Long eyelashes, thick eyebrows, beautiful, well-groomed hair are indicators of natural beauty.
Therefore, trichotillomaniacs are often rejected and ridiculed by society. The term trichotillomania comes from the Greek words trichos (hair), tillo (pulling out), mania (attraction). This is an impulsive mental disorder, expressed in an irresistible urge to pull out hair in different parts of the body. It was first described in 1889 by the French dermatologist Allopo F.A.
Trigger
According to official data, about 5% of people worldwide suffer from trichotillomania. But this figure is inaccurate, since the lion's share of patients hide their addiction. People are able to hide their addiction for 20 years.
The majority of patients are women. More often, the disease debuts in childhood or adolescence, less often in the range of 20-30 years, and even less often after 40.
The development of the disease is based on the emerging feeling of tension and anxiety. The cause may be a guilt complex, fear, anger, anger and many other conditions that provoke a feeling of anxiety.
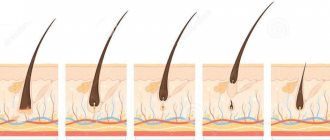
The skin where hair grows is well innervated thanks to a dense network of nerve fibers. This increases her sensitivity. A person who pulls out a hair feels pain. In this way, the patient switches attention from mental stress to physical sensations.
Self-inflicted pain acts as a way of self-punishment. Trichotillomaniac uses this method to relieve the stress that torments him. Endorphins, released under the influence of painful impulses, give a feeling of satisfaction, but only for a short time. Soon the feeling returns. The process is repeated.
There is an assumption that the disorder can also satisfy masochistic desires. Allegedly, the patient deliberately intensifies the pain in order to subsequently receive pleasure when the pain subsides. But this theory is just a guess.
Vitamin complexes and mineral supplements
Hair loss causes and treatment - all this interests people who are faced with baldness. As already mentioned, hair loss in women, like men, can be stopped using an integrated approach. The treatment uses both medications against hair loss and vitamin complexes.
One of such vitamin preparations with effective action is Tricologic®, which contains Keraton TM. This complex includes:
- amino acids that activate keratin production;
- para-aminobenzoic acid;
- extracts of valuable plants;
- vitamins E, C;
- pantothenic acid;
- iron;
- beta-carotene;
- selenium;
- vitamin elements of the B group.
The vitamin complex is taken orally and delivers valuable substances to nourish hair through the blood, directly to the follicles. Thanks to the presence of vitamins E, C, beta-carotene, free radicals are blocked, aging and hair loss are slowed down.
The complex is also useful thanks to:
- Vitamin A helps normalize sebum production and restore skin health;
- vitamin E actively restores the functionality of processes occurring in tissues;
- Vitamin C helps in the formation of connective tissue;
- vitamin B elements are necessary for proper division and growth of cells, including those located in the follicle matrix;
- biotin normalizes metabolism and gland secretion;
- para-aminobenzoic acid is necessary to maintain natural hair pigmentation;
- pantothenic acid is needed to maintain healthy hair;
- silicon helps maintain hair elasticity;
- minerals such as zinc, iron, chromium, copper, etc., support the health of hair shafts and follicles, nourish cells, and improve metabolism.
Hair loss treatment can be carried out using other vitamin complexes, for example Tallium-plus, Revalid, Aurita, Perfectil. It is important that the body, during active hair loss, receives a sufficient amount of nutrients and minerals necessary to improve health and improve the functionality of all processes occurring in the tissues.
Soil for the development of the disease
Trichotillomania is provoked by various reasons:
- Scientists are conducting research to confirm the genetic nature of the disease. It was found that the same gene, SLITKR1, was damaged in a number of patients.
- Trichotillomania becomes a manifestation of a number of other mental disorders - schizophrenia, depression, neurosis, dementia. It is a symptom of bipolar affective disorder. In most cases, pathological hair pulling is a compulsive action within the framework of OCD - obsessive-compulsive disorder.
- The disease provokes organic damage to the brain.
- Lack of serotonin becomes a provocateur of the disorder.
- Hormonal surges can rightfully claim a role in the occurrence of trichotillomania. The theory is confirmed by the fact that the disease flourishes in adolescence.
- The disorder often develops in people with a special personality type – suspicious, scrupulous, sensitive.
- Trichotillomania can be triggered by severe or prolonged chronic stress. The strongest emotional tension that arises during stress requires an outlet and finds it in such a perverted form.
Forms of loss
There is no point in proving the fact that men’s hair thins out more often than women’s. According to statistics, approximately 25% of guys who reach the age of 30 begin to gradually lose their strands.
Experts identify 7 main stages of alopecia: 1. Normal hairstyle without any significant changes in the structure of the hairline. 2. Loss along a wedge-shaped curve. 3. Strands in the temporal and frontal areas stop growing at a normal pace. 4. In these same places, significant thinning of the strands is observed. 5. The density of curls decreases. 6. The stripes that connect the sides of the head disappear. 7. Complete loss of hair. The only exceptions may be the occipital and lower zones.
Having considered the main types and stages of baldness in men, a logical question arises - how can the disease be cured. There are methods and preparations that will significantly slow down the process and restore hair.
How it manifests itself
The disease manifests itself suddenly. The patient begins to pull out hair on any part of the body:
- more often - on the head;
- brows;
- eyelashes;
- pubis;
- armpits;
- stomach;
- breast.
As patients themselves note, the desire to pull out hair is so strong that the impulse cannot be drowned out. After completing the action, a feeling of pleasant relaxation appears.
For a trichotillomaniac, hair pulling is a ritual. The strand is wound around the finger in a special way. If the hair is short, it is clamped in a certain way.
The boy fixed the hair bun between his index and middle fingers. The big one pressed it against the index finger, then, using a scrolling method, pulled it out hair by hair. According to the mother, the entire scalp was removed in this way. Afterwards the baby switched to eyebrows and eyelashes.
After the ritual, the person must make sure that the hair is removed. The patient passes the strand between the teeth and bites off the onion.
Typical is trichophagia - eating torn strands. It happens that the patient even eats other people's hair. The phenomenon was noticed back in the 18th century: a French doctor discovered a hairball in the gastrointestinal tract in a 16-year-old boy.
In addition to trichophagia, trichotillomania is accompanied by nail biting and skin trauma. Patients pull out hair from animals and pull threads out of fabric.
Another type of disorder is trichothema mania : a person “thins out” gray hair, believing that in this way he relieves itching.
Pulling out hair strands can be total, to the point of complete baldness, or zonal. Bald skin has a normal appearance with clearly defined follicular ostia.
A trichotillomaniac performs the ritual consciously and unconsciously. Unconsciously, the process occurs in a state of boredom, loneliness, while performing everyday activities - talking on the phone, watching TV, reading a book. Unconscious impulses are born both in a calm state and during a period of peak tension. After complete auto-depilation, a person becomes bewildered when those present tell him about what he did, since he does not remember how he performed the ritual.
Carrying out the procedure consciously, the patient carefully prepares for it. Prepares instruments, tries to retire.
People with trichotillomania carefully hide the areas of forced baldness. To do this, they use improvised methods. They wear hats, scarves, and wigs. Eyebrow tattooing and eyelash extensions.
Leave a request
All products are good in the fight against unwanted facial hair, but not all are as effective as the LightSheer DUET laser.
Smooth, soft and pleasant to the touch - this is how facial skin should be. Feelings of prickling or visually visible dark hairs where they should not be seriously spoil the first impression of a person and leave unpleasant sensations from close contact. Removing unwanted facial hair is easy, but to get rid of it forever, you need to know how and what to do it with.
Childhood variant of the disorder
The development of trichotillomania in children is primarily influenced by the way they are raised:
- The disorder in most cases develops in a child with a developed sense of guilt or an inferiority complex. This is facilitated by raising children in an atmosphere of increased severity, total control, constant reprimand and inflated demands;
- overprotective parenting model;
- coldness, lack of attention. So, a 4-year-old boy pulled out all the hair on his head. When his mother brought him to the reception, during the conversation it became clear that the boy was experiencing an acute lack of parental love. The father drinks heavily, so he does not pay attention to his son. The mother works two jobs to support the family. Due to lack of time, he communicates little with the child;
- conflicts between parents, their parents' divorce.
The lack of an emotional response from loved ones also affected the 9-year-old girl Lena. She did not have a father, her mother paid little attention to her daughter, devoting all her free time to organizing her personal life. Lena has a guilt complex. The girl believes that she caused her mother a lot of grief. She is constantly told stories about how her mother suffered during pregnancy. The birth itself caused complications in the uterus, which had to be removed.
Lena went to kindergarten early. The girl let her mother go every morning with tears. The woman did not show a drop of sympathy. The child had to be calmed down by the teachers.
At the age of 5, Lena developed a tendency to pull her hair while lying in bed before going to bed. Unnoticed bald patches appeared on the head. The mother took the child to the doctor who prescribed treatment. There was no desired effect after therapy. They did not find out the reason.
Only at the age of 9, when the girl went completely bald, became fearful and closed, did Lena’s mother take her to a psychiatrist, who diagnosed trichotillomania.
In childhood, the disease begins to manifest itself after 3 years. Such kids carry out auto-depilation uncontrollably: while playing, watching cartoons, and also in situations of stress. The child does not try to hide pathological actions.
In adolescents, in addition to the costs of education, trichotillomania is provoked by a tense environment in the school community and problems in communicating with peers.
Adolescent trichotillomaniacs are already prone to deliberately causing hair mutilation to themselves. They perform rituals manually or prepare tweezers. The procedure requires privacy. The disease brings them discomfort. Children try to control their actions, but control over rituals only strengthens their manifestations.
A 13-year-old girl went on summer holidays with a friend and her family to relax at their dacha. The girl was so struck by her friend’s warm relationship with family members, in contrast to her relationship with her parents, that two weeks later the mother did not recognize her daughter. Upon arrival home, the girl returned completely without eyelashes. Trichotillomania was triggered by contrasting relationships between parents and children in different families.
The clinical picture of the disease is similar in adolescents to adults. There is an element of awareness of the mutilation. Teenagers also try to hide traces of auto-depilation: they wear hoods and robes. Often, a half-plucked eyebrow becomes an indicator.
What are the dangers of trichotillomania?
The consequences of the disease include physical and social impairment.
Among the physical consequences, it is worth highlighting the damage to the gastrointestinal tract that occurs when eating hair. During the process of trichophagia, a bezoar is formed in the stomach - a hairball. It causes a lot of inconvenience - from stomach pain to indigestion. The extreme of this disorder is called “Rapunzel syndrome” - a condition where a strand of hair extends from the stomach into the intestines.
Rapunzel syndrome is an extremely dangerous phenomenon that threatens the patient with death. A case was described in which a hairball weighing 4 kg was removed from a girl’s gastrointestinal tract.
In addition, eating hair affects the condition of tooth enamel.
Skin that is traumatized at the site where the hair follicle is pulled out can become infected. In addition, if you systematically remove hair in a certain area over a certain period of time, it grows more slowly. On the head, in the area of eyelashes, eyebrows, complete baldness becomes an aesthetic problem.
The absence of eyelashes provokes vision problems:
- inflammation of the eyelids, mucous membranes of the eyes;
- conjunctivitis;
- blepharitis;
- furunculosis;
- microtrauma of the eye.
Socially, the disease causes no less problems than physically. Patients realize the absurdity of their condition, hide their pathological tendencies and unattractive consequences. They try to fight, but it doesn’t work out well alone.
It is worth noting that society is poorly aware of the problem of trichotillomania. Therefore, an unevenly bald person without eyebrows and eyelashes involuntarily causes bewilderment and sarcasm on the part of others.
Self-flagellation and public bullying make trichotillomaniacs depressed and force them to isolate themselves from their surroundings, which threatens complete social isolation, loss of friendly contacts, and loss of self.
Cost of laser and photo hair removal of head areas
| Procedure | Old price (S) | Discount* from 3 zones | New price | |
| Laser hair removal of the head | from 2500 rub. up to 5000 rub. (depending on the area of the head to be epilated) | |||
| Laser facial hair removal | 4,500 rub. | 15% | RUB 3,825 | |
| Laser hair removal for forehead | 3,000 rub. | 15% | RUB 2,550 | |
| Laser eyebrow hair removal | 500 rub. | 15% | 425 rub. | |
| Laser hair removal for chin | 3,000 rub. | 15% | RUB 2,550 | |
| Laser hair removal of cheekbones | 750 rub. | 15% | 640 rub. | |
| Laser hair removal of the upper lip | 1,300 rub. | 15% | RUB 1,105 | |
| Photo facial hair removal | 4,500 rub. | 15% | RUB 3,825 | |
| Photo of forehead hair removal | 3,000 rub. | 15% | RUB 2,550 | |
| Photo eyebrow hair removal | 500 rub. | 15% | 425 rub. | |
| Photo of chin hair removal | 3,000 rub. | 15% | RUB 2,550 | |
| Photo hair removal of cheekbones | 750 rub. | 15% | 640 rub. | |
| Photo epilation of the upper lip | 1,300 rub. | 15% | RUB 1,105 |
Cost of laser hair removal using the Clarity device