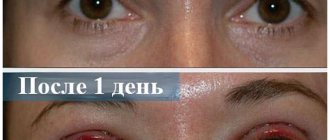
After discharge
The duration of postoperative rehabilitation averages from 6 to 12 weeks and depends on the type of surgery. The approximate recovery time will be explained to you by your attending physician. Upon returning home, you may experience discomfort and general weakness - this is a normal rehabilitation process.
Activity
After surgery, we recommend that you be as active as possible in your health. Try to walk every day. Just walking down the street or walking on a gym will do. If the weather is not very suitable for walking, you can spend time in the shopping center. Climbing stairs is also suitable as a workout. Do not lift more than 3-5 kg for 4-6 weeks after surgery. Before returning to work, discuss this with your operating surgeon at your first postoperative visit. We do not recommend that you drive a car until the pain is eliminated.
Pain
Moderate chest pain is common after thoracic surgery. The intensity and duration of pain is individual for each patient, but usually goes away within the first month. In addition to pain, you may experience numbness in the suture area and below, tingling and/or increased sensitivity of the skin in this area. These sensations are normal and will also subside in the postoperative period. If pain or other sensations begin to intensify for several days in a row, this is a reason to contact your doctor.
Medicines
Mostly you will be prescribed painkillers. We prefer non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: ketanov, ibuprofen (Nurofen-express), Nise (imisulide), xefocam (lornaxicam), diclofenac. Other painkillers will also work. It should be remembered that these medications irritate the stomach and should be taken after meals. Food should not be too spicy or irritating. If you take painkillers for more than 5-7 days, you should start taking medications that protect the stomach (omeprazole 20-40 mg at night).
You need to watch your diet, drink more fluids, eat more fruits and other foods containing fiber. The intestines should be emptied at least once every 2-3 days. If you are prone to constipation, you can take magnesia or Duphalac.
Postoperative wound care
The surgical incision area should be kept dry and clean. Do not use creams or ointments. You should shower once a day. You can wash with soap or shower gel and do not rub the seam area with a washcloth. After a shower, the postoperative wound should be carefully dried and treated with a solution of brilliant green or potassium permanganate. There is no need to apply any bandages. After all the crusts fall off from the wound on their own and a pink, smooth scar appears, treatment can be stopped. Avoid taking baths for the first 3-4 weeks.
What is rehabilitation and how should it be carried out?
Rehabilitation - “rehabilis” - lat. restoration of ability.
Who is suitable for cardiac rehabilitation?
- patients with myocardial infarction
- after operations CABG, MCS
- after stenting
- after valve replacement
- after surgical treatment of arrhythmias
Rehabilitation after heart surgery is a set of medical and psychological measures aimed at:
- prevention of further development of the disease
- disability prevention
- improving quality of life
- maintaining the patient's ability to work
- returning him to social activity
Rehabilitation assistance is provided:
- regardless of the duration of the disease
- subject to the stability of the patient’s clinical condition
- in the presence of rehabilitation potential, i.e. physical, psychological, social resources of a person that will help him regain strength
- in the absence of contraindications to various techniques
- based on established diagnosis
What diseases can cause removal of the uterus
For normal functioning of the uterus, a woman must have hormonal balance. After the removal of an organ, a woman’s metabolic processes in the body are disrupted, and the main thing during this period is to normalize them, restore hormonal levels and increase the ability to recover so that the sutures heal as quickly as possible.
There are many reasons why a woman may have an organ removed:
- oncology;
- myoma;
- endometriosis;
- pelvic inflammatory diseases.
In any of these cases, diet becomes a “lifeline” for quick and high-quality restoration of the female body. Serious interference with the reproductive system has a negative impact on physical and emotional health. Therefore, a woman needs to survive this condition more gently, replenishing her diet with the necessary elements to improve her overall health.
When is a metal structure installed?
Of course, it may not always help, and this operation is not used in all problematic cases. During a surgical operation, metal is placed on the vertebral bones in case of serious damage.
MRI of the lumbosacral spine
The spinal column may be damaged for the following reasons.
- A person falls from a significant height.
- Road car accident.
- The collapse of something (roof, avalanche, etc.) and a strong blow to the spine.
- Diseases of the spine leading to degenerative-dystrophic consequences.
A person who has undergone spinal surgery to install metal structures must be prepared for the fact that he may be contraindicated in any kind of sports.
Most often the lower back and neck are injured. Moreover, if a person can survive with a lumbar injury, but find himself completely immobilized, then with a cervical injury the most likely outcome is death.
Compliance with the rules of rehabilitation after surgery will allow you to avoid serious complications and restore your ability to work in a timely manner.
The operation carried out to install a metal structure is necessary in the following cases.
- The diameter of the spinal canal is reduced.
- Degenerative changes occurred in the ligamentous apparatus.
- Intervertebral discs are damaged.
- An intervertebral hernia has formed.
Spinal disc protrusion
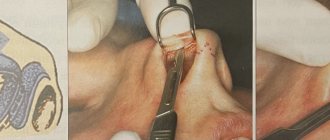
In all these and a number of other cases, an operation with the installation of stabilizing plates or rod structures becomes necessary. These foreign bodies are designed to immobilize the desired area in order to immobilize it and promote fusion (healing).
Surgery
By the way. The surgical method is used quite widely due to the fact that the period of post-traumatic rehabilitation is significantly reduced, and the patient can almost completely regain a normal lifestyle.
Thanks to the development of medical technology, structural implants for spinal surgeries have a variety of shapes, many sizes and are classified in a certain way.
Vertebral fracture - before and after surgery
Table. Classification of operating structures.
| View | Installation method |
| Solid rod | Attached inside the bone canal |
| Hollow rods | Inside the channel |
| Locking rods | Inside the channel |
| Rods without locking | Inside the channel |
| Staples | Placed on the dice |
| Helical designs | On the bone |
| Plates | On the bone |
Titanium plate in the spine
By the way. After the installation (implantation) of structural devices, the consequences of spinal damage are minimized, and the postoperative recovery procedure is reduced several times in terms of time.
However, the insertion operation is a surgical insertion of increased complexity. And the degree of return of the body’s vital functions largely depends on the quality of the subsequent rehabilitation.
Hypospadias
WHILE YOU ARE IN THE HOSPITAL
- After surgery, your child will be asked to drink clean water when he or she is fully awake.
- He will be discharged home from hospital when he can drink without vomiting. Nausea and vomiting are common after anesthesia and may last for 24 hours after surgery.
- Don't worry if you see bloody discharge through the bandage or on the penis.
- If your child has received a “spinal shot,” their legs and feet may feel slightly numb or have difficulty moving. Don't worry. All sensations will return.
- It is recommended that you talk and touch your baby while he is in the room.
AFTER ARRIVING HOME
DIET
- You can feed your baby juices, jellies and empty broth on the first post-op day/evening.
- The transition to regular food is possible the next morning or earlier if possible.
- You should not feed your baby, especially if he is feeling nauseous. His appetite will return over time.
CLOTH
- The penis will be wrapped in a special bandage. This dressing will be removed in the hospital according to your doctor's specific instructions.
- Don't worry if you see a few blood spots through the bandage.
- Try to keep the dressing and surrounding areas clean by frequent wiping with a damp sponge.
- Don't worry if the dressing becomes contaminated with stool or urine. She may also smell. There will be no infections on the penis.
- If the bandage comes off, please tell your doctor. Do not try to put the bandage back on.
- Levomekol ointment with antibiotic is suitable for use on the penis or on the tip of the bandage.
NAPPIES
- Double swaddle your baby for extra protection (see: Creating a Double Swaddle)
- Prepare several double diapers in advance of your surgery date.
- Continue to position the urinary tube and penis in the diaper as directed by your doctor and nurse.
- Change your baby's diaper more frequently during the first week after surgery.
TUBE IN THE PENIS
- A tube may be placed that goes through the penis into your child's bladder. This is used to continually drain urine from the bladder so your child does not need to go to the toilet. He may, however, feel the urge to go to the toilet because the tube may irritate the bladder. He will take a medication, Novocaine 0.5%, to relieve this urge and bladder-related spasms. Bladder spasms are not dangerous.
- Bladder spasm may cause some leakage or "spraying" of urine around the tube. This is normal and Novocain will help cope with this.
- Avoid kinking the tube as this will prevent the free flow of urine.
- Do not push or pull the catheter - be careful when changing diapers.
- Remember - the tube is in the bladder and urine is drained. Urine will leak from the catheter during diaper changes.
- Bleeding may occur after surgery. Blood in the catheter and on the diaper is not unusual and should stop within a few days.
BLADDER SPASMS
- Bladder spasms occur from the tube irritating the bladder as well as from the normal healing process.
- Signs of cramping include arching your baby's back associated with irritability, spraying urine through and around the tube, suddenly waking up from deep sleep, and a strong urge to urinate.
- For a one-time spasm, try stroking and comforting your baby.
- For more frequent cramps, your doctor will prescribe Novocaine.
- Constipation will increase cramping. Make sure your child has soft stools daily. If you notice a change in his stool, start giving him straight apple juice or diluted prune juice. Try giving baby prune puree. Add fiber.
- Avoid flour, dairy and other foods that cause constipation.
TREATMENT
- You can give your son Nurofen for any pain or discomfort.
- For severe pain, your doctor may prescribe a different drug.
- Driptan is a drug that relieves one-time spasms. Use it as prescribed by your doctor.
- The antibiotic should be taken as prescribed by your doctor.
LOADS
- Carry your baby while supporting him from behind. There should be no pressure in the penis area!
- NO active toys (bicycles, tricycles, or rocking chairs) for at least ten days unless otherwise directed by your doctor. Do not carry the patient on your hips.
- Child seats, strollers and high chairs can be used.
- Your child can ride in the car, take walks, and walk up and down stairs.
POSTOPERATIVE VISIT TO THE DOCTOR
Make an appointment with your child's doctor to have the dressing removed or the catheter removed.
Stages of cardiac rehabilitation
There are three stages of rehabilitation after heart surgery and myocardial infarction:
- Stage I – hospital, where stenting/bypass surgery is performed according to indications
- Stage II – sanatorium-resort treatment
- Stage III – outpatient follow-up of the patient after heart surgery or heart attack
is especially important, since it is the longest in time, and, ultimately, determines the further development of the disease.
And if everything is clear with the first and second stages of rehabilitation - a hospital, where the patient is taken by ambulance, and, if possible, a sanatorium, then the third stage of rehabilitation, outpatient, the most important for maintaining health in the future, remains at the patient’s choice.
At the EXPERT Clinic you will be able to undergo the third stage of rehabilitation under the supervision of experienced specialists. In rehabilitation, a multidisciplinary approach is always used, i.e. interaction of specialists of various profiles, namely:
- cardiologist-rehabilitologist
- neurologist
- psychotherapist
- nutritionist
This provides various types of assistance to overcome the consequences of the disease, change lifestyle, reduce the impact of risk factors; assessment of the need and sufficiency, duration, consistency and effectiveness of the participation of each specialist at each specific point in time during the rehabilitation period.
If necessary, at the EXPERT Clinic you will be advised by a council of doctors of various profiles.
Third (outpatient) stage
The “Third Stage of Cardiac Rehabilitation” program at the EXPERT Clinic includes:
- appointment with a cardiologist
- Patient School – group classes with a cardiologist, which discusses the problems patients face and their solutions
- performing ECG, Echo-CG, 24-hour ECG and blood pressure monitoring according to indications
- general blood test, biochemical blood test (lipidogram, coagulogram, electrolytes, homocysteine, CRP, etc.)
- psychological testing
- consultation with a psychotherapist
- consultation with a neurologist
- nutritionist consultation
- genetic analysis of all cardiac markers, including the risk of sudden death, for the patient and his relatives
- genetic analysis of drug doses in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases
When to see a doctor during rehabilitation
Contact your doctor immediately if the following symptoms appear:
- back pain that does not subside and intensifies;
- burning in the area of the damaged disc;
- urinary disturbance;
- pain in the abdomen, arms, legs;
- numbness of hands, feet;
- heat;
- spasm, tension in the back muscles;
- too much swelling in the area of the diseased disc;
- ichor that oozes from the stitches.
These symptoms indicate complications that may result from infection in the wound, purulent inflammation, the onset of pathological narrowing (stenosis) of the spinal canal, when bone/cartilaginous structures affect the nerve roots, and other complications, including recurrence of intervertebral hernia.