Doctors Cost
Price list Doctors clinic
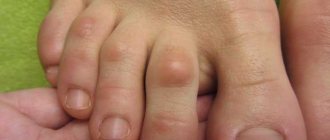
Ingrown nail is a disease in which the lateral edge of the nail plate abuts the soft tissue of the periungual fold. Mechanical impact and tissue injury from the sharp, hard corner of the nail leads to chronic inflammation. This disease most often affects teenagers and active young people. The first toe is more common because it has the hardest nail and fleshy periungual ridges. Removal of an ingrown toenail should be carried out according to indications. In the case of acute purulent inflammation, this is the only method of treatment, but in the early stages it is often possible to cope with the pathological process using conservative methods.
Types and symptoms
Symptoms of ingrown toenails depend on the severity of the disease. There are three stages of the formation of the disease:
- 1st degree: the lateral edge of the nail plate presses under the edge of the periungual fold, swelling, redness, and slight tissue growth occurs. This stage is characterized by discomfort when walking.
- 2nd degree: the lateral edge of the nail goes under the roller, noticeable thickening and inflammation of the roller occurs. The redness intensifies, pronounced swelling, pulsation, and pain occur. Discharge, including purulent discharge, may appear.
- 3rd degree: the nail plate is deeply hidden under the periungual fold, deformation of the finger occurs due to pronounced tissue proliferation on one side. A wound is formed filled with inflammatory tissue (“wild meat”). Copious purulent discharge appears, bleeding, and pain intensify.
Hypergranulation, or inflammatory tissue, is an open wound, so there is a high risk of infection. In this case, the inflammatory process can spread to the posterior ridge (base of the nail), and purulent paronychia occurs. This process is characterized by severe pain, swelling and redness of the ridges on both sides.
You can do without surgery for an ingrown toenail only at the first stage of the disease. In other cases, the only way to eliminate inflammation is surgery.
Options for surgeries at the clinic
Regular or simple removal
We resect the ingrown edge of the nail plate. Using a Volkmann spoon, we scrape out pathological granulations and treat the growth zone.
Cost - 2500 rubles
Radio wave removal
We remove the ingrown edge of the nail and pathological granulations. We treat the growth zone with radio wave electrodes (Surgitron or Fotek E81M). They give reliable results
.
Cost - 3500 rubles
Operation according to Schmieden
Resection of
the ingrown edge of the nail plasty with excision of the ridge and part of the bed. We apply stitches (atraumatic suture material). We use this type of intervention in advanced situations or in case of relapse.
Cost - 4500 rubles
Causes of ingrown toenails
Ingrown toenails occur for several reasons. The most common are the following:
- care: too much cutting of the edges of the nail plate or corners;
- improperly selected shoes: with a narrow toe, narrow, high heels, made of poorly ventilated materials;
- injuries: wounds received during trimming pedicures, frostbite, blows and bruises;
- individual structural features of the feet, fingers, nails: flat feet, clubfoot, deformation of the fingers, too large nail plates, etc.;
- hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating of the feet);
- mycoses of the feet, nails;
- excess weight;
- diabetes;
- systemic diseases in which onychodystrophy and deformation of the nail plate are observed;
- inadequate physical activity;
- pregnancy.
In many cases, there is a combination of several factors.
More about the operation
A poorly or poorly done pedicure, fungal infections, flat feet, tight narrow shoes, injuries - all this threatens the deformation and ingrowth of the nail plate into the soft tissue.
Currently, ingrown toenail removal is performed using modern, low-traumatic techniques aimed at speedy recovery. Electroradio wave surgery is used to remove or trim an ingrown nail plate. This allows, even in the most difficult clinical cases, to minimize surgical trauma and ensure a short healing period. These procedures are performed using “one-day surgery” technology and are carried out in an outpatient operating room. After the procedure, you can go home straight away. Preparation for the intervention is minimal, and the operation itself lasts a few minutes.
Diagnostic features
Diagnosing ingrown toenails is not difficult. A visual examination by the surgeon and a short questioning are usually sufficient. Additional research methods are required only to exclude other pathologies. The following diagnostic tools can be used:
- X-ray if there is a suspicion of bone tissue damage;
- blood test for glucose levels if diabetes is present or suspected;
- scrapings of the skin and nails if a fungal disease is suspected.
The diagnosis and surgical removal of an ingrown toenail should be performed by a surgeon. However, in cases where the disease could be provoked by other pathologies, it is important to obtain advice from other specialists. If you have diabetes, you will need to be examined by an endocrinologist; mycoses of the feet and nails will be dealt with by a dermatologist, etc.
What happens if you do not resect the nail plate?
In the absence of timely treatment, complications most often arise from the chronic course of an ingrown toenail. Complications include:
- Lymphangitis lymphadenitis - the infection spreads through the lymphatic vessels, causing their inflammation (lymphangitis) to the nearest lymph nodes (popliteal and inguinal lymph nodes), where it lingers, causing their enlargement and pain (lymphadenitis).
- Toe abscess is a purulent inflammation of the soft tissues of the toe, accompanied by swelling and redness of the entire nail phalanx, requiring surgical intervention.
- Osteomyelitis of the nail phalanx of the finger - the transfer of purulent infection to the bone, difficult to treat, amputation of the phalanx of the finger may be required. Diagnosis is based on the results of an X-ray examination of the finger bones.
- Toe gangrene is an irreversible necrosis of the soft tissues of the foot, accompanied by blackening of the skin. The only treatment is amputation of the nail phalanx or the entire toe.
Conservative treatment methods
Non-surgical treatment is carried out only in the absence of purulent inflammation. Two methods can be used for this:
- tamponing and the use of local medications: the doctor will prescribe antiseptics that eliminate inflammation and stop the growth of granulation tissue;
- orthonyxia, or the use of correction devices: a specialist installs special staples and plates that allow you to direct the growth of the nail plate in the right direction and correct the condition. This treatment may take several months.
Despite the fact that conservative methods in some cases allow one to avoid surgery, they are not without a number of disadvantages. They can be resorted to only in case of uncomplicated inflammatory process. When there is suppuration of tissues and granulations, it is not advisable to use them. The course of therapy will take quite a long time, from several weeks to several months. Correctors are an expensive tool, and it is important to visit a doctor regularly to evaluate the condition. The specialist will not be able to guarantee the effectiveness; the likelihood of the need for intervention still remains.
This decision is advisable only in the absence of pronounced painful symptoms or high risks of infection. It is suitable for patients who are contraindicated for surgical interventions.
Treatment of ingrown toenails with medication
It is practiced only in mild forms and at the beginning of the onset of phalanx deformity. This treatment is allowed if:
• mild ingrown nails;
• absence of inflammatory processes and suppuration;
• the pathology occurs in a mild and almost painless form.
The first is foot baths . They are made with a weak solution of potassium permanganate (potassium permanganate) and baking soda. The injured leg is immersed in warm water for 10 or 15 minutes. Stays on until the skin softens. After this, the plate is slightly cut off using nail scissors. The procedure is performed 3 times a day. And so on until the ingrown toenail is completely cut off.
The second is local ointments . They most likely will not get rid of the defect, but will help avoid tissue infection. The best and proven remedy is Vishnevsky ointment (ichthyol ointment). It is applied to a small piece of bandage, folded several times. Then apply to the affected area and bandage tightly.
To prevent the ointment from spreading, some people use a small piece of polyethylene. A sock is put on top. This allows you to better immobilize the bandage and finger and prevent contamination of the bandage. The best time for the procedure is at night. In the morning, the applied bandage is carefully removed and an attempt is made to cut off the ingrown plate. If pain occurs and suppuration increases, you should immediately contact a surgeon.
Third, drying the edge of the nail plate . For this, special solutions are used. They treat the problematic area. For example, you can use iodoxun. It contains two important components - glycerin and iodine. The first one softens, the second disinfects and dries. For the best effect, lubricate the nail grooves 3-4 times a day. And so on until the pain completely disappears while walking.
In addition, antibacterial ointments are used. They are applied to the affected area. After prolonged use, the nail fold (the edge of the skin into which the nail is embedded) softens. Then it gradually comes out. And then it is carefully cut off. This method is useful only for minor damage to the finger.
Surgical methods of treatment
Surgery to remove an ingrown toenail is the gold standard of care. The main indication for intervention is the presence of granulation and purulent inflammation. There are several treatment principles:
- when the disease first appears, a marginal resection is performed (removal of part of the plate) with removal of the overgrown tissue of the cushion;
- in case of ingrowth caused by onychomycosis (fungal disease), the nail plate is completely removed to form a nail bed;
- in case of recurrent ingrowth, resection with plastic surgery of the nail bed and fold is performed.
It is important to understand that the operation must be accompanied by measures to prevent relapse, otherwise there is a high probability of recurrent disease as the nail grows. In addition, in many cases, the doctor accompanies the procedure by prescribing medications with local and systemic effects to speed up the elimination of inflammation and cure fungal and other diseases.
There are several ways to remove an ingrown toenail:
1. Complete. This technique is almost never used in modern clinics. Despite the fact that with the help of such an operation it is possible to achieve rapid relief of the condition, the method does not guarantee the absence of relapse in the future. This intervention has strict indications: detachment of the nail plate over the entire surface after mechanical damage, nail infection with fungus.
2. Regional resection. This approach is used much more often. This is a low-traumatic and effective method that involves removing only the ingrown edge of the nail. In this case, the procedure is accompanied by cleansing of granulations and tissue treatment.
3. Schmiden's operation. During this intervention, a marginal resection of the nail is performed with the destruction of a fragment of the growth zone, and the periungual ridge is excised. The operation involves relatively more trauma, but reduces the likelihood of relapse to 5-10%. Indicated for recurrent ingrowths.
Marginal resection can be performed not only with a conventional scalpel. Advanced technologies make it possible to minimize tissue trauma and carry out the procedure faster and more efficiently. Thus, the use of a laser beam allows the procedure to be performed faster, more efficiently and safely. It lasts on average from 10 to 30 minutes and provides local anesthesia. It is not necessary to stay in the hospital after the intervention; if the patient feels well, he goes home.
Laser treatment of ingrown toenails
This is, in fact, laser correction of the emerging pathology. It is concentrated mainly in the area of the nail fold. Using a laser device, all overgrown tissue is removed. The duration of the procedure is about half an hour.
The stages of laser correction include:
• local anesthesia;
• elimination of the defective part of the nail plate to its normal width;
• excision and cleaning of inflammation on the side wall of the finger.
Finally, a patch and bandage are applied to the treated area. Blood loss is much less due to coagulation of blood vessels (sealing with a laser beam). The next day, the tampon is removed and the wound is left to heal in the open air. This speeds up the process. Powders, creams and ointments are prohibited.
Despite the progressiveness and painlessness (compared to surgery), this method has its disadvantages. The first and most decisive thing is that the soft skin of the skin is burned out with a laser. Because of this, healing takes much longer.
Benefits of laser removal
Removal of an ingrown toenail using laser technology is performed on an outpatient basis and does not require hospitalization. There are several significant advantages of laser removal:
- less damage to the nail bed, low traumatism;
- no risk of bleeding due to the coagulating properties of the laser beam. Thanks to this, the likelihood of complications is reduced, and the doctor receives a greater overview of the surgical field, which means he can cope with the task faster;
- evaporation of hypergranulations is a less traumatic method in comparison with their mechanical scraping;
- a significant reduction in the risk of wound infection, as well as help in the fight against fungal diseases. The laser beam destroys fungal spores and pathogenic microorganisms, which helps reduce inflammation;
- short healing period, rapid recovery;
- reducing the likelihood of developing granulations in the wound area, which minimizes the risk of relapse.
The cost of removing an ingrown toenail using a laser is slightly higher, but it is important to consider the significant reduction in the likelihood of re-ingrowing.
Content
- Treatment of ingrown toenails – marginal resection surgery
- Causes of pathology
- Consequences of onychocryptosis
- Treatment with staples
- Surgery
- Laser removal
- Radio wave treatment
- Cryodestruction
Treatment of ingrown toenails – marginal resection surgery
Onychocryptosis, or ingrown nail, is a pathology accompanied by the ingrowth of the lateral edge of the nail plate into the surrounding nail fold. Mechanical compression of soft tissues causes damage, inflammation, hyperemia and swelling. The patient feels pain, pulsation and a local increase in temperature. The injury is accompanied by hypergranulation - the growth of excess tissue. Onychocryptosis interferes with walking, wearing shoes, and causes discomfort even at rest.
Causes of pathology
An ingrown toenail most often appears on the big toe, since it bears the main mechanical load, but onychocryptosis is also noted on other toes. One edge of the nail plate or both may grow in. This disease is one of the most common in outpatient practice and is caused by:
- genetic abnormality in the structure of the nail plate;
- metabolic disorders in the body, such as diabetes;
- fungal infections (onychomycosis);
- finger injuries;
- wearing tight shoes;
- immunodeficiency of various origins;
- circulatory disorders in the lower extremities caused by atherosclerosis, obliterating endarteritis, varicose veins;
- choosing the wrong nail shape when trimming;
- flat feet or hallux valgus (bump of the big toe).
A chromosomal abnormality is manifested not only by a violation of the shape of the nails, but also by the abnormal development of soft tissues under the nail. Under the influence of pathogenic factors, the growth zone of the nail changes. As a result, the growth vector is disrupted - the nail begins to grow in the lateral direction, the plate is deformed and compresses the soft tissues, penetrating into their depths.
Consequences of onychocryptosis
Lack of treatment or improper treatment of an ingrown toenail can lead to:
- to acute or chronic inflammatory process;
- purulent inflammation;
- diffuse purulent process in soft tissues from the bones of the foot;
- proliferation of tissues of the nail fold;
- the addition of mycosis, papillomavirus;
- development of periungual warts;
- hemangiomas accompanied by bleeding;
- hyperkeratosis;
- keratomas;
- fibroids;
- malignant neoplasms;
- hyperplastic scars.
To avoid progression of the pathology, timely and adequate treatment is necessary. Conservative therapy brings symptomatic relief, but does not eliminate the cause. The only effective way to get rid of onychocryptosis is surgery. There are about 70 methods of treating pathology.
Treatment with staples
Conservative methods of treating ingrown toenails include the method of correcting the shape of the nail plate using orthopedic devices:
- Fraser staples;
- wire bracket – ZTO brackets;
- elastic plastic B/S plate;
- Goldstadt correction system – half brace for correcting unilateral onychocryptosis.
The devices are attached to the nail plate and promote its alignment, protect the periungual fold from pressure, and prevent the development of inflammation and hyperplasia. This correction method is not always effective, since it does not affect the growth zone. When the orthopedic system is removed, a relapse of the disease may occur.
Surgery
When choosing a method of surgical treatment, preference is given to minimally invasive techniques:
- laser therapy;
- radio wave exposure;
- cryosurgical treatment.
The most effective is the combination of traditional surgical techniques with the minimally invasive treatment methods listed above.
To eliminate the disorder, two methods of surgical treatment are used:
- marginal wedge resection of an ingrown nail;
- selective removal of the nail plate matrix.
Wedge resection does not prevent re-ingrowing of the nail, since the growth layer (matrix) is preserved. When excision or scraping of part of the nail matrix, the ingrowth of the plate stops. The operation is performed on an outpatient basis under infiltrative (local) anesthesia. In case of significant deformation of the nail, fungal infection or frequent relapses, complete removal of the nail plate and the entire matrix is performed. The defect is covered with a skin flap - autodermoplasty. The recovery period takes 12-14 days.
Laser removal
The impact of carbon dioxide laser radiation on a pathological focus contributes to:
- removal of the ingrown part of the nail plate;
- partial destruction of the growth zone;
- vaporization of overgrown soft tissues;
- sanitation of the source of inflammation.
The bloodless, low-traumatic operation is performed under local anesthesia. The chance of relapse is less than 0.1%. The recovery period does not exceed 5-7 days. As a side effect, nail growth may be impaired.
Radio wave treatment
Radio wave surgical treatment is the most effective and least traumatic method. Under local anesthesia, the ingrown part of the nail plate is removed, and then the matrix is subjected to controlled exposure to radio waves, which causes coagulation of the tissue. At the same time, other tissues are not damaged. The zone of coagulation necrosis when using the radio wave technique is 8 times less than resection using ultrasound and 10 times less than laser exposure. The rehabilitation period is reduced to 3-5 days. The risk of relapse of onychocryptosis is negligible.
Cryodestruction
Cryodestruction in the treatment of ingrown toenails is less popular than previous methods. Deep local freezing has:
- denervating effect;
- anesthetic effect;
- destructive effect on pathological tissues;
- antiseptic and hemostatic effect.
Tissue freezing is carried out to a depth of 1.5-2 mm, exposure time depends on the volume of tissue undergoing cryodestruction, and averages 30-45 seconds. For large granulomas (more than 2.5 cm), the operation is performed in several stages. Cryosurgical treatment of ingrown toenails results in a good cosmetic effect, no risk of relapse, and a reduction in rehabilitation time to 10 days.
Recommendations after surgery
After surgery, it is important to follow your doctor's recommendations. He will prescribe antibacterial and antifungal (if indicated) drugs, painkillers to relieve symptoms after the anesthesia wears off. It is necessary to choose the right comfortable shoes in size to avoid injuring your toe. The first dressing is performed 1-2 days after the intervention. Next, the doctor will explain the rules for self-treatment of a postoperative wound; local anesthetic and antiseptic medications may be required.
It should be understood that inattention to the “trigger” factors for the development of the disease can lead to re-ingrowing of the nail. It is necessary to take into account the root causes and eliminate them if possible.
Who is contraindicated for surgery?
Surgical treatment may be contraindicated for the following diseases:
- diabetes;
- atherosclerosis;
- bleeding disorders;
- tuberculosis.
In each specific case, the doctor makes a decision based on the general condition of the patient and the presence of serious diseases. Sometimes it is advisable to postpone the procedure for a while until the condition stabilizes; in some cases, permission from a specialized specialist (cardiologist, endocrinologist, etc.) is required.
Why choose us
The outpatient surgery department of the GMS Clinic uses the entire arsenal of the latest techniques for surgical treatment of ingrown toenails - the classical approach, laser and radio wave surgery. The operations are performed by experienced surgeons with many years of experience. We use only the most effective intervention techniques that avoid relapses and provide the following benefits:
- minimal trauma to surrounding tissues;
- fast healing;
- painlessness of the procedure;
- 100% sterility;
- minimizing complications and relapses.
GMS Hospital specialists successfully perform surgeries for resection of ingrown toenails of any degree of complexity.