The arsenal of practicing surgeons is constantly updated with various tools for correcting functional and cosmetic problems in the midface. Among them: lifts of varying degrees of aggressiveness, blepharoplasty to correct the position of the lower eyelid and preserve its youthful shape, removal and reposition of fat in the lower eyelid area, various implants for the zygomatic and orbital zones, volume replenishment using autologous fat tissue and fillers available on the market. However, the surface of the skin remains a separate task - wrinkles and sagging skin require action on the surface of the skin in order to compress collagen and tighten the skin. Laser and radiofrequency devices are successfully used for this purpose. In this article, Dr. Fred Fedok, a plastic surgeon from the USA, talks about procedures for correcting the middle third of the face: the lower eyelid.
Correction of the middle third of the face: anatomy of age-related changes
When considering the mechanisms of aging of the midface, which must be taken into account when choosing procedures for correction, the doctor pays attention to three main anatomical zones:
- lower eyelids;
- connection of the lower eyelids and cheeks;
- directly to the cheeks.
The movement and structural integrity of this area are interrelated: aging causes several negative changes to occur simultaneously in the structures mentioned above.
Various dynamic factors that influence the aging of the midface include:
- decreased skin elasticity;
- stretching of the retaining ligaments in the cheeks and eye sockets, which are connected to the skeleton, muscles and the skin itself;
- involutional changes in fatty compartments, which are a consequence of the weakening of their supporting structures and direct atrophy of adipose tissue.
All these processes occur against the background of bone loss in the orbital area and structural loss of projection.
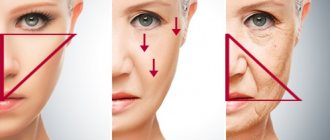
As a result of the above changes, drooping of the eyelid margin is observed, the orbicularis oculi muscle lengthens vertically, resulting in folds under the eyes, and the fat pad of the cheek moves downwards (Fig. 1).
Rice. 1. Age-related changes in the lower eyelid and middle third of the face
The nasolabial fold becomes more pronounced, but not due to its deepening, but due to the displacement of the zygomatic tubercle downward, closer to the nasolabial fold. Thus, due to the contrast, the fold visually appears more pronounced.
At the junction of the lower eyelid and cheek, a characteristic deformation appears - a double bulge of the lower eyelid and the junction of the middle part of the face (Fig. 2). This deformation is a consequence of changes in the volume of bone and soft tissue in the periorbital and zygomatic region, as well as ptosis of soft tissue.
On a young face, this anatomical area has smooth contours and is presented as a gradual transition from the contour of the lower eyelid through the orbital ridge to the cheek. With age, these structures separate from each other, and their contours become more noticeable.
The above changes are more pronounced in patients with insufficient bony projection of the orbital rim and midface, resulting in the formation of a negative vector (Fig. 2). Signs of aging in the midface appear earlier in these patients. Insufficient support of periorbital structures leads to the appearance of:
- unaesthetic appearance of the lower eyelids;
- skeletonization of the orbital ridge;
- functional eyelid retraction;
- ectropion.
Rice. 2. (Left) A characteristic double bulge is a deformation at the junction of the lower eyelid and cheek. (Right) “Negative vector” of facial anatomy. The projection of the pupil is larger than the projection of the cheek.
Conversely, in patients with good bony projection in the midface (or positive vector), the periorbital structures are less prone to downward displacement due to age-related stretching of the cheek retinaculum muscles.
Rehabilitation
It is very important to talk about the recovery period, since quite often it is rehabilitation that causes fears and questions in patients planning an operation. Despite the relatively low tissue trauma during midface lifting, recovery time is required after surgery.
Rehabilitation time
The duration of rehabilitation is several months. It takes about 3-4 weeks to return to normal activities and work. The final result of Cheek-lift can be assessed after the swelling disappears.
First days
At this time, good rest, light nutrition, and good healthy sleep are necessary. Give yourself the opportunity to relax, give up petty work and affairs.
Early postoperative ailments
In the first days after lifting, swelling of the tissues in the correction area is observed, discomfort and pain, tearing, and runny nose may occur. Gradually, such ailments will go away on their own.
1-2 weeks after surgery
The swelling gradually subsides, the condition of the tissues and general well-being improves at this time.
One month after surgery
You will already be able to see positive changes.
Modern methods for correcting signs of aging in the middle third of the face
Understanding of age-related anatomical changes, the popularization of new techniques and the development of new biomaterials have led to a change in the approach to midface correction. As a result, doctors are able to obtain better facial rejuvenation results compared to traditional facelift techniques. Due to the significant influence of this anatomical region on the appearance of the entire face, plastic surgeons pay special attention to rejuvenating the middle third. Modern cosmetic surgeons have a wide selection of instruments to solve a whole range of anatomical problems associated with age-related changes. These include:
- restoration of volume with fillers or autologous fat;
- blepharoplasty;
- lifting;
- correction of bone tissue.
Volume restoration for correction of the middle third of the face
The problem of soft tissue volume reduction and skeletonization, which lead, for example, to deformation of the tear trough, is in most cases solved with the help of fat and fillers.
It is volume restoration that is the most common method of correcting the middle third of the face, especially in younger patients. Both injections of your own fat and fillers available on the market provide excellent results. But fillers are used more often because their injection procedure is non-surgical and less expensive.
Based on the patient's anatomical changes, the appropriate procedure for correcting the midface can be selected. In case of slight changes, it will be enough to just replenish the volumes:
- In patients with slight excess skin and wrinkles (without eyelid displacement), slight protrusion of fat in the lower eyelid area, mild skeletonization and downward displacement of the malar fat pad, the author injects filler along the eye ridge (Fig. 3).
- To work with patients who experience more pronounced changes with a noticeable downward displacement of the malar fat pad, a slightly different volume replenishment strategy is chosen. As in the previous case, the filler is injected along the orbital ridge, but the contour of the cheekbones itself is also changed. Here, volume replacement is performed to elevate the buccal cusp. Improving the malar contour also helps reduce the severity of the nasolabial fold. Carefully introduced filler will smooth out the skeletonization of the orbital ridge, as well as the deformation of the tear trough.
Rice. 3. (Left) before and (right) after injection of HA filler along the infraorbital margin to correct tear trough deformity and skeletonization of the orbital ridge.
HA fillers, which distribute very well and have a slight lifting effect, are ideal for injection into the orbital area: they provide volume without the need for bone support; we self-align in the tissues, which reduces the risk of lumpiness in the injection area.
In the midface and lateral cheeks, it is better to use HA with a greater lifting effect and less spreading ability to restore volume and provide structural support. Such materials are introduced deeply, above the level of the periosteum. With proper assessment of the anatomy and choice of insertion technique, this procedure is performed safely, painlessly and with minimal risk of complications.
Autologous fat can also be injected into the malar region (Fig. 4). Deep fat injection makes the procedure simple, painless and safe.
Injecting fat into the tear trough should ideally only be carried out by experienced professionals, otherwise lumps of fat will be visible through the relatively thin skin of the eyelids and can only be removed surgically.
The safety of volume replacement for correction of the middle third of the face depends on the chosen technique of drug administration and the correct assessment of anatomical changes.
The author typically injects HA fillers and the patient's fat into the midface using a blunt cannula, which reduces the risk of bruising, as well as intravascular injection.
Rice. 4. Before (left) and after (right) fat grafting to correct tear trough deformity and restore cheek volume
Preparation and carrying out the procedure
The procedure does not require complex preparation. A week before the procedure, you must stop smoking, taking medications that affect blood clotting, and anti-inflammatory drugs. Give up alcoholic beverages for at least 2-3 days. Facial contouring with hyaluronic acid takes on average no more than 1 hour.
To accurately administer the drug, the doctor first makes marks on the skin with a special marker. An anesthetic cream is applied to the desired area. The drug is administered with a thin needle, then distributed with soft massage movements. If the filler is of high density, it is injected using a cannula that has a rounded end. It does not cut tissue like a needle, but moves it apart. At the end of the procedure, the skin is treated with antiseptics and recommendations for further care are given.
After completion, slight swelling and redness of the skin are possible, which should not cause concern; they go away on their own within a few days. After injections, for 1-1.5 weeks it is forbidden to visit the bathhouse, swimming pool, sauna, solarium, steam the face, scrubbing and other aggressive manipulations.
Facial contouring at the Estelab clinic is performed by high-level doctors. The main task of our specialists is to maintain the health and youth of the patient’s skin. We always find the most optimal and effective option that is suitable specifically for a given client. To get detailed information about facial contouring in Moscow, call the number provided or leave a request on the website.
Blepharoplasty for correction of the middle third of the face
Excess soft tissue and laxity in the area in question can be corrected through various surgical techniques:
- blepharoplasty;
- blepharoplasty with fat reduction;
- lifting (both transpalpebral and transtemporal).
Blepharoplasty should be performed in case of more pronounced signs of aging: excess skin on the eyelids, a large amount of protruding fat and displacement of the eyelid.
There are many techniques for performing blepharoplasty. According to the author, it is best to choose a transconjunctival or transcutaneous approach for the operation. The choice of approach is based on the patient's anatomy and history of blepharoplasty. The author, as a rule, performs lower blepharoplasty transconjunctivally with removal of excess tissue. According to the author, this is the best way to preserve the function of the orbicularis oculi muscle.
If it is necessary to perform a midface lift, correct eyelid retraction, ectropion, or install an implant, the author in most cases is inclined to transcutaneous blepharoplasty.
Transcutaneous incisions are typically made below the eyelid, at least 4 mm from the lash line, to preserve the pretarsal region of the orbicularis oculi muscle. The younger the patient, the closer the incision is made to the eyelash line. The medial part of the incision should be limited in order to preserve the innervation of the orbicularis oculi muscle.
Until the mid-90s, the surgical approach to rejuvenation of the periorbital area was limited to lower blepharoplasty with lifting the soft tissues of the eyelid, removing excess skin and excess orbital fat. Later, blepharoplasty for correction of the middle third of the face began to be performed with reposition of orbital fat (as a biological internal implant) onto the orbital rim.
In the case of a large amount of visually noticeable orbital fat, a certain part of it must be removed. If there is significant deformation of the tear trough, the author removes the lateral fat pad and repositions the nasal and central fat pads over the orbital rim.
Injection sites
The best places for intramuscular injections are the upper part of the buttock, the vastus femoris muscle and the deltoid muscle of the shoulder. When performing an injection into the buttock, it must be visually divided into 4 quadrants. The injection is made in the upper outer quadrant - this is the safest area without large nerves and blood vessels. In the case of the hip, its anterior surface is also divided into 4 quadrants. Inject into the outer outer quadrant.
The correct place for an injection in the shoulder can be found like this: mentally divide the arm from the elbow to the shoulder joint into 3 equal sections. The center of the middle area will be the most suitable location. However, it is more difficult to give an injection in the shoulder without assistance than in the thigh or buttock.
- Advice
: if IM injections are prescribed as a course and not as a single procedure, choose a different place each time, and also try not to hit the points of previous injections, so as not to provoke inflammation and compaction. - Important
: before performing an injection into any muscle, it must be relaxed as much as possible to prevent the needle from breaking in the process.
Lifting options for correcting the middle third of the face
There are different techniques for performing lifting procedures to tighten the midface. Most often, surgeons use a transtemporal endoscopic approach to perform this procedure. Some lifting correction techniques are performed together with blepharoplasty through transcutaneous or transconjunctival access. The goal of a midface lift is to correct the contour and position of the lower eyelid, as well as improve the eyelid-cheek connection and reposition the malar fat pad (Figure 5).
Rice. 5. Before (left) and after (right) transtemporal/transpalpebral lift with double convexity correction and cheek tubercle lift