A mole (birthmark) is a pigmented skin neoplasm, which extremely rarely can be congenital and appears on the skin after the baby’s first walks in the sun. In medicine, there is a more official term for moles - nevus. In their structure, color, shape and size, nevi can differ significantly from each other and are located on any part of the face and body. Nevi are mostly benign neoplasms, but under certain circumstances moles can become malignant.
Why moles appear
If we talk about the structure of a mole at the cellular level, then it consists of pigment cells of melanocytes (they produce the pigment melanin) and has an overgrown vascular network. These neoplasms are present in any person.
Among the main reasons that contribute to the formation of birthmarks are the following:
- Hereditary prerequisites;
- Prolonged exposure to the sun or artificial ultraviolet rays;
- Changes in hormonal levels (for example, pregnancy, etc.);
- Skin injuries;
- Viral skin lesions;
- Exposure to radiation.
Over the course of a person’s life, moles on the face and body may become more numerous, they may also increase in size or change their shape. In addition, under the influence of certain factors, birthmarks can degenerate into melanoma.
What does a birthmark on the face mean?
A birthmark on the face, the photo of which is presented below, is a modified area of the skin, distinguished by its surface structure and color. It is noteworthy that the shade of the spot varies and can be:
- beige;
- pinkish;
- dark brown;
- black.
Most facial birthmarks are congenital or appear during infancy. Some moles appear throughout life.
Often, birthmarks are not dangerous and are not associated with discomfort. However, their presence on the skin requires constant monitoring. Under the influence of certain factors, birthmarks can pose a danger to life and health.
A birthmark on the face has a certain meaning for women. The interpretation of the appearance of moles depends on the area of their occurrence:
- Lip. This location of the mole indicates the owner’s great ambitions, his unrestrained character, and his tough disposition. However, the woman is honest and fair. From a medical point of view, the accumulation of melanin in the lip border area indicates a weak immune system, a tendency to ARVI and herpetic rashes.
- Forehead. When located in the hairy upper part of the head on the right, one can assume the presence of abilities in the exact sciences. Women think soberly in difficult situations, but are susceptible to depression. A mole above the eyebrow on the right indicates the makings of a leader, as well as a speaker. These representatives often have bone and joint diseases. A birthmark on top, located on the left side of the forehead, characterizes a person who is fickle in love relationships and a careerist. People are prone to nerve diseases. A mole above the left eyebrow is considered a bad sign. People should be especially careful.
- Between the eyes, in the middle of the forehead. This mark distinguishes a purposeful and active, strong person. It is noteworthy that moles with such localization can be inherited.
- Nose. A mole is a sign of a good mother of the family. Women are susceptible to endocrine disorders and infections.
- Cheek. The birthmark often appears in women who are prone to excess weight and who are not restrained in food and alcoholic beverages.
- Neck and back of the head. Usually this localization is characteristic of vascular nevi. Women are aggressive and have a weak nervous system.
Attention! The interpretation of moles is a science called morphoscopy.
Moles that need to be removed for preventive purposes
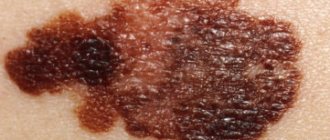
Moles themselves do not pose a health hazard if their structure and size do not change over time. And yet, potentially, the danger of degeneration into malignant melanoma exists if the nevus:
- often gets injured, for example, while shaving or combing, or rubs against clothes;
- rises significantly above the surface of the skin or has a long stalk;
- located in an “inconvenient place” of the body, for example, in the natural folds of the body, in the armpits, etc.;
- exposed to excessive sunlight or solariums;
- located on an area of the body that is inaccessible to the person himself.
In all of the above cases, it is better to remove birthmarks.
Types of birthmarks
There are 2 large groups of birthmarks:
- vascular;
- pigmented.
Vascular marks occur due to defective development of veins, blood vessels, or arteries. Typically, vascular moles are localized on the face or neck. Their peculiarity is their color, which can be either light pink or dark red. If the birthmark is red in color and has a flat surface, it is considered to be the result of capillary proliferation. With a convex shape, they speak of damage to the arteries or veins.
The following types of vascular birthmarks are called:
- Hemangioma. This term refers to a red mark of rich color that rises above the skin and has a smooth surface and clear edges. Hemangiomas can disappear on their own. With the subsequent growth of birthmarks of this type, their removal is recommended.
- Wine stain. This is a flat, crimson-colored mole that does not disappear over time.
- Kiss the stork. The mark is a red, orange or light yellow defect and has uneven edges and uneven coloring. The stork's kiss disappears during the baby's first year of life.
Experts do not classify birthmarks as dangerous skin tumors. They are not prone to degeneration into a malignant tumor. Removal of such birthmarks is recommended for severe aesthetic facial defects.
Age spots or moles appear due to excessive production of melanin by the cellular elements of the skin. Their color can vary and can be light brown, black or brown. Moles have both flat and convex shapes. The surface of birthmarks can be rough, bumpy or smooth.
Types of age spots include:
- Lentigo. This variety is considered the most common. Lentigo is a brown spot.
- Mongolian spot. It has a gray, graphite or black color, as well as uneven edges. The Mongolian spot is characterized by a large area of skin damage and the absence of serious complications.
- Blue nevus. This is a convex mole with a dense structure that has a light blue or dark blue tint.
- Neurofibroma or coffee stain. The mole is characterized by a faint brown color, uneven edges and a flat shape.
Pigmented birthmarks are considered melanoma-dangerous. The exception is the Mongolian variety.
The greatest danger is from spots localized in the facial area. This is due to their frequent traumatization, for example, during shaving or scrubbing. These moles need to be monitored constantly.
Attention! If you have symptoms of degeneration of birthmarks, you should consult a specialist. Removal of a melanoma-dangerous tumor prevents the development of a malignant tumor.
Sometimes white birthmarks appear on the skin of the face. Their occurrence is due to insufficient melanin production. The size and shape of such moles vary. The risk of their degeneration is considered insignificant and is associated with trauma or excessive insolation. Usually white moles are not removed due to the inappropriateness of the procedure. The defect does not pose a problem from an aesthetic or oncological point of view.
Birthmarks are differentiated by their size:
- small (up to 1.5 cm);
- large (over 10 cm);
- gigantic (occupies a third of the surface of the facial skin).
Cosmetic indications for birthmark removal
The mere presence of a mole is not a medical indication for its removal - but if the mole becomes a cause of complexes due to its poor aesthetic appearance, the doctor can remove it.
The “it’s better not to touch” principle, which many doctors used to adhere to, is already outdated. It is important to meet the following conditions:
- Carry out the removal procedure in a clinic, such as ours, with a certified experienced specialist using professional equipment;
- Make sure that the mole does not contain malignant cells. And for this, before removal, it is necessary to conduct a study - DERMATOSCOPE. In our clinic, this is a mandatory free study before removing any skin tumor!!!!
When removal is urgent
There is one rule for all moles - if they don't bother you, don't bother them. However, there are a number of indications for removal.
Injury
If a mole has been injured or abraded (for example, by a fall or clothing), it must be completely removed to avoid degeneration into melanoma.
After an injury occurs, stop the bleeding with a cotton swab containing hydrogen peroxide, and then apply a gauze bandage for 10-15 minutes. If the mole comes off completely, wrap it in a bandage soaked in saline solution and submit it for histological analysis. If damage occurs frequently, be sure to have the mole removed by a surgeon and be sent to a laboratory for analysis.
Interfering mole
In the case where the nevus is located where clothing constantly rubs against it (for example, a laundry strap), or in a folded area (such as the armpit), or in places where it can be easily torn off (hands, feet, neck), it is better delete it. It is also better to get rid of moles with “legs” - they can get twisted and are the easiest to tear off.
Suspicion of degeneration
If your mole changes in size, changes shape and color, or begins to peel, become inflamed or bleed, you need to get rid of it as soon as possible. Contact a dermatologist, or even better, immediately an oncologist, to rule out its malignant nature. If melanoma is removed in a timely manner, it almost never recurs, and recovery occurs in 95% of patients. In advanced cases, this is one of the most dangerous diseases.
Doctors often recommend removal of melanoma-dangerous moles—those that have a high probability of becoming a tumor.
In other cases, the issue of removal is decided individually, in consultation with an experienced doctor (dermatologist, surgeon, oncologist).
Moles that need to be removed for medical reasons
It is recommended to remove moles if they:
- located in the hair area or perineum;
- have a size exceeding 5 mm;
- changed color; peeling or hardening of the surface appears;
- changed shape;
- pain, itching, burning or bleeding appeared;
- hair fell out of the nevus;
- are constantly injured (for example, while shaving);
- have a high risk of degeneration.
There are no other treatments for birthmarks other than removing them.
How to disguise a birthmark on the face
Sometimes it becomes necessary to disguise a skin defect, for example, if a birthmark covers the floor of the face. The cosmetics industry produces many products that can hide nevi of various sizes.
Before masking nevi, you must thoroughly clean your face with foam or milk. Then the skin is moisturized with toner. To camouflage a mole, a foundation with a thick texture is best suited. It only needs to be applied in 1 layer directly to the mole. For convenience, you can use a sponge or brush. To eliminate other defects, use a corrector and cover the face with foundation.
For small moles, use a corrective pencil or cream with a brush. The product is applied to 1 layer of foundation and lightly powdered.
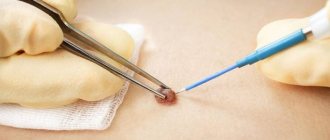
Removal methods
In order to remove a birthmark in our clinic, no additional tests are required. The removal procedure is carried out directly on the day of treatment if, during dermatoscopy, our doctor confirmed the benign nature of the neoplasm.
Our specialists offer almost all methods of non-surgical removal of skin tumors. However, based on our extensive experience, we recommend two main methods for effective and safe removal of nevi:
- Removal using the radio wave method using the Surgitron - DF 120 device (Ellman International Inc, USA). This device generates high-frequency radio waves. The procedure is non-contact, requires a minimum of time and can be performed without anesthesia. After removal, a barely noticeable area of hypopigmentation or a small scar may remain at the site of the mole if the formation was large.
- Removal by diathermocoagulation - plasma using the Plasmaskin device (Ultramed, Russia). In this case, the mole is exposed to very high temperatures (about 2500°C). The method is non-contact and provides a targeted effect, so surrounding tissues are not injured.
The choice of the optimal removal technique depends on the location of the tumor, its diameter and the result of dermatoscopy.
Our experts do not recommend laser removal of birthmarks due to the high risk of increased melanocyte proliferation.
If necessary, the removed mole is sent for histological examination, which will help clarify the nature of the formation. The bed of the removed tumor is treated with Fukortsin solution.
Possible side effects
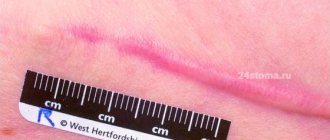
The main undesirable effects include the formation of scars on the skin of the face. Its severity depends on the size of the nevus, the method of removal and the qualifications of the specialist.
After removal of the defect, there is a risk of a keloid scar appearing. The term implies the growth of fibrous, rough connective tissue of a tumor-like nature. This phenomenon is more often observed when stitches are applied, in particular, after removing a huge birthmark on the face.
Attention! Dangerous complications include recurrence of a mole, which is possible if it is not completely removed due to violations of the surgical technique. Partial excision can lead to cell degeneration.
During the first days after the procedure, the patient may experience discomfort in the area of treatment. As a rule, itching and redness go away on their own. Otherwise, you should visit a doctor.
What happens after removal
During the first day after the procedure, a dark brown crust will form at the site of the removed tumor. Healing takes from 2-3 days to 2-3 weeks, it all depends on the volume of treatment. After healing, the crust will come off on its own. Within 1-3 months, the area of skin at the site of removal will have a bright pink color, then it will acquire a normal skin color. If you follow all the doctor’s recommendations and properly care for your skin, scars will either not form at the site of removal at all, or areas of hypopigmentation or small scars may remain.
As a rule, tumors up to 7 mm in size are removed simultaneously and no additional sessions are required. If the mole is large and benign, removal can proceed in several stages in order to achieve better epithelialization and obtain an optimal cosmetic effect. In any case, after the crust is rejected, you will need to see our specialist.
The experience and highly qualified doctors of our clinic, clear diagnostics, as well as the availability of very professional equipment allow us to remove a birthmark without harm to health or any consequences. In each individual case, our specialists try to maintain a proper balance between removing the nevus in full and obtaining the best possible cosmetic effect from the procedure.
How to remove a birthmark from your face
Elimination of the neoplasm should occur exclusively in a medical institution. The doctor selects the optimal method according to the characteristics of the facial defect. The safest methods include cryodestruction, laser coagulation, electrocoagulation and radio wave method. In some cases, surgical excision of the formation is necessary.
Cryotherapy
The method involves the use of liquid nitrogen. During the cryodestruction process, the affected area is frozen. After crystallization, the cells are rejected. The specialist removes frozen tissue using a scalpel.
Cryotherapy is considered a gentle technique. The facial skin heals quite quickly. As a rule, scars do not form. In some cases, multiple sessions may be required.
Laser coagulation
This is one of the most popular methods. Experts note that the procedure is short and painless. The absence of bleeding and subsequent scar formation is essential. The disadvantages of this method include the high cost of the procedure.
The laser beam acts in a targeted manner. In this case, healthy cells are practically not affected. Laser coagulation allows the vessels to be sealed simultaneously, which prevents the risk of bleeding. The procedure lasts several minutes.
Laser coagulation is performed under local anesthesia. The beam is used to remove birthmarks of various sizes. During the manipulation, the patient notes only minor discomfort.
Electrocoagulation
A red birthmark on the face can be removed using electric current. This is a budget procedure that is often used in public medical institutions.
The essence of the method is to remove moles with electric current. After the procedure, a crust or scab forms on the skin of the face, which is torn off after a few days. If the scab sheds prematurely, it may leave a scar.
Attention! Electrocoagulation leads to the formation of a burn. This is a rather painful method that has many disadvantages.
Radio wave method
Many people with birthmarks on the face prefer the radio wave method of removing formations. This is the safest method of surgical treatment, allowing you to act exclusively on pathological tissues. The advantages include effectiveness, safety and simplicity of the procedure. The manipulation takes a short period of time and is performed under local anesthesia.
After radio wave removal, the doctor can remove the material for subsequent research, which will confirm or exclude the presence of a malignant process. The procedure leaves no traces and has a short recovery period.
Surgical removal
A large mole on the face may require surgical excision. As a rule, the method is used for oncological suspicion.
Important! If you remove a birthmark on your face with a scalpel, scars will remain. However, in some cases, this method is the only one possible for removing malignant structures.
What cream to remove a birthmark on the face
You can significantly lighten a stain using special products with a lightening or bleaching effect. A good result is observed when using Vaseline, which is used to treat birthmarks.
Cream based on papaya or apricot contains special enzymes that help lighten the skin. Cosmetics should be applied to the face several times during the day.
Rubbing cream with vitamin A helps stimulate cell division and collagen production. Renewing and exfoliating the skin of the face helps reduce the pigmentation of moles. The cream should be applied at least 2 times a day, completely covering the mole area.
Attention! If a birthmark appears on the face, its removal is possible only after consultation with an oncodermatologist.
Traditional methods
It is believed that vitamin C in tablet form helps lighten birthmarks. On average, about 10 procedures are required, which consist of applying a crushed tablet to the skin of the face.
To lighten defects on the skin, you can lubricate the areas with fresh potatoes. The juice of onions, as well as garlic and lemon, and fresh celandine works in the same way. The procedure should be carried out for several months to obtain the desired result.
Apple cider vinegar helps remove birthmarks. It is recommended to treat problem areas with the product several times during the day. Fresh fruits help lighten blemishes on the skin. Their use is to apply to the stain for 10 minutes.
Many experts emphasize that the use of traditional medicine methods in the presence of birthmarks is not only useless, but also dangerous. Various infusions and decoctions can provoke the growth of formation due to uncontrolled cell division.
Attention! Treatment of birthmarks on the face should be carried out exclusively by a doctor. Self-medication can lead to irreparable consequences.
Contraindications to the removal procedure
Mole removal may not always be possible. There are a number of situations when it is better to postpone the procedure to a later time. These may be exacerbations of chronic diseases, pregnancy and breastfeeding, diseases of the cardiovascular system, etc. In the presence of other diseases and conditions, the feasibility of the procedure is determined individually.
For more information on moles, see the article “Moles - Frequently Asked Questions”
What causes birthmarks on the face?
The following are the causes of birthmarks on the face:
- Genetic predisposition. If parents have a significant number of moles, a similar phenomenon is observed in children in 80-90% of cases.
- Hormonal changes. With concomitant immune imbalance, an increase in the number of melanocytes and their atypical location in the skin of the face may occur. This phenomenon is typical for adolescence, pregnancy, breastfeeding, and menopause. The appearance of new spots is expected against the background of diseases of the thyroid gland and adrenal cortex.
- Pathologies of the heart and blood vessels. Heart disease, coagulation disorders, increased thrombus formation, and taking medications that interfere with blood clotting provoke the appearance of vascular nevi.
- Exposure to ultraviolet radiation. This factor influences the appearance of genetically determined birthmarks.
Necessary examinations before removal
The condition of nevi is assessed in 2 stages:
- examination with a magnifying glass and palpation;
- dermatoscopy (conventional or computer).
Sometimes an ultrasound is also required.
Hardware examinations are not traumatic and safe, but they make it possible to examine the mole in detail.
During the examination, under no circumstances should you damage the mole, and under no circumstances should you take a piece of it for histological examination (biopsy).
If you are offered such a study, refuse it - it can be dangerous.