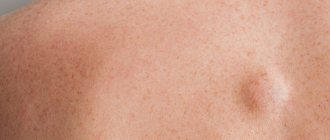
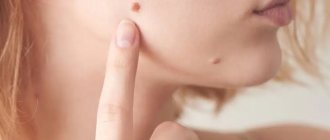
Papilloma is a benign neoplasm of a viral nature. It is a small growth that can appear on any part of the body or mucous membranes. The formation looks like a papilla on a narrow stalk. The cause of papillomas is the human papillomavirus (HPV). Papilloma does not go away on its own, it can spread, and in most cases the tumor is removed. Papillomas located on the genitals have a high risk of malignancy. Occurs in men, women and children.
Causes of papillomas, their types and location
The cause of skin papillomas is the human papillomavirus (HPV). Science knows more than 150 types of HPV, they are divided into three groups:
- Non-oncogenic papillomaviruses - types 1, 2, 3, 5.
- Papillomaviruses of low oncogenic risk (6, 11, 42, 43, 44).
- Papillomaviruses of high oncogenic risk (16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 51, etc.).
Viruses of the last two groups, with varying degrees of probability, can cause the development of malignant neoplasms.
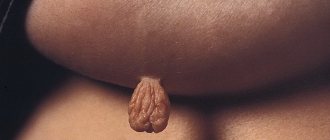
Depending on the type of HPV, papillomas are divided into the following types: ordinary papillomas - also known as vulgar warts, filamentous growths, flat papillomas, genital papillomas - also known as condylomas, plantar warts, juvenile warts and papillomatosis.
The most common are vulgar, filiform and genital papillomas.
- Thread-like forms of papillomas are more common in people aged 40+ and are localized in areas with thin skin - on the chest, armpits, neck, etc.
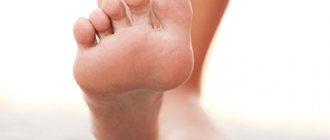
- Vulgar warts most often “attack” the skin of the feet, palms, fingers and toes, but can appear on any other parts of the body. Often recur in conditions of decreased immunity.
- Condylomas appear only on the mucous membranes. They can affect the glans penis, foreskin, vagina, and labia minora.
- Plantar warts appear on the rough skin of the feet and on the balls of the toes.
- Papillomatosis is a generalized form of the disease, manifested by the formation of growths throughout the body.
A liquid nitrogen
Effective methods for removing moles and papillomas include cryodestruction. The procedure uses liquid nitrogen, the temperature of which reaches -196 °C. This substance freezes the liquid in the altered cells, after which they are completely destroyed. The procedure is painless, so there is no need for anesthesia. After using liquid nitrogen, crusts may remain at the site of the growth. They are completely rejected after two weeks. As a rule, there are no scars at the site of removal of a mole or papilloma. Unfortunately, this method cannot be used if a tumor biopsy is required.
How does HPV infection occur?
The mechanism of transmission of the virus is contact; the source of infection is the patient or the virus carrier. HPV can be released not only from growths on the skin, but also circulate in the blood, saliva and urine. In this case, infection can occur in 4 main ways:
- through contact and everyday life;
- sexually;
- during childbirth from mother to child (which may be the cause of laryngeal papillomatosis);
- during autoinoculation (self-infection or dispersion of the pathogen from existing foci during combing, shaving, or using a hard washcloth).
The risk of HPV infection usually depends on the state of the human body’s immune system, viral load and the presence of microtraumas and other inflammations on the skin and mucous membranes.
Even when infected with the HPV virus, papillomas do not always form on the skin and mucous membranes. The virus is localized in the basal layer of the epithelium and can remain inactive for a long time. Only under certain conditions (weakening of the immune system, stress, exposure to unfavorable environmental factors) do the processes of its replication start, which leads to cell proliferation and the appearance of tumors.
Do papillomas need to be removed?
Changes in color and size are one of the possible signs of the onset of malignant processes in the body. Experts recommend contacting a medical facility if the papilloma is bleeding, it is inflamed and bothers you, it is a cosmetic defect, and also if there are signs of its degeneration. If papillomas are not removed in time, then the risk of its growth and degeneration is very high. Formations detected in the early stages, including malignant ones, are almost always curable.
Indications for removal
The only way to treat already “formed” papillomas is to remove them. Indications for removal of tumors primarily include:
- Aesthetic problems. Papillomas are skin growths that are perceived as an aesthetic defect, especially when they are localized in open areas of the face and body.
- Papillomas can be constantly injured, cling to clothes, combs, etc. and due to this, quickly spread throughout the skin, soreness, inflammation, cracks and even bleeding may appear in the area of the tumors.
- Considering that some types of papillomaviruses have a high risk of oncogenicity, large papillomas (more than 6-10 mm) may be prone to degeneration, so timely removal of such tumors will prevent a serious illness in the patient.
Contraindications for the procedure
Laser removal of benign tumors is prohibited if the following contraindications are present:
- Diabetes mellitus of the first and second degree.
- Oncological pathologies.
- Diseases of the endocrine system.
- Aggravated herpes.
- Epilepsy, thrombocytopenia, photodermatosis.
- Autoimmune diseases.
- Inflammatory processes accompanied by fever.
If contraindications are neglected, undesirable consequences may develop after removal of the tumor. For example, pigmentation due to photodermatosis, allergies, swelling due to autoimmune pathologies, keloid scar due to endocrine system disorders.
Methods for removing papillomas
In our medical center, before removing a tumor, a dermatologist examines it and, if necessary, performs dermatoscopy in order to differentiate the type of papilloma and select the optimal method of removal.
It is possible to get rid of papillomas in our clinic without surgery using the destruction of formations using a laser, radio knife and plasma. Removal of papillomas with a laser, especially removal of papillomas on the face, is not carried out so often due to the high traumatic nature of the method and the possibility of hypopigmentation and scarring. Preference is given to radio wave destruction, as well as diathermocoagulation. These methods are highly effective and low traumatic.
- The radio wave method is one of the most effective and least traumatic ways to remove almost all types of papillomas. It is performed on the Surgitron DF-120 device (Ellman International Inc, USA). Removal of the tumor occurs due to local evaporation of cells under the influence of heat generated in the tissues in response to the penetration of radio frequency waves. The cells evaporate and the tissues move apart as if cut with a scalpel. In addition, instant coagulation of blood vessels occurs in the treatment area, so there is no bleeding and no damage to surrounding healthy tissue. In this aspect, laser removal of papillomas is significantly inferior to the radio wave method.
- Diathermocoagulation using the Plasmaskin device (Ultramed, Russia) is a non-contact effect on the affected tissue with a plasma beam. The high temperature of the plasma (up to 2000-2500 C) is combined with the bactericidal effect of an air flow containing a high concentration of ozone and has a virus-destructive effect, destroying HPV DNA, which prevents its spread.
The use of radio wave energy on the SURGITRON DF-120 device (Ellman International, Inc., USA) is the method of choice for removing most forms of papillomas, regardless of their location (face/body), and here’s why:
- Radical - no relapses;
- Rapid epithelization - healing;
- Atraumatic - no complications, no marks or scars remain on the skin;
- Painless - anesthesia is required only in cases of large tumor sizes.
- Complete safety of procedures.
During the destruction of papillomas, anesthesia is usually used. Application anesthesia with the application of lidocaine cream can be used, or infiltration anesthesia, when the site of papilloma localization is injected with an anesthetic solution (Ultracaine). The choice of pain relief method is determined by the size and location of the papilloma.
If the patient has no contraindications, removal of papillomas in Moscow in our clinic can be carried out on the day of treatment, immediately after an appointment and examination by our specialist. In this case, no additional tests are required.
In order to prevent relapses after removing a large number of tumors, our experts recommend taking immunomodulatory drugs. Immunomodulatory therapy is selected individually.
Prevention of papillomavirus
Doctors at Dr. Novikov’s clinic take a comprehensive approach to the treatment of papillomas, therefore, after removal, in order to avoid the reappearance of formations, they recommend undergoing antiviral and immunostimulating therapy.
In order to avoid relapse, as well as to prevent infection, carriers of this virus are recommended to:
- Get tested periodically for the presence of HPV in your blood.
- Control the growth of existing formations
- Have only protected sex
- Use only your own hygiene products
- Eat properly
- Strengthen the immune system
- When visiting saunas and baths, use your own replacement shoes
What will happen to the skin after papillomas are removed?
The next day after the procedure, a brown crust forms at the site of the removed tumor. Healing takes from 2 to 7 days, it all depends on the size of the removed papilloma. After healing, the crust will come off on its own. The main thing at this time is not to wet or injure this area.
After the procedure, the doctor gives some simple recommendations for further skin care.
In our clinic, it is carried out using modern equipment by highly qualified doctors, which allows us to solve problems of papillomas removal quickly, efficiently and safely. We use disposable consumables, which guarantees maximum patient safety.
Electrocoagulation
High-frequency current is often used to combat tumors. This method of removing moles and papillomas is quite painful, so the doctor must use anesthesia. During the procedure, the doctor brings a special needle to the head of the growth, which conducts an electric current. A spark occurs between the device and the skin. It burns the neoplasm cells to the very foundation. There is no blister after the procedure. But a scar forms on the surface of the skin, which resolves over time.
Where to remove a mole, polyp, condylomas, papilloma or wart in St. Petersburg
At the Diana St. Petersburg Medical Center, all methods of removing tumors are used, but preference is given to modern laser and radio wave techniques. The clinic has the latest radio wave apparatus. Treatment is carried out without pain and complications under ideal sterile conditions.
Here you can take tests for oncology and blood clotting, undergo all types of ultrasound, get advice from a urologist, gynecologist, dermatologist and oncologist. All doctors have the highest qualification category and extensive experience.
Surgical intervention
The safest way is to remove moles and papillomas using a surgeon's scalpel. It is this method that is used if there is a suspicion of malignant degeneration of the growth. The operation is performed using anesthesia, so it is comfortable for the patient. Surgical intervention guarantees complete removal of the tumor, unlike laser or cryodestruction. In addition, the risk of relapse is eliminated. Many patients do not know where to remove papilloma and mole - in a private clinic or a public one. In fact, it all depends on the experience of the surgeon. It is important to find a qualified doctor. As practice shows, most often such specialists work in government agencies.
There are no contraindications to surgical removal of growths. Sometimes it is necessary to postpone the procedure. The doctor will advise you to undergo surgery in the following cases:
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding.
- Exacerbation of herpes.
- Inflammatory process.
- Exacerbation of a chronic disease.
- Viral or bacterial infection.
The duration of the operation usually does not exceed 60 minutes. After excision of the tissue, the doctor applies stitches. If necessary, the removed nevus or papilloma is sent for histological examination. The wound is treated with an antiseptic daily. Do not remove the resulting crust yourself. In addition, the affected area must be protected from exposure to sunlight for two to three months. Non-absorbable sutures are removed 10 days after the intervention. A barely noticeable scar remains after the operation. If the neoplasm was located quite deep, a more pronounced mark may remain. You can smooth it out using a special patch or absorbable cream.