 2022. p. 270-274. Agents that stabilize the walls of blood vessels, sedatives, and artificial tears (for eye damage) are indicated.
Non-drug therapy complements treatment. This includes laser treatment for rosacea, IPL therapy, microcurrent treatment, and cryotherapy.
In case of complications, pronounced phymatous formations, surgical removal of the affected areas of rosacea is indicated.
Main indications for taking Ascorutin
The drug is prescribed to prevent the development and treatment of pathologies accompanied by insufficient blood circulation, blood disorders or vitamin deficiency. Among them:
- tendency to increased platelet formation;
- vascular damage by salicylates;
- hemorrhagic diathesis;
- hemorrhage in the retina;
- violation of intraocular pressure;
- atherosclerotic changes;
- rheumatism;
- Iron-deficiency anemia;
- some forms of hypertension;
- venous insufficiency;
- varicose veins: lower extremities, rectum;
- trophic ulcerative lesions;
- thrombophlebitis;
- consequences of severe scarlet fever, measles;
- frequent nosebleeds;
- changes in blood composition as a result of radiation exposure.
In most cases, Ascorutin is indicated in combination with other medications or vitamin-mineral medications.
As an adjuvant, Ascorutin is used in vitamin therapy for menstrual disorders: for heavy or irregular discharge. Its regular use helps to normalize pancreatic function and the absorption of glucose by cells. This helps stabilize the condition of diabetic patients at an early stage.
For diseases of the joints and spine, the product improves metabolic processes in the tissues of cartilage and skeleton, prevents the leaching of calcium, supports the formation of intra-articular lubrication, and slows down inflammatory reactions.
Acne vulgaris (acne)
Acne vulgaris usually occurs between the ages of 14 and 25, while rosacea occurs between 30 and 50 years. It is also necessary to carry out a differential diagnosis with late acne .
Common manifestations with late acne
Appearance after 40 years
Papulopustular skin rashes
Overproduction of sebum – oily skin
Possibly - prolonged exposure to the sun - a common “trigger”
Differential diagnosis
Criteria not typical for acne are diagnostic for rosacea:
Centrofascial erythema is redness of the central part of the face, which may be accompanied by subjective sensations of itching, burning or tingling. A must-have for rosacea!
Outbreaks of erythema - occur when nerve endings are irritated by provoking factors: stress, heat exposure, drinking hot and alcoholic drinks, etc.
Couperosis – appearance on the face, because the disease affects the vascular bed.
No comedones!
Anamnesis
An important part of any consultation. If the rash was present at a young age, the development of late acne is most likely.
How to use Ascorutin correctly
Tablets are recommended to be taken after or during meals. This way the vitamins are better absorbed and act faster. The drug should be taken with plain water. In the absence of contraindications - berry or fruit juices. It is not advisable to use alkaline mineral water, as it neutralizes the acids contained in the tablets.
Adults are recommended to take 200–600 mg. Ascorutin per day (2–6 tablets), depending on the type of pathology present. To prevent hypovitaminosis, it is enough to drink 1 piece. twice a day. For treatment - repeat the dose 3-4 times a day. The drug should be swallowed whole, without chewing, so that the acids do not harm tooth enamel.
Ascorutin is allowed for children from 4 years of age: 0.5–1 tablet per day. For babies, it is recommended to grind the product into powder or dilute it in 1 tsp. slightly warm water. After taking it, it is advisable to rinse your mouth thoroughly with water.
Recommended course of continuous intake of the vitamin complex: 2–4 weeks. If necessary, the doctor can prescribe a prolonged dose - up to 2 months, or a cyclic dose - up to six months. To avoid complications, you should not prolong taking Ascorutin or increase the dose yourself.
Pharmacotherapy of rosacea
Rosacea is a polyetiological chronic recurrent disease (usually of the facial skin), characterized by a staged course.
This disease affects patients aged 30 years and older, predominantly fair-skinned.
Despite the presence of numerous works by domestic and foreign researchers devoted to the study of rosacea, the etiology of this disease is still not completely known, and the pathogenesis is not fully understood.
Factors in the occurrence of rosacea include the detection of the Demodex folliculorum , disruption of the gastrointestinal tract, endocrine and nervous systems, changes in immune status, and primary pathological vascular reactions.
For a long time, Demodex folliculorum was considered the main cause of rosacea, until, as a result of numerous studies, new data on the pathogenesis of the disease emerged. However, there is an assumption about an indirect effect of Demodex folliculorum on the formation of rosacea. However, the possibility of clinical recovery in patients with rosacea when prescribing therapy that does not include acaricidal agents indicates that demodex is not involved in the occurrence of rosacea. At the same time, favorable soil for the life activity and reproduction of the tick contributes to the deterioration of the clinical picture of the disease, increasing, in particular, various subjective sensations.
Exogenous causes of rosacea are nutritional (alcohol, hot drinks, spicy, smoked foods), meteorological factors (solar radiation, high or low air temperature), and the presence of foci of chronic infection. However, the role of insolation in the development of rosacea remains insufficiently studied to date, since the literature describes cases of the onset of clinical remission of the disease after a patient’s prolonged exposure to the sun.
Of particular interest in the formation of rosacea is Helicobacter pylori, which is important in the occurrence of gastric ulcers and the development of rosacea in 67% of patients. The appearance of hot flashes on the facial skin is associated with the activation of vasoactive peptides under the influence of Helicobacter pylori and the accumulation of toxins that have a vasodilating effect.
Data have been published on the occurrence of rosacea in women before menstruation, during pregnancy and menopause, which indicates the importance of functional disorders in the pituitary-adrenal-gonadal system. Of course, various endocrinopathies can contribute to the occurrence of relapses of rosacea, but the pathology of the endocrine glands cannot be considered as the main cause of the development of this disease.
The role of vegetative-vascular dystonia and astheno-neurotic syndrome is shown. There is a theory that the predominant localization of rosacea rashes over the inactive muscles of the face is apparently due to the fact that the swelling in these areas is not drained by muscle contractions. At the same time, dilated blood vessels accommodate more blood, promoting hyperemia. The role of disturbances in the functional activity of the brain is evidenced by the frequent combination of rosacea and migraine in women over 45 years of age.
Rosacea is predominantly observed in areas where seborrhea is localized, but no quantitative changes in the secretion of the sebaceous glands are observed.
Currently, there are several classifications of rosacea proposed by different authors. In 1976, E. I. Ryzhkova developed a clinical and morphological classification of rosacea, according to which four stages are distinguished:
- erythematous (rosacea erythematosa);
- papular (rosacea papulosa) with a peculiar cystic form (rosacea cystosa);
- pustular (rosacea pustulosa);
- infiltrative-productive (rhinophyma).
The cystic form is now known as granulomatous or lupoid rosacea.
There is a classification described by J. Wilkin:
- prerosacea - periodic hot flashes;
- vascular rosacea - erythema and telangiectasia;
- inflammatory rosacea - papules and pustules;
- late rosacea - rhinophyma.
A special form is ophthalmic rosacea.
G. Plewig, T. Jansen, A. Kligman proposed a classification taking into account the sequence of stages of rosacea and atypical variants of the disease.
The clinical manifestation of rosacea is episodic hot flashes: rosacea-diathesis.
Stage I: erythematotelangiectatic (persistent moderate erythema, isolated telangiectasias).
Stage II: papulopustular (persistent erythema, telangiectasia, papules, pustules).
Stage III: pustular nodular (persistent erythema, numerous telangiectasia, papules, pustules and edematous nodes).
Special forms of rosacea: steroid; granulomatous, or lupoid; gram-negative rosacea; conglobate; fulminant; rosacea with solid persistent swelling; ophthalmic rosacea; rhinophyma and “phymas” of other localizations: gnathophyma (chin), metaphyma (forehead area), otophyma (ear), blepharophyma (eyelids).
The initial signs of the disease are characterized by transient erythema, mainly in the central area of the face. Subjective sensations arise in the form of tingling, itching, burning. Subsequently, against the background of persistent congestive erythema, moderate infiltration and capillary telangiectasias appear. Itching occurs, the appearance of which is often associated with an increase in the population of the mite Demodex folliculorum . Transient erythema progresses over time, becomes permanent, acquires a bluish-congestive tint and spreads to the face and neck.
During the transition to the papular stage, against the background of erythema, isolated or grouped inflammatory pink-red papules with a diameter of up to 3-5 mm, dense elastic consistency, not prone to fusion, appear. Localized on the cheeks, forehead, chin, sometimes above the upper lip.
With further progression of the disease, papulopustules and pustules up to 1–5 mm in diameter appear. Elements tend to group in the area of the nose, nasolabial folds, and chin. The rash can spread to the front surface of the neck and chest.
Under the influence of increased levels of androgens, hyperproduction of sebum develops, culminating in hyperplasia of the sebaceous glands. The emerging fibrosis of connective tissue impairs blood and lymph circulation, causing pastiness and swelling of the face. Tumor-like growths are localized on the nose and cheeks, creating a disfiguring effect; rhinophyma is formed.
In 20–60% of patients with rosacea, the eyes are involved in the pathological process. Patients complain of burning, itching, soreness, lacrimation, and photophobia. Blepharitis, chalazion, conjunctivitis, iritis, iridocyclitis, keratitis are diagnosed.
As a result of prolonged application of highly active corticosteroid drugs to the skin of the face, steroid rosacea develops. Corticosteroid therapy for papular rosacea promotes its transition to pustular and granulomatous forms. The most common side effects of local corticosteroid therapy are telangiectasia, atrophy, skin pigmentation, and the appearance of papules and pustules. 7–10 days after the last use of external corticosteroids, a “withdrawal” syndrome may occur, i.e., a sharp exacerbation of the skin process occurs - hyperemia and swelling of the face, papules, and pustules appear.
Rosacea must be differentiated from perioral dermatitis, seborrheic dermatitis, Haber's syndrome, acne vulgaris, red stippling of the nose, tuberculous lupus, Besnier-Tennesson lupus pernio.
The choice of treatment tactics depends on the clinical form of the disease, severity, duration, drug tolerability, the presence of concomitant somatic pathology, age, gender, and psycho-emotional characteristics of the patient.
In complex therapy, much attention is paid to diet. Patients are advised to limit the consumption of animal fats, smoked meats, extractives, alcohol, spicy and hot foods. Patients should not stay in a room with high air temperatures for a long time; insolation should be avoided.
Before treatment, it is recommended to conduct a clinical and laboratory examination to find out the cause of this disease and risk factors.
Laboratory tests include: general blood test, biochemical blood test (determination of total bilirubin and its fractions, triglycerides, transaminase, cholesterol, creatinine alkaline phosphatase, glucose), isolation and identification of microbial flora of the skin with determination of sensitivity to antibiotics; bacteriological examination of intestinal flora, scraping from the skin of the eyelids and face to identify Demodex folliculorum .
- The use of medicinal products from the following groups is indicated:
- Therapeutic agents that suppress microbial colonization: - antibiotics for systemic and external use; — sebosuppressive medications: retinoids; Antiandrogens are used only in severe cases of rosacea.
- Medicinal products that normalize keratinization processes (have a comedolytic effect). They are fundamental for anti-relapse treatment.
Therapy should be comprehensive and should be carried out jointly with a gastroenterologist, ophthalmologist, and gynecologist.
At the initial, erythematous stage, local use of vasoconstrictor medications is recommended. Treatment tactics aimed solely at stopping the inflammatory process are insufficient. It is equally important to prevent the formation of new elements, since as a result of persistent inflammation, persistent cosmetic defects are formed on the skin - telangiectasia, as well as “fimas”.
For patients with problem skin prone to increased sebum secretion and irritation, special gels and lotions with keratoregulating, sebum-regulating and anti-inflammatory effects are recommended for daily cleansing of the facial skin.
Cleanance gel cleanses the skin without disturbing its hydrolipidic film and is washed off with water.
Preparations from the “Clerasil Ultra” series, such as cleansing lotion and washing gel, have anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and sebicide effects. Deep cleansing gel exfoliates dead skin cells, opens pores, softens the skin.
For daily cleansing and skin care, Cetaphil series products are used - gel and lotion, applied 2-3 times a day or as needed. The lotion can be washed off with water or left on the skin.
To reduce inflammation and reduce the risk of pathological scarring, use a spray with Avene thermal water. It is recommended to apply Avene cleansing lotion for hypersensitive skin to irritated facial skin and eye contours. Foaming gel "Keraknil" for daily hygiene of skin with a tendency to develop acne has a keratoregulating, bactericidal, sebum-regulating, moisturizing effect, does not contain soap. Apply morning and evening.
At the first erythematous stage, cold lotions are prescribed with a 1-2% solution of resorcinol, weak tea, and a 2% solution of boric acid, which reduce the subjective sensations of itching and burning.
In the presence of erythrocouperosis, especially with pronounced subjective symptoms, such as itching, a feeling of discomfort and burning, skin tightness, Diroseal is prescribed - a medicinal cream for local redness with a dual (preventive and therapeutic) effect. It contains a complex of complementary active substances that activate cellular metabolism, thicken the surface layers of the skin and make the network of blood vessels less noticeable; have an anti-edematous effect that improves blood microcirculation. The cream contains green pigments and has a masking effect.
At the pustular stage, antibiotics of the tetracycline group and macrolides are used.
Erythromycin ointment (10,000 units/g) is applied 2 times a day. The duration of use should not exceed 5 weeks due to the risk of developing microflora resistance.
The complex "erythromycin - zinc acetate dihydrate" has an anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, comedolytic effect. Available in powder form in combination with a solvent and applicator for preparing a solution for external use. Apply a thin layer to the affected areas of the skin 2 times a day; in the morning (before applying makeup) and in the evening (after washing) for 10–12 weeks. After drying, the solution becomes invisible.
Azelaic acid in the form of 15% gel, 20% cream is applied evenly in a thin layer 2 times a day to previously cleansed affected areas of the skin. A marked improvement is observed after 4 weeks. Local adverse reactions in the form of burning, tingling, redness disappear on their own within 15 minutes. In case of severe skin irritation in the first weeks of treatment, it is recommended to use the drug once a day.
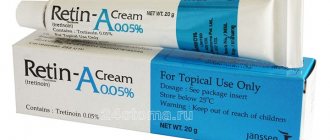
The complex of therapeutic drugs includes vitamins B6, C, P, etc., desensitizing agents (sodium thiosulfate, antihistamines). Preparations of the retinoid group are also prescribed, such as tretinoin (Retin - A) in the form of a cream or lotion, which are evenly applied to the washed and dried surface of the affected skin 1-2 times a day. The course of treatment is 4–6 weeks. Side effects may develop in the form of dryness, hyperemia, swelling, hyper- or hypopigmentation, photosensitivity.
Adapalene is a retinoid metabolite. It has an anti-inflammatory effect, has comedolytic activity, normalizes the processes of keratinization and differentiation of the epidermis. 0.1% cream or gel is applied evenly, without rubbing, to the affected areas of dry, clean skin once a day before bedtime. The therapeutic effect develops after 4–8 weeks, persistent improvement after 3 months of use. Side effects include hyperemia and peeling of the skin. Not recommended for use during pregnancy and breastfeeding. Avoid contact with eyes and lips and avoid exposure to sunlight; It is not recommended to use cosmetics with a drying or irritating effect (including perfumes, ethanol-containing products). Therapy begins with a gel, and for sensitive and dry skin, a cream containing moisturizing components is prescribed.
Retinoic ointment 0.05% and 0.1% has dermatoprotective, antiseborrheic, anti-inflammatory, and immunomodulatory properties. Inhibits hyperproliferation of the epithelium of the excretory ducts of the sebaceous glands, reduces the formation of sebum, facilitates its evacuation, reduces the inflammatory reaction around the glands and enhances regeneration processes in the skin. However, the ointment should not be prescribed to patients receiving other drugs from the retinoid group. The effect of the ointment is weakened by the simultaneous administration of tetracycline antibiotics, as well as the local use of glucocorticosteroids.
Considering the role of Demodex folliculorum in the development of the disease, after the disappearance of acute inflammatory phenomena, one should proceed to treatment with antiparasitic (sulfur-tar) pastes and ointments, gradually increasing the concentration of sulfur and tar in them from 5 to 15%, with “Yam” ointment. This ointment should be applied on the first day for 15 minutes, and then removed with vegetable oil and lubricate the skin with cold cream, which eliminates the feeling of tightness and discomfort, reduces irritation caused by dryness, and restores hydrolipid balance. If there is no burning sensation, the next day increase the duration of application by 5 minutes and bring it to 1.5 hours. Then gradually reduce this time daily by 5 minutes until the ointment is completely discontinued.
For the purpose of anti-demodectic effects, a 5-10% suspension of benzyl benzoate is also prescribed or a course of treatment is carried out according to the Demyanovich method (sequential treatment of the skin with a 60% solution of sodium thiosulfate, and after 15 minutes - with a 6% solution of hydrochloric acid).
Nitroimidazole derivatives are prescribed, which enhance the protective and regenerative functions of the mucous membrane of the stomach and intestines. The drugs have a bacteriostatic effect against obligate anaerobic bacteria and an antiparasitic effect against Demodex folliculorum . However, metronidazole can immobilize treponemes, leading to a false-positive TPI test (Nelson test). During drug therapy, it is possible to obtain false results when determining the activity of liver transaminases, levels of lactate dehydrogenase, triglycerides and glucose in the blood plasma. At the same time, 1% cream or 1% gel containing metronidazole (Metrogyl) is prescribed. Apply a thin layer to the skin 2 times a day (morning and evening) for 3–6 weeks. Avoid contact of the gel with mucous membranes, including the eyes (contains alcohol). Prescribe with caution to persons with hypersensitivity to sunlight and a tendency to photoallergic and phototoxic reactions (sun exposure is excluded during treatment). Use is contraindicated in the first trimester of pregnancy. Breastfeeding should be stopped during treatment.
"Rozamet" - a cream containing 10 mg of metronidazole, has proven itself as an effective remedy for the topical treatment of rosacea and perioral dermatitis. Thanks to its light creamy base, it penetrates well into the skin, softens and moisturizes it for a long time. The drug is applied 1-2 times a day in a thin layer after acute inflammatory phenomena in the affected areas have subsided. For blepharitis, “Rozamet” is applied to the skin of the upper and lower eyelids once a night. After 3-4 weeks of regular use, there is a significant reduction in swelling, lacrimation, and the amount of exudate in the corners of the eyes.
It is also possible to prescribe combination therapy, including isotretinoin and antiandrogenic drugs (spironolactone or cyproterone).
During treatment, dryness, irritation, and peeling may occur. To eliminate the side effects of therapy, it is recommended to use the moisturizing soothing cream “Klin AK”, which contains thermal water, zinc gluconate, jojoba oil, and shea butter. It should be applied to cleansed skin in the morning and/or evening.
For hypersensitive skin, specially developed products are used to restore comfort: Avene cream for hypersensitive skin, which contains Avene thermal water, white petroleum jelly, polyols, and squalene of plant origin, which eliminate irritation and restore the protective function of the skin. The cream is applied to cleansed facial skin 2 times a day. Soothing cream for hyperreactive skin “Tolerance Extreme” instantly gives a feeling of comfort, reduces skin reactivity, relieves irritation, and improves the tolerability of drug treatment. Produced under sterile conditions in accordance with the standards for the production of injectable drugs. Produced in sealed packaging in sterile mini-doses, without fragrances, preservatives, or surfactants. The cream contains: Aven thermal water, cartama oil, glycerin, liquid paraffin, silicone polymer, titanium dioxide, pH = 6.
For daily care and protection against erythrosis, rosacea and a tendency to redness, Antiruger is prescribed - a cream or emulsion against redness. "Rosaliak" is a moisturizing corrective product without perfumes for skin prone to redness.
"Sensibio AR" is a cream containing anti-inflammatory and restorative components that prevent the appearance of redness and eliminate the feeling of heat already at the first application.
Sensibio AR can be recommended as monotherapy or in combination with other treatment methods (laser, electrocoagulation or cyclins, metronidazole). The cream is recommended to be applied in the morning and/or evening to thoroughly cleansed skin.
These products are especially indicated for patients during periods of increased skin sensitivity to external irritants, after surgical interventions.
Physiotherapeutic methods accelerate the resolution of inflammatory elements of rosacea.
Methods for the destruction of telangiectasia are also used: electrophoresis of chloroquine or epinephrine on the lesions daily or every other day, course - 12-15 procedures (for the erythemal stage); cryotherapy (cryomassage) - 2-3 times a week, course - 10 procedures; electrocoagulation - from 20 to 100 procedures depending on the stage and extent of the process; laser therapy.
Treatment of rhinophyma usually involves surgical excision of hypertrophied tissue.
For the treatment of secondary post-inflammatory skin changes - hyperpigmentation, pseudoatrophy, scars - microcrystalline dermabrasion is used, carried out once a week, a course of 5-10 procedures. Mandatory conditions are: complete relief of the inflammatory process on the skin, protection of the skin from insolation during and for 1 month after treatment. Superficial chemical peels with a-hydroxy acids (30–70%; pH less than 3.5). Properly performed acid peeling of the skin can achieve positive results in most cases. However, like any other procedure, various types of chemical peeling must be performed according to a strictly defined protocol, taking into account skin type, its sensitivity, indications and contraindications. An irrational desire to increase the degree of exposure of the skin to acid can lead not only to an increase in the number of complications and unwanted side reactions, but also to reduce its effectiveness.
To prevent the formation of atrophic scars that form after pustules, it is recommended to use the Contractubex gel, which has a fibrinolytic, anti-inflammatory, and keratolytic effect. The gel stimulates cellular regeneration without hyperplasia and inhibits the proliferation of keloid fibroblasts. Apply 2-3 times a day to scar tissue. The course of treatment for fresh scars is on average 4 weeks.
If the integrity of the skin is compromised and there is a high risk of secondary infection, it is advisable to prescribe the restorative cream “Sicalfate”. The regenerating effect of the drug is achieved due to the sucralfate included in its composition, and the zinc-copper complex provides an antibacterial effect.
If the integrity of the epidermis is damaged, “Epithelial A.N.” is prescribed, a restorative cream containing 0.2% hyaluronic acid and having an active regenerating effect at the level of the epidermis and dermis.
Prevention of rosacea includes protection from sun rays, diet, thorough cleansing of the skin, and temperature control.
Sunscreens from the “Angelios” series do not contain chemical filters, are odorless, are well tolerated, and are adapted to each skin type, each phototype in accordance with the received dose of solar insolation.
When treating patients with rosacea, an integrated approach to drug administration is important. Long-term pathogenetic therapy is required along with basic care.
A. G. Pashinyan , Doctor of Medical Sciences, Russian State Medical University , Moscow
Prevention
There are no effective measures to prevent rosacea. There are a number of recommendations for patients who already suffer from this pathology. Useful for relapse prevention:
- reduce your time outdoors in strong winds, frost and extreme heat, use protective equipment;
- exclude active exposure to UV radiation, use photoprotectors;
- do not visit swimming pools, saunas, steam rooms;
- adjust your diet;
- maintain optimal temperature and humidity in places of residence;
- eliminate bad habits;
- avoid aggressive cosmetic procedures;
- select skin care products together with your doctor;
- When taking medications, evaluate their possible side effects.
Sources:
- Clinical manifestations of rosacea. Polyakh Ya. A. Dermatovenereology. Cosmetology. Sexopathology No. 10, 2007. p. 370-373
- Genetic markers of rosacea. E. V. Agafonova, L. S. Kruglova, M. A. Avagumyan. Bulletin of new medical technologies No. 4, 2022. p. 137-144
- Innovations in topical therapy for rosacea. Olisova O.Yu., Kochergin N.G., Smirnova E.A. Russian Journal of Skin and Venereal Diseases No. 5, 2022. p. 270-274
- Molecular mechanisms of rosacea pathogenesis. Davydova A.V., Bakulev A.L., Morrison A.V., Leonova M.A. Saratov scientific and medical journal No. 3, 2013. p. 561-565
- Triggering factors for the development of rosacea. Mustafina G.R. Social and humanitarian knowledge, 2022. p. 141-144
- Modern approach to the treatment of rosacea. Teplyuk N., Shurubey V. Doctor No. 12, 2015. p. 72-75
Masks from Ascorutin for rosacea
Treatment procedures using the drug are easy to carry out at home. Masks with ascorutin for rosacea are applied to cleansed skin so that the substances penetrate deeper into the epidermis. First, the remaining makeup is removed, and then a gentle peeling is done. After this, you can apply the mask.
With green tea
The mask will not only cope with rosacea, but will also refresh the complexion, protect against puffiness and increase local immunity. To prepare it you will need the following substances:
- flour – 1 tbsp;
- ascorutin – 2 tablets;
- green tea – 1 tbsp.
Tablets of the drug are crushed into powder, which is added to flour. Green tea is brewed as usual. When it cools down, all parts of the mask are connected using it. Stir the mixture until a homogeneous paste forms.
The mask is applied in several layers. The first is distributed in a thin layer over the entire face, and the second - only in the place where rosacea develops. The layers should be washed off after 20 minutes. In this case, you need to try not to damage the epidermis with sudden movements.
With gelatin
This mask is suitable for sensitive skin that is easily injured. After its use, the skin of the face is smoothed, looks fresher and more youthful. The composition of the mask is as follows:
- ascorutin – 10 tablets;
- food gelatin – 1 tbsp;
- jojoba oil – 15 drops.
Soak gelatin in warm water. Crush the tablets into powder. Add ascorutin and aroma oil to the swollen mass. Distribute everything over the face with massage movements. Wash off the mask after half an hour.
With lingonberries
This mask solves several problems at once. It eliminates rosacea, smoothes wrinkles, and cleanses the skin and pores well. Complexion improves, pigmentation decreases. The mask includes:
- lingonberries – 1 handful;
- ascorutin – 2 tablets;
- flour or starch - 1 tbsp;
- yolk – 1 pc.
Mash the berries with a fork until pureed. Add crushed tablets, flour (starch). Beat the yolk first, then pour into the mixture. Leave the mask on your face for about half an hour. Then you should carefully wash it off. Lingonberries can be replaced with another berry: wild strawberries or strawberries.
With clay
The mask will cope with any skin inflammation, rosacea, acne and more. In addition, it will perfectly cleanse the epidermis and even out its color. For this you need the following ingredients:
- clay – 1 tbsp;
- ascorutin – 2 tablets;
- any oil - a few drops.
- milk – 1 tbsp.
Use the clay that suits your needs. If your skin is prone to oily skin, then black is perfect. The white or pink appearance will not harm those with sensitive dermis.
Distribute the treatment mixture over the entire face. After 20-30 minutes, rinse with warm water and then wash with cool water. After cleansing the skin from the mask, lubricate your face with olive or coconut oil (clay dries out the epidermis and it needs to be moisturized).
Chamomile tonic
The ingredients of this product accelerate skin restoration. They remove rosacea, bruises and pimples. In addition, signs of fatigue disappear from the face and the epidermis is toned. The composition here is as follows:
- chamomile – 1 sachet;
- ascorutin – 2 tablets.
First you need to make a decoction of chamomile. To do this, lower the filter bag into a glass of boiling water. When the broth has cooled, add crushed tablets. Shake the resulting liquid and pour into a glass container. Use the solution as a tonic 2-3 times a day.
Skin care tips for rosacea
This disease affects delicate, dry skin, which requires regular and careful care. There are some rules you should know:
- It is not advisable to steam this type of epidermis in a bathhouse, sauna or with hot compresses;
- It is not recommended to do chemical facial cleansing (peeling);
- Creams that contain salt or any citrus fruits should be avoided. These components act very aggressively on the skin;
- should not sunbathe;
- you need to spend as little time as possible under the scorching sun;
- use protection from ultraviolet rays (SPF at least 20);
- Avoid using various fruit acids on your skin. These substances make the epidermis thinner;
- use cosmetics made from natural ingredients;
- When going outside in winter, smear your face with a rich cream;
- It is advisable to add aromatic oils (jojoba, almond, avocado and others) to caring cosmetics. 3-5 drops are enough for one tube. Such substances strengthen blood vessels well, toning them;
- adhere to the correct daily routine;
- eat quality food;
- use cosmetics that are designed to combat rosacea.
Other uses of Ascorutin for the face
The unique properties of the drug allow it to be used when caring for any type of epidermis. It can improve the properties of cosmetic products (cream, tonic, serum, gel and others). Ascorutin is used not only for rosacea, but also in the following situations:
- enrichment of skin care cosmetics. Tablets are added to creams or gels before use. For mixing use a separate container. The dragees are turned into powder. Take a little cream and mix it with the tablets. You should not add the latter to a whole jar of product. Otherwise, Ascorutin, due to its chemical composition, will change the shelf life downward. Use cosmetics with the drug twice a week, and for rosacea - four times;
- improving the characteristics of the tonic. Chamomile is a universal antiseptic. The plant gently cleanses the skin of impurities, destroying pathogens. If you add Ascorutin tablets to the chamomile decoction, the epidermis will recover much faster. It is recommended to use the medicinal solution several times a day. Pay special attention to problem areas;
- preparing an infusion for washing. Cosmetics made from natural ingredients care for the skin without harming it. It is not difficult to make the solution yourself. To do this, take one filter bag of sage and infuse it in a glass of boiling water. Add 200 grams of milk and 3 crushed tablets of the drug to the decoction. You can use the solution every day. It has anti-inflammatory, antibacterial and restorative properties;
- preparing compresses for express care. To make it, you will need a bunch of parsley, from which a decoction is made. The same amount of milk and several Ascorutin tablets are added to it, which were crushed before this. Gauze, which is folded in several layers, is dipped into a warm solution and applied to the face. The compress will refresh the skin, brighten it and moisturize it well.
- Taking the drug orally. This medication is used to eliminate vitamin deficiency, as well as to treat vascular diseases. If the skin is affected by rosacea, it is necessary to use one tablet three times a day for 3 weeks.
The development of rosacea on the face is associated with the weakness of the blood vessels located in this area. With age they become deformed. First, the skin turns red, and then the dilated capillaries themselves become visible. The disease “nests” on the cheeks, wings of the nose or chin. In this case, the epidermis often becomes inflamed. It is difficult to disguise rosacea with cosmetics. It will still be noticeable.
To get rid of the capillary network, doctors recommend using Ascorutin internally and also adding it to various masks, creams or lotions. With regular use of the drug, the blood vessels are toned and strengthened. The capillary network disappears from the face. The medication itself will also help get rid of fine wrinkles, even out the skin color, giving it a healthy appearance.