09/24/2020 Alena Masheva Health
There are cases when a child is born with a convex groove in the middle of the forehead. Sometimes such formation appears in the first year of life. In this case, the baby’s skull has a triangular shape. Such defects may be associated with early healing of the metopic suture. Can this anomaly affect the health and development of children? Is this pathology curable? We will answer these questions in the article.
Table of contents
- Etiology and pathogenesis
- Clinical manifestations
- Principles of treatment
Furrows on the face (deep wrinkles, creases, folds) are visible changes in the relief of the facial skin in the form of local depressions of more than 3 mm. Usually combined with other signs of chrono- and photoaging of the skin, underlying structures and the whole organism.
In our company you can purchase the following equipment for treating furrows:
- AcuPulse (Lumenis)
- UltraPulse (Lumenis)
Etiology and pathogenesis of furrows
The famous dermatologist Albert Kligman compared the evolution of wrinkles with the state of leather gloves: “New products are always smooth, but gradually creases appear in places of bending and pressure, which progress over time.” This analogy can be projected onto a person - wrinkles on the face appear in places of increased activity of facial muscles and then only get worse. The primary factor in their appearance is considered mechanical. This is confirmed by the absence of wrinkles, for example, on the outer side of the forearm, although the skin here often shows pronounced signs of photoaging.
But facial activity alone is not enough - for the appearance of deep furrows, nasolacrimal and others, other components are needed. One of them is ultraviolet radiation . It causes photoaging of the skin, resulting in increased activity of matrix metalloproteinases, which begin to actively destroy the extracellular matrix. In addition, the structure of elastin fibers changes, excessive production of glycosaminoglycans is observed, and the density of the microfibrillar network in the area of the dermal-epidermal junction and in the dermis decreases. This leads to a qualitative change in the structure and function of the skin, exacerbating wrinkles that appeared due to mechanical pressure.
A decisive role in the formation of deep grooves on the face is played by changes in the bones of the facial skeleton and the state of the superficial muscular aponeurotic system (Superficial muscular aponeurotic system, SMAS). SMAS is a special muscle structure whose free ends are attached to the skin using cords. Gradually, the strands degrade, and this happens at different rates - as a result, the tension of different parts of the face changes, they begin to sag, and wrinkles and deep furrows form on the face.
Gravity affects the appearance of deep tear troughs, causing sagging skin and increasing the appearance of wrinkles. Smoking significantly aggravates the condition of the skin, increasing the number and depth of wrinkles ( Fig. 1 ). Losing teeth plays an important role not only in changing the appearance of the face, but also in the appearance of deep wrinkles. For example, the loss of teeth on the lateral (side) side of the jaw leads to a narrowing of the face and hollowing of the cheeks, which changes the tension of the skin and leads to the formation of furrows.
A certain role in the appearance of deep wrinkles on the face is played by genetic predisposition (including race and skin phototype), general condition of the body (illness, chronic stress, hormonal levels, menopause), nutrition and lifestyle (including bad habits), place of residence (pollution air, number of sunny days per year), etc.
In vivo experiments noted an interesting feature of deep wrinkles: they can protect the skin inside the fold from the negative influence of external factors (for example, ultraviolet radiation). Since almost no sunlight penetrates into the deep fold, elastosis does not progress, and the condition of the skin in this area does not deteriorate as significantly as around the wrinkle.
Rice. 1. Skin of an 80-year-old non-smoker ( left ) and a 78-year-old smoker ( right ) (Osman O., Elbashir R., Abbass E., Kendrick I., et al. Automated Assessment of Facial Wrinkling: a case study on the effect of smoking. 2017)
Formation of the infant’s skull: soft areas, asymmetry, is it possible to level it
Every woman, seeing her newborn child for the first time, tries to make sure that everything is okay with him, and is very upset when she notices the unusual shape of the head: when the back of the head is flat, and the child’s skull is asymmetrical. Parental worries are understandable, so doctors explain why babies have an uneven head.
Parents worry if their newborn's head shape does not meet standard standards
What does a newborn's skull look like?
The anatomy of newborns is such that immediately after birth they may have an unusual appearance of the skull. In pediatrics, it is believed that whatever the method of birth, the head will be like that: elongated, flattened or even. In order not to worry again, you need to know why this is the norm:
Important! When characterizing the baby's head, its disproportion with the body is noted, so it looks disproportionately large. This is the difference between the body proportions of a baby and an adult.
In addition, the child’s head appears disproportionate due to the fact that its circumference is approximately 2 cm larger than the size of the chest. This is considered an age-related feature of the skull of a newborn child and an indicator of his health.
The pediatrician monitors the dynamics of development, comparing indicators using the anthropometric table.
Changes in the baby's skull during childbirth
Why does a newborn baby have a large, prominent forehead?
During childbirth, it hurts not only the mother, but also the newborn, as he has to push the soft tissues apart with his head. At this moment, enormous pressure comes on it, deforming it and causing swelling.
The mobility of bones during childbirth plays a big role, so changing the baby’s skull during childbirth is a physiological necessity.
Deformation of the skull in a newborn
Newborn head size
It is the mobility of the bones that allows them to connect, protecting the baby’s head from injury and helping to move along the birth canal. The shape of a newborn baby’s skull depends on the structure of the mother’s birth canal and can be:
- brachycephalic - in caesarean children, that is, round, with clearly visible frontal tubercles;
- elongated oval, that is, dolichocephalic - in children born naturally.
Due to the difficulties of passing along the mother's path, the baby may be born with asymmetry of the head, sometimes with a cephalohematoma. Deformation of the skull in infants is, to a greater extent, caused by this reason.
Within a few months, the shape of the newborn’s skull returns to normal.
Immediately after birth, the newborn’s skull is elongated in the anterior and posterior regions, after a few months it increases in the transverse region, and the shape of the head takes on its usual appearance. The normal size of a newborn's head is about 36 cm.
It is not dangerous if the size is larger. Sometimes a baby inherits this feature from its parents; with age, everything returns to normal. Indicators below the norm are found in premature babies, in children with compression, and Down syndrome.
Deviations from the norm
The main reason for deviations from the norm is birth trauma and congenital diseases. Injury can occur if the fetal head does not fit the size of the woman's tract or she suffers from diabetes. Many consequences can now be cured and the head can be straightened by the year.
For your information! Any deviations from the norm frighten adults; they do not know what to do. Doctors reassure: as long as the fontanel is not ossified, all the flaws can level out on their own.
Pathologies of the skull
It is much more difficult to cure congenital diseases, for example, hydrocephalus or hydrocephalus, which is a serious and dangerous disease. A symptom of another rare pathology, microcephaly, is a too small head, which indicates underdevelopment of the brain.
Such problems can be detected during pregnancy, with an x-ray, and then treatment can begin. There is also a pathological deformation of the head in a child:
- sloping and asymmetrical back of the head – plagiocephaly;
- acrocephaly or elongated form;
- curvature of the frontal or occipital areas - scaphocephaly.
Asymmetry of the skull in children can lead to neurological pathologies and retardation in mental or physical development.
The size of a newborn's head must correspond to certain parameters
What is a fontanel
Flat back of the head in a baby - how to fix it
A fontanelle is a formation between the bones where they should connect to each other. The pattern of the infant's skull is represented by a large number of bones, between them there are open seams that close from the age of three months:
- The lateral fontanelles in full-term infants are usually closed;
- At the back, the fontanel is located at the level of the occipital parietal bones, is open in about a quarter of newborns and closes no later than eight weeks;
- At the top, the large fontanel is located at the junction of the coronal and longitudinal sutures, has different sizes, the measurement scheme is from 3x3 cm to 1.5x2 cm.
Important! According to standards, overgrowth of the fontanel from above occurs within one and a half years. Its rapid closure indicates excess calcium. Delayed closure with flattening of the occiput and enlargement of the parietal tuberosities may indicate rickets.
The timing of fontanel overgrowth is an important diagnostic sign; if there are any abnormalities, you need to consult a pediatrician who will refer the child to a neurologist.
Changes in head shape in newborns
Parents often ask how long it will take for their child's uneven head to begin to straighten out. Experts explain that this process can last up to a year. To help the child get back to normal faster, parents must follow the rules of caring for him.
Impact of improper care
Sometimes during childbirth the shape of the head does not suffer, but by doing the wrong things the mother can harm the baby:
- An elongated and sloping nape is a consequence of the baby’s incorrect position, lying on his back most of the time;
- A flat back of the head indicates rickets, which means that additional intake of calcium and vitamin D and a change in the diet of the nursing mother are necessary;
- When the fontanel is open, you should carefully wash the child, trying to prevent jets of water from falling on him.
A baby's head with an open fontanel requires great care when caring
For your information ! Lying on the right or left side for a long time can cause deformation of the cranial bones, that is, torticollis. This pathology leads to a crooked, inclined position of the head, which is accompanied by abnormalities in the development of the spine.
What not to do to change the shape of your head
Some mothers use home massage, that is, “rolling out,” to straighten the shape of the baby’s head. It is carried out in a circular motion clockwise while pressing on uneven areas.
However, pediatricians believe that such a massage is useful only if it is performed by a specialist; in the absence of experience, it is better not to take risks. Pressing too hard on the convexities of the skull can further increase the deformity.
For your information. In most cases, by the age of one year, the child’s head takes on the shape that is laid down at the genetic level.
Examination of a child by a neurologist
During the first month, asymmetry of the skull may be noticed by parents or a pediatrician during a routine examination, who will give a referral to a neurologist. In difficult cases, it is necessary to consult a neurosurgeon.
You should visit a neurologist for the first time when you are a month old. The main task of a specialist is to correctly diagnose the pathology, preventing the disease from developing. An experienced doctor will determine what abnormalities exist in the circumference and girth of the head. Up to a year, visits to a neurologist are scheduled every 3 months.
Treatment of asymmetry
Pediatricians say that untimely correction of head asymmetry can lead to undesirable consequences in the form of strabismus, deviated nasal septum, malocclusion and many others. Therefore, they recommend both special treatment and home measures on how to correct skull deformation in an infant:
- Change the baby's headboard more often;
- Breastfeed from different sides;
- Support the head with a bolster, preventing it from falling to the side or back;
- Constantly pick up the baby in your arms in an upright position.
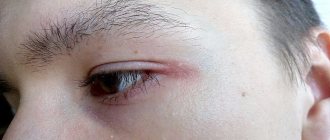
Clinical manifestations of the tear trough
The main places where deep furrows appear are in the eye area (in the corner, above and below the eyelids), on the cheeks, near the ears, between the eyebrows, in the corners of the mouth, and on the chin. It is also worth noting the nasolabial folds and horizontal lines on the forehead and neck, which gradually deepen with age.
Classification of wrinkles according to the Modified Fitzpatrick Wrinkle Scale (MFWS):
- Class 0 (no wrinkles) - no visible wrinkles, skin uniformly smooth.
- Class 0.5 (very small) - wrinkles barely visible to the eye.
- Class 1 (minor) - slight indentations in the skin.
- Class 1.5 (pronounced) - depressions less than 1 mm.
- Class 2 (medium) - clearly visible relief bends from 1 to 2 mm.
- Class 2.5 (medium deep) - visible wrinkles more than 2 mm deep, but less than 3 mm.
- Class 3 (deep) - grooves on the skin more than 3 mm.
Despite the general similarity of localization, wrinkles are located differently in each person, forming an individual pattern - the so-called “wrinkleprint”, similar to fingerprints. In experiments, it was found that the future localization of wrinkles and furrows on the face can be determined approximately 8 years before their appearance. Moreover, for this you do not need to perform complex tests - just smile ( Fig. 2 ).
Rice. 2. Diagnosis of wrinkles at rest ( Baseline neutral ), when smiling ( Baseline expression ) and after 8 years at rest ( 8-year neutral ). In the third row of each column you can see the features of the patterns of periorbital wrinkles at rest, when smiling and after 8 years at rest (Farage MA, Miller KW, Maibach HI (Eds.) Textbook of Aging Skin. Springer 2010: 916)
Medicine Live
A 40-year-old patient, who had not visited a medical facility for a long time, came to the Hospital de la Salpetriere, (France) with complaints of a “dent” on the scalp (image A).
According to him, he first began to notice the asymmetry of the skull about five years earlier. Subsequently, these changes gradually increased.
On examination, no pathological changes were detected in the skin of the scalp. A CT scan of the head revealed a significant area of bone tissue destruction in the bones of the skull with fairly clear contours (image B – tomogram in the horizontal plane; image C – CT scan of the skull with three-dimensional reconstruction). Bone scintigraphy with technetium 99-methylene diphosphate showed increased metabolic activity in the marginal zones of the lesion (Panel D).
These changes correspond to the signs of Gorham's disease, a rare idiopathic condition in which processes of destruction and replacement of bone tissue with connective or vascular tissue develop in one or more bones. Gorham disease of the ribs or thoracic vertebrae can lead to chylothorax and death due to respiratory failure. The main methods of treatment are radiation therapy and surgical interventions.
Principles of treatment and correction of facial furrows
Pronounced wrinkles on the face are quite difficult to correct with cosmetics. But cosmetics can be used to stop the progression of furrows - in particular, to moisturize the skin and protect it from external factors.
For example, apricot extract (Prunus Armeniaca Extract) gives a good effect for correcting tear troughs. It contains a lot of vitamin E (helps improve the elasticity and firmness of the skin, creates an antioxidant effect and helps reduce the depth of wrinkles), vitamin A (has a pronounced anti-aging effect, helps even out the complexion and reduce signs of aging) and vitamin C (enhances the effect of previous vitamins). Masks based on apricot kernel oil (Prunus Armeniaca Kernel Oil) can be used to nourish and moisturize aging skin.
With pronounced stretching and sagging of the skin with the presence of deep wrinkles, the results of peelings will be relatively weak. In this case, several methods should be combined, including minimally invasive injection or surgery.
Wrinkles on the face can be partially corrected using botulinum toxins . They block neuromuscular transmission and relax the muscles in a given area. It is important to understand that with pronounced age-related changes in the skin and underlying facial structures, the effect of this method may be insufficient.
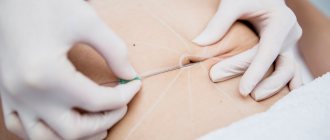
Deep nasolacrimal grooves can be corrected by injections of fillers based on hyaluronic acid, collagen or the patient’s autologous (own) fat . They temporarily fill wrinkles and deep furrows, can correct the oval of the face, and make the surface of the skin more even and smooth. The effect lasts until the filler is completely destroyed.
Threads can be installed in some areas of the face and neck . Reinforcing threads, due to a special mechanical effect on tissue and stimulation of metabolic processes, provide the so-called reinforcing effect (moderate lifting + biostimulation). Lifting threads tighten the skin more, but do not have a biostimulating effect. The choice of threads depends on the condition of the patient’s skin, aesthetic goals and the experience of the specialist.
In some cases, PRP therapy (plasma therapy) - injection of platelet-rich plasma into the tissue. The use of autologous plasma from the patient can reduce the number of possible side effects, provided that the technique is followed.
Deep wrinkles can be radically eliminated with the help of surgery - a circular facelift (facelift). This operation is quite traumatic and carries certain risks.
Laser techniques that are aimed at remodeling the dermis can also significantly correct tear and other facial grooves First of all, this is deep fractional photothermolysis. By working with the bottom of the furrow (crease) using a fractional laser, creating micro-zones of influence at a depth of 1 mm or more, it is possible to initiate the synthesis of a new structural matrix of the dermis, while destroying the old one, which has partially lost its mechanical properties.
ablative fractional photothermolysis (Acupulse, Ultrapulse) is more suitable The fact is that ablative fractional lasers make it possible to obtain the effect of “tightening” the skin: when they act on a large area of the skin where wrinkles are located, the area of this area is reduced due to contraction of collagen and partial evacuation of the dermal substance evaporated by the laser. With a large percentage of coverage, you can achieve up to a 30% reduction in area, which causes skin tension and, as a result, straightening of the furrows.
Fractional lasers do not affect the mechanical causes of furrows, in particular, the work of facial muscles. Therefore, their combination with other techniques, for example, botulinum toxin injections, is optimal.
A pit on the forehead after a bruise in a child
Children are inquisitive and restless, and therefore no one can completely avoid injuries, falls and bruises. In the process of learning about the world, babies fall quite often.
But if falling on the butt or back does not cause panic attacks in parents, then the situation changes dramatically if the child hits his head.
An authoritative pediatrician, author of numerous books and articles on children's health, Evgeniy Komarovsky, explains why such falls are dangerous and when you need to start worrying.
Features of child physiology
The head of a small child is designed in such a way that it is relatively large compared to the rest of the body, so babies most often fall on their head when they lose their balance. But there is also a positive thing: the child’s brain is quite reliably protected from injury when falling.
If a small child fell from the sofa upside down, then the greatest injury (of a psychological nature) was received by his parents, and not by himself. The bones of a baby's skull are very soft, and the "fontanelle" and dynamic "sutures" between the bones of the skull provide them with mobility. The larger the fontanel, says Evgeny Komarovsky, the less likely it is to get injured if you fall upside down.
In addition, nature has come up with another shock-absorbing mechanism - a large amount of cerebrospinal fluid.
If a child at 6-7 months, when he becomes more mobile, turns over unsuccessfully and falls from the sofa or changing table, do not immediately panic. The baby, of course, will scream heart-rendingly.
But parents must understand that he is crying not from terrible pain, but more from fear caused by a sudden movement in space.