More than a hundred years passed between the first observation indicating the increased sensitivity of adipose tissue to low temperatures and the invention of the first cryolipolysis apparatus. However, scientists are still arguing about the mechanism of cold action on adipocytes.
Procedures for removing local fat deposits are the fastest growing branch of aesthetic medicine. The continuous spread of the problem of overweight and obesity, which WHO calls the problem of the 21st century, as well as the demand for a slim figure dictated by the media, are forcing more and more patients to resort to the services of specialists in the field of aesthetic medicine. Specialists have a large number of techniques at their disposal to rid the patient of excess fat deposits, from classical surgical liposuction to modern non-invasive lipolysis methods. A special place among them is occupied by cryolipolysis - local exposure to low temperatures on adipose tissue. This method, on the one hand, triggers intracellular lipolysis, on the other hand, stimulates apoptosis of adipocytes - a natural process for the body. This distinguishes cryolipolysis from other techniques, in which direct cell destruction (necrosis) and the immediate release of large amounts of lipids occur. After cryolipolysis, the reduction in fat deposits occurs gradually, so there is no sharp increase in blood lipid levels. This, as well as the long-lasting result, the high safety of the method and the ability to immediately return to your daily activities after the procedure, have allowed cryolipolysis to gain popularity among both patients and doctors.
History of cryolipolysis
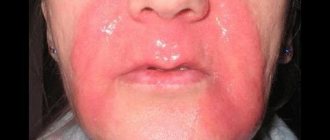
The first scientific report on the specific effect of low temperatures on adipose tissue appeared more than a century ago - the Austrian pediatrician Carl Hochsinger published an article in 1902 about cases of cold panniculitis (inflammation of subcutaneous fat tissue). He described children aged 4 to 10 years who, after exposure to unusually cold weather, experienced the appearance of dense, slightly reddened nodules in the submental area, rich in subcutaneous fat, which spontaneously resolved within 2–3 weeks [1]. In 1941, Danish dermatologist Holger Haxthausen reported similar cases in 4 young children and one teenage girl after exposure to extreme cold in winter (Fig. 1) [2]. He called such changes adiponecrosis e frigore - “freezing adiponecrosis.” Over the following years, reports of cold panniculitis following severe cooling in both children and adults appeared in the scientific literature [3].
Rice. 1. Cold panniculitis - diponecrosis e frigore - in a boy
In 1970, American doctors Ervin H. Epstein and Mark E. Oren encountered a case of buccal fat necrosis in an infant who ate ice cream, and coined the new term “popsicle panniculitis” [4 ]. At the same time, there was an assumption about increased sensitivity to cold effects of tissues with a high lipid content. However, scientists began testing it much later. In 2008, a group of researchers from Harvard Medical School led by Dr. Dieter Manstein conducted the first studies in pigs and coined the term “cryolipolysis” to refer to the destruction of fat tissue under the influence of cold [5]. A year later, in 2009, the first cryolipolysis device was created - Coolsculpting (Zeltiq® Aesthetics, Inc., USA).
Coolplas-2 SVC-101
The equipment is made in China and has high power (up to 1500 W), which makes it possible to remove up to 10 cm of fat deposits in 10 sessions. The device is capable of lowering the temperature to -11 ºС.
Coolplas-2 SVC-101 is equipped with 2 handles that allow you to process large and medium folds. The doctor can work with them simultaneously. This increases the effectiveness and speed of the procedure. For convenience, such attachments also have additional buttons that simplify the operation of the device.
The device has 5 built-in programs and a security system that strictly controls the temperature down to 0.1 ºС.
Mechanism of cryolipolysis
It is known that in response to cooling of the tissue in the affected area, an inflammatory reaction develops, followed by phagocytosis of adipocyte breakdown products and a gradual decrease in the thickness of the fat layer. Histological studies immediately after the cryolipolysis procedure did not show any noticeable changes in the tissues. After 3 days, the number of macrophages, neutrophils, lymphocytes and monocytes increases in the affected area. By days 7–14, the inflammatory process becomes more and more pronounced and reaches its maximum by the end of the first month (then the first results of the procedure become visually noticeable). Then the intensity of inflammation decreases, the thickness of the interlobular septa in the subcutaneous fatty tissue increases. It is assumed that the latter is the result of selective death of adipocytes, a decrease in the thickness of adipose tissue and, thus, an increase in the proportion of collagen in the hypodermis. The process completely subsides after approximately 90 days - by this time the results of cryolipolysis become maximally pronounced (Fig. 2) [5, 12, 13].
Rice. 2. Histological changes in adipose tissue at different times after the cryolipolysis procedure (in pig models)
The exact mechanisms of adipocyte death as a result of cryolipolysis are still unclear; many data on the effect of low temperatures on tissues have been transferred from observations in the field of transplantology and surgery. Currently, there are several hypotheses, each of which has a right to exist.
One hypothesis (accepted by most Western experts) associates the destruction of adipocytes during cryolipolysis with their mechanical damage by crystals of chilled fats. Studies have shown that intracellular “lipid ice” is formed at a temperature significantly higher than the freezing point of water—about +10 °C [5–7]. This is due to the transition of triglycerides with saturated fatty acids, which make up a significant part of the contents of the adipocyte, from a liquid to a solid state. The formation of such lipid crystals may contribute to immediate death (necrosis) or delayed death (apoptosis) of adipocytes. Immediate death is associated with mechanical rupture of cell membranes, and apoptosis is associated with damage to cell membranes and organelle membranes, primarily mitochondria. It is believed that the selective death of adipocytes in the case of cryolipolysis is associated precisely with the unique presence of a large number of triglycerides deposited inside them.
Another hypothesis explains the effect of cryolipolysis by triggering adipocyte apoptosis through the mechanism of its intracellular activation. Thus, it is known that under conditions of low temperature, the activity of membrane enzymes decreases, including the cascade of mitochondrial enzymes involved in ATP synthesis. Prolonged hypothermia causes a decrease in the level of intracellular ATP and inhibits all ATP-dependent processes inside the cell. This causes a delay in the active transmembrane transport of Ca2+ ions and an increase in the concentration of Ca2+ inside the cell, which is the “trigger” for launching the apoptosis program. In response to cold ischemia, osmoregulation of cells is disrupted (swelling occurs), the activity of Na-K-ATPase and the amount of ATP decreases, which leads to disruption of all energy-dependent processes, as well as the formation of intracellular acidosis due to an increase in the level of lactic acid [8]. The selectivity of cryolipolysis for adipocytes can be associated with a reduced ability of adipocytes to adapt to conditions of a prolonged decrease in ATP synthesis. The “white adipose tissue paradox” is that adipocytes contain a huge amount of stored energy in the form of triglycerides, but cannot effectively use the reserves to synthesize their own ATP, since their mitochondrial apparatus is very modest compared to other cells, for example, muscle and nervous.
In addition to the mechanisms described above, it is assumed that the initial crystallization and cold ischemic damage are aggravated by the subsequent restoration of blood flow in the tissues (reperfusion) and a sharp increase in the oxygen content in them. A high concentration of oxygen causes the formation of a large number of its active forms (ROS), which disrupt the functioning of transmembrane enzymes. There is an increase in the level of intracellular calcium, stimulation of some Ca2+-dependent and Ca2+-independent proteolytic enzymes, including caspases. This leads to the fact that a significant portion of cells with sublethal levels of damage are also involved in the process of apoptosis [9–11].
It has been experimentally shown that the temperatures used during cryolipolysis do not have a damaging effect on the epidermis, dermis, hair follicles, sweat glands and muscles [5, 12].
Nerves
Early histological studies of the effects of cryolipolysis on peripheral nerves did not reveal any long-term changes in either nerves or numbers [16]. However, the latest work of a group of scientists led by R.R. Anderson (RR Anderson), published in 2015, showed a decrease in the number of epidermal nerve fibers in the area of cold exposure, which gradually recovered, but did not reach baseline levels 56 days after the procedure. Myelinated nerve fibers were primarily affected, which is presumably due to their high levels of lipids, which undergo the same changes as fatty inclusions in adipocytes. However, almost all types of sensitivity returned to the baseline level by the end of the observation period [17].
Blood vessels
In the early works of Dieter Manstein, no damaging effect of cryolipolysis on blood vessels was revealed [5, 12]. However, a recent study of the characteristics of paradoxical fatty hyperplasia, which occurs as a complication of the procedure (will be described below), showed a decrease in the number of vessels in the area of exposure to cold [18]. So far this message is the only one and requires further research.
Review of preclinical and clinical studies
The earliest work on the effectiveness of cryolipolysis was carried out in 2008–2009. on pigs and showed a decrease in the thickness of the fat layer after one procedure by an average of 25–30% [5, 12]. Further studies on this topic were carried out directly on people and were quite different in design: different parts of the body were treated, the duration and number of procedures changed, some of them were accompanied by massage, others were limited only to cold exposure. In 2015, a team of American scientists led by Gordon H. Sasaki conducted a large-scale systematic review of studies from Medline and the Cochrane Library regarding the effectiveness, safety and features of cryolipolysis. From more than 300 articles, 19 of the most reliable works were selected and analyzed (Table 1) [19], on the basis of which the following conclusions were drawn:
- the average reduction in fat fold thickness after cryolipolysis ranges from 14.67 to 28.5% (when measured using a caliper);
- the average reduction in the thickness of the fat layer after cryolipolysis ranges from 10.3 to 25.5% (using ultrasound).
The authors also analyzed the side effects of cryolipolysis: erythema, bruising, changes in sensitivity and pain. In the vast majority of cases, they disappeared in the first days after the procedure [19]. Separately, it is worth highlighting a very rare phenomenon that is specific to cryolipolysis - paradoxical fatty hyperplasia. This is the growth of adipose tissue in the area of cold exposure, repeating the shape of the applicator and occurring 2–3 months after the procedure (Fig. 3). The mechanisms of this complication are still unclear. It was previously assumed that it develops due to an increase in the number of microvessels and interstitial cells.
Rice. 3. Pathological proliferation of adipose tissue according to the type of paradoxical adipose hyperplasia (about 5 months after cryolipolysis)
However, one of the latest studies showed the opposite changes: a decrease in the number of viable adipocytes, interstitial cells and vessels in the affected areas compared to control healthy tissues [18]. Follow-up revealed thickening of adipose tissue in the area of paradoxical fatty hyperplasia. It is possible that in conditions of less blood supply, fibroblasts increase collagen production, leading to fibrosis. Another likely explanation is the subjectivity of assessing changes. Scientists believe that in some cases, paradoxical fat hyperplasia may be the result of a visual error - the fact is that after the cryolipolysis procedure, a more intense reduction in the fat layer is observed in the marginal areas adjacent directly to the applicator, compared to the central areas [18].
The situation with assessing the risks of developing such a complication as paradoxical fatty hyperplasia is interesting. The Zeltiq company, which keeps statistics on the occurrence of this complication, has published various data over the years. To date, apparently, the most objective figure is the development of paradoxical fatty dysplasia in 0.025% of cases (data published in the second quarter of 2015), which is determined by the ratio of 473 recorded cases of this complication to 2 million treated areas. However, a number of authors claim a much higher incidence of this complication. For example, Emma Killey et al., analyzing cryolipolysis treatment of 510 patients, reported the development of paradoxical hyperplasia in 0.78% of cases, which is more than 30 times higher than the official Zeltiq statistics [22].
One way or another, the risk of developing paradoxical fatty hyperplasia (even if summed up with other risks of complications from this procedure) does not make cryolipolysis more dangerous than other techniques, but if you compare cryolipolysis with procedures that have comparable effectiveness (results per procedure), you can We can safely say that cryolipolysis is one of the safest techniques in the hands of cosmetologists.
Liposonix
The device is made in the USA and is based on the effect of ultrasound on fat deposits. The focused energy flow penetrates 13 mm into the tissue, where a non-thermal reaction occurs. It does not affect nerve endings and blood vessels, does not violate the integrity of the epidermis and focuses only on lipids.
In 90% of cases, the ultrasound procedure gives a good result, and after one session the fat layer can decrease by 2.5 cm. Patients observe the maximum effect after treatment for 10-12 weeks. It helps with local deposits, cellulite, and decreased skin elasticity.
What determines the effectiveness of cryolipolysis?
The effectiveness of cryolipolysis is assessed by the amount of removed adipose tissue - the difference in the thickness of the fat layer before exposure and after 2 months. after completing the procedure. The more adipocytes are exposed to cold and the more intense it is (which is determined by the temperature and duration of cooling), the more pronounced the result of the procedure. It will also depend on the use of the so-called. effect enhancers - local (massage, lymphatic drainage, shock wave therapy) and general (diet and physical activity). In general, this dependence can be represented as the following formula:
The effectiveness of cryolipolysis (the amount of adipose tissue eliminated) = The amount of cooled adipose tissue × Temperature in the treatment area × Duration of the procedure × Factors that enhance efficiency.
Table 1. Studies on the effectiveness of cryolipolysis*
| Research | Type | Number of participants | Procedure settings | Observation period | results |
| Garibyan, 2014 [29] | P | 11 | CIF 41.6, 60 min | 2 months | The average decrease in the volume of adipose tissue is 56.2 cm3, the average decrease in the thickness of the fat fold is 14.9% |
| Pinto, 2012 [26] | P | 16 | 3.1 °C, 25–35 min, 1–2 sessions | 40 days | After the 1st procedure, the average reduction in the thickness of the fat fold was 19.7%, after the 2nd - 28.5% |
| Boey, 2014 [23] | P | 17 | CIF 42, 60 min + 2 min massage | 4 months | The average reduction in fat layer on the side where the subsequent massage was performed was 68% after 2 months and 44% after 4 months. |
| Dover, 2009 [31] | P | 32 | Manufacturer's CIF | 4 months | The average reduction in fat layer thickness was 22.4% 4 months after the procedure. A decrease in body fat was observed in 100% of patients |
| Sasaki, 2014 [24] | P | 112 | CIF 42, 60 min + 5 min massage | 6 months | The average reduction in the thickness of the fat fold is 21.5%; average reduction in fat layer thickness - 19.6% (abdomen) |
| Klein, 2009 [14] | P | 40 | CIF 42, 30 min | 12 weeks | There were no significant changes in lipid metabolism and liver function during 12 weeks of observation |
| Lee, 2013 [32] | P | 14 | CIF 42, 60 min | 12 weeks | Reduction in hip circumference by 19.55%. Indicators of lipid metabolism and glucose were within normal limits throughout the entire observation period |
| Riopelle, 2009 [15] | P | 10 | Not specified | 12 weeks | Against the background of a decrease in the thickness of the fat layer, no pathological changes in lipid metabolism and liver function were observed in studies 1, 4, 8 and 12 weeks after the procedure |
| Coleman, 2009 [16] | P | 9 | CIF 33, 60 min and CIF 37, 45 min | 6 months | The average reduction in fat layer thickness was 20.4% after 2 months and 25.5% after 6 months. Histological studies showed no long-term changes in peripheral nerves |
| Rosales-Berber, 2009 [33] | P | 42 | Intensity and duration not specified, 1 or 2 sessions | 6 months | 79% of subjects noted the effectiveness of the procedure |
| Dover, 2011 [34] | P | 15 | Not specified | 6 months | 80% of patients are satisfied with the results (6.6 on a scale of 1 to 10) |
| Shek, 2012 [25] | P | 21 | CIF 41.6, 60 min, 1 session | 2 months | Average reduction in fat fold thickness - 14.7% |
| Shek, 2012 [25] | R | 12 | CIF 41.6, 60 min, 2 sessions | 2 months | The average reduction in the thickness of the fat fold after the first procedure is 14% in the abdominal area, 13.4% in the sides; after the second - 7.2% in the abdominal area and 4.3% - in the sides |
| Dierickx, 2013 [35] | R | 518 | Not specified | 1 and 2 months | In 94% of patients, there was a decrease in the thickness of the fat fold by an average of 23% |
| Stevens, 2013 [36] | R | 528 | 60 min | 2 or 3 months | Statistics: increase in the number of procedures performed from 2010 to 2012 by 823% |
| Kaminer 2009 [37] | R | 50 | Not specified | 6 months | In 89% of cases, a difference was recorded between the circumference of the treated area before and after the procedure |
| Brightman, 2011 [38] | KS | 1 | CIF 42, 60 min, 2 sessions | 5 months | Reduction of abdominal circumference by 2.4 cm |
| Jalian, 2014 [20] | KS | 1 | Manufacturer's CIF | 5 months | Gradual, painless growth of adipose tissue in the treatment area (paradoxical fatty hyperplasia), which stabilized after 5 months |
| Bernstein, 2013 [39] | KS | 1 | CIF 42, 60 min | 2 years | 2 years after the procedure, there was a persistent decrease in the circumference of the treated area (comparison of before/after photographs) |
| Bernstein, 2013 [39] | KS | 1 | CIF 34, 60 min | 5 years | 5 years after the procedure, there was a persistent decrease in the circumference of the treated area (comparison of before/after photographs) |
* Measurement of the thickness of the fat fold in the studies was carried out using a caliper, the thickness of the fat layer - using ultrasound scanning. P—prospective study. R—retrospective study. CS is a clinical case. CIF - Cooling Intensity Factor, introduced by Zeltiq as a measure of the rate of heat removal from fabric, high CIF determines a higher rate of heat removal or a colder cycle: CIF 33 corresponds to heat removal with an intensity of 64 mW/cm2; CIF 37 - 68.3 mW/cm2; CIF 42 - 72.9 mW/cm2
Lipofreeze
Equipment made in Italy is characterized by low power (up to 700 W) and is capable of lowering temperatures to -10 ºС. The device effectively removes fat cells in the hips, abdomen and back. It breaks down up to 25% of lipids. The final result of this process is visible already in the first 2 months.
Lipofreeze is equipped with 1 vacuum nozzle, its service life is up to 5000 hours. To avoid overcooling the tissue, a cloth with a special gel is used between the skin and the applicator.
Amount of chilled adipose tissue
Bowl volume
The larger the volume of the applicator bowl, the potentially larger the volume of the fold that can be drawn into it using a vacuum. Ideally, the applicator should fit a specific fat fold size, but this is not possible because fat deposits vary in size and shape and vary greatly from person to person. Currently, none of the manufacturers have presented an applicator with variable geometry - companies follow the principle of developing applicators of different shapes and volumes. The specialist’s task comes down to correct planning of the procedure, so that during the process, the maximum volume of fat from the problem folds is drawn into the correctly selected applicator. The more applicators in a particular device, the more anatomical areas the procedure can be performed on: for example, small ones for treating the shoulder area, large ones for capturing the fat fold on the abdomen. The principle “larger applicator volume = greater efficiency” does not always apply in the case of cryolipolysis. If you increase the size of the applicator and, in particular, the distance between its side walls, the adipose tissue in the center of the fold will cool less than at the periphery. Also, more intense blood circulation will remain in the large fold, providing tissue heating.
Rice. 4. Temperature on the surface of the skin and in the fat layer when cooling the skin (panel temperature –7 °C, procedure time – 10 min)
Vacuum force
It is with the help of vacuum that the fat fold is aspirated into the applicator bowl. The stronger the vacuum, the more fat will be drawn in and the better the result. During the cryolipolysis procedure, they strive to completely fill the applicator cup with fat. However, in some cases, such as when processing dense fat, the vacuum pressure (suction of the fold) causes discomfort. The winners are devices in which this parameter can be adjusted within a wide range - stronger or weaker, depending on individual readings.
Preparation
The date of the procedure is set in advance. Formally, cryolipolysis does not require any special preparation, and it can be done at any time. But it is better to come to the office with a relatively empty stomach, especially if the problem area is the stomach.
Immediately before the session it is not advisable to:
- drink;
- There is;
- sunbathe.
Do not combine therapy with procedures that injure the skin. Otherwise, it all comes down to identifying contraindications and choosing a nozzle.
Temperature in the affected area
It is believed that apoptosis of adipocytes is triggered at a temperature of +10 °C and below, and cooling to +7 °C is optimal [5–7]. It should be noted that we are talking about the temperature inside the fat fold, and on the surface of the skin adjacent directly to the cooling plates, it will be much lower, reaching negative values (Fig. 4). Despite widespread concerns, cooling the skin to subzero temperatures does not always lead to the development of necrosis, since the skin has excellent adaptive abilities, incl. and to the low temperatures that it constantly encounters. Another thing is that when carrying out cryolipolysis procedures, it is necessary to observe a strict temperature regime, when the temperature of the cooling plates of the applicator should not fall below -10 ° C, and at the same time, the epidermis must be saturated with a substance that prevents the formation of an ice crust - propylene glycol, and between the applicator and the skin There should be a special mat impregnated with this substance and ensuring uniform heat dissipation.
There are 2 types of cryolipolysis machines:
- with a fixed cooling temperature - for example, in the Coolsculpting device (Zeltiq® Aesthetics, Inc., USA);
- with adjustable temperature - for example, in Z Lipo (Zimmer, Germany) you can set the temperature of the cooling panels in the range from –10 to +5 °C.
Devices that do not have the ability to regulate temperature have both pros and cons. On the one hand, all patients undergo cryolipolysis according to a unified protocol, which guarantees a high level of safety. On the other hand, a specialist cannot influence the effectiveness of the procedure by changing the temperature.
A strict temperature regime also means that the temperature on the surface of the skin will be maintained at the desired “effective” value, but will not cross the critical line. But this rule is not so easy to follow, since cryolipolysis devices take heat from living tissue, which is heated from the inside, and the degree of this heating directly depends on the anatomical and physiological characteristics. An ideal cryolipolysis apparatus should instantly respond to the appearance of critically low temperatures and stop cooling. To achieve this, devices such as the aforementioned Z Lipo device are equipped with temperature sensors and a feedback mechanism that help maintain the temperature at the desired level throughout the procedure.
Indications for use
Cryolipolysis is used to partially or completely eliminate fat deposits. The technique is recommended if the problem is:
- Dissatisfaction with your figure;
- Inactive lifestyle;
- Hormonal or “stagnant” fat;
- Local entities;
- Malfunctions of the body due to diseases and/or long-term use of drugs;
- Deposits do not go away when body volume is corrected in other ways;
- Initial stages of obesity;
- Eating disorders.
The patient’s BMI should be in the range from 25 to 30. With a higher indicator, the volume of fat mass is reduced using traditional methods (sports, proper nutrition, psychologist) and only then the procedure is prescribed. The main indication is a fat layer 2.5-6 cm thick.
Cold therapy reduces volume and has a beneficial effect on overall skin tone. But if there are problems with the conductivity of the lymphatic system, the treated area may hurt for a long time after cryolipolysis. Warn your doctor if you are prone to severe/regular swelling: it may affect the effectiveness and speed of rehabilitation.
Duration of the procedure
The cooling time is usually 1 hour. However, to date there have been no published studies that have proven a direct connection between the duration of cooling and the effect. The procedure time of 1 hour was determined by Zeltiq specialists during the very first studies - they found that cryolipolysis procedures that last more than 1 hour provide virtually no increase in efficiency compared to hourly ones. In addition, an aesthetic procedure that lasts more than 1 hour is unlikely to be in demand (inconvenient for the patient). Therefore, in almost all cryolipolysis machines, the cooling time is 1 hour or less. However, in some devices it can be changed depending on individual needs.
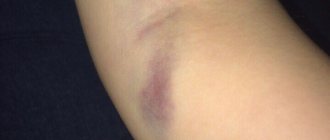
Bruises
Slight redness of the skin in areas in contact with the device is normal. Hyperemia completely disappears after a few days. There may be temporary numbness and loss of sensation in these areas.
If bruises appear, this indicates that:
- Not all contraindications were identified;
- The patient was taking medications that affect hormonal levels and blood clotting.
If you follow all the rules mentioned in the patient leaflet, the likelihood of hematomas is extremely low.
Efficiency enhancing factors
Massage
A study by Canadian scientists showed that a 2-minute manual massage immediately after the procedure (1 minute of vigorous kneading of the treated tissue between the thumb and fingers, and then 1 minute of circular massage) statistically significantly improves the results of cryolipolysis both 2 and 4 months after the procedure [ 23]. The use of mechanical massage (5 minutes during the procedure) has also been shown to be highly effective [24]. The same result is achieved if, at the last stages of the cryolipolysis procedure, a pulsed vacuum mode is used, as, for example, in the Z Lipo device.
Researchers explain the phenomenon of increasing the effectiveness of cryolipolysis with the addition of massage by the fact that triglycerides, converted inside adipocytes into the solid state of “lipid ice,” additionally damage the cell walls and organelles of fat cells during mechanical compression. As a result of massage, a larger percentage of adipocytes receive critical damage and die as a result of apoptosis and necrosis, which explains the increase in the effectiveness of cryolipolysis. Another possible explanation: massage improves blood circulation and, as a result, increases the concentration of oxygen in the tissues. With a sharp increase in oxygen concentration, a large number of its active forms are formed, which disrupt the functioning of transmembrane enzymes, which ultimately can lead to the triggering of apoptosis through the intracellular pathway of its activation.
Shock wave therapy
The mechanism for increasing the effectiveness of cryolipolysis when exposed to a shock wave is presumably the same as that of massage. The advantage of shock wave over massage is that shock wave is energy that penetrates deeper and acts more intensely. Also, when using shock wave therapy (SWT), the human factor is manifested to a lesser extent: practically nothing depends on the skill of the specialist, whereas with massage such skills are important.
Number of procedures
Repeating sessions in the same anatomical area has been shown to produce greater results than performing only one procedure. However, subsequent interventions give less pronounced results compared to the first [25, 26]. Presumably, this is due to an increase in the tolerance of surviving adipocytes to cold exposure or better warming of the thinned fat layer by the muscle layer, and therefore the critical temperature for triggering apoptosis is not reached.
Area of influence
It is known that the effectiveness of cryolipolysis differs when applied to different parts of the body, but it is still unknown which of them are most sensitive to cryolipolysis. The influence of various factors, such as features of vascularization, local cytoarchitecture and metabolic activity of specific fat depots, is assumed. In addition, it is believed that cryolipolysis has the maximum effect in patients with small or moderate fat deposits, as well as cellulite [27].
Interestingly, the aforementioned paradoxical fatty hyperplasia, according to some data, develops more often when treating the anterior abdominal wall, when a large applicator is used.
Beco ETG50-4S
The equipment is manufactured in China. The devices of this model are characterized by average power, which explains the low productivity. They are able to maintain temperatures from +5 ºС to -10 ºС.
The Beco ETG50-4S kit includes 2 handpieces that can be used to treat 2 zones at the same time. The device is also equipped with additional attachments. They destroy fat cells well on the abdomen, sides, outer and inner thighs, and on the back in the area of the shoulder blades. The device removes up to 18% of lipids after the first procedure, but it cannot be used in the neck, face and décolleté.
The model is equipped with sensors that help monitor the patient’s heartbeat, skin temperature and vacuum. It has an emergency shutdown system.
The equipment uses wavelengths at 630 nm and 570 nm in the red and green spectrum. It must be stored in a room with a temperature of up to +25 ºС.
Cryolipolysis with Z Lipo
In 2015, the German company Zimmer, which has been developing and manufacturing medical devices for cryotherapy for more than 45 years, introduced the Z Lipo cryolipolysis device (Fig. 5). Its uniqueness lies in the ability to change all parameters of the cryolipolysis procedure, which allows you to select the optimal settings for each patient and each zone:
- temperature selection and control;
- adjusting the vacuum strength and mode (continuous and massage effect);
- individual selection of application duration.
These three parameters can be individually adjusted not only for each patient, but also on the scale of one application. Each application consists of three stages that automatically alternate with each other; the parameters of each stage can be individual.
To regulate the amount of cooled adipose tissue, 3 vacuum applicators have been developed:
- Small;
- Medium;
- Large.
Using the Large applicator, large areas of fat deposits are treated, for example the front surface of the abdomen. The Small applicator allows you to carry out procedures in difficult areas with a small amount of fat. At the same time, independent control allows you to simultaneously use any 2 applicators, which reduces the duration of procedures.
Rice. 5. Z Lipo device (Zimmer, Germany) with Small, Medium and Large attachments
The intensity of tightening the fat fold is adjusted by adjusting the vacuum strength in the applicators. There are a total of 10 vacuum power levels, which can be set individually on each applicator. In addition to the continuous operating mode, there are 3 pulse programs that provide vacuum massage at the first and final stages of the procedure. Thus, in one procedure it is possible to switch between three different vacuum modes.
The temperature of the cooling panels can be adjusted within the range from –10 to +5 °C. The Z Lipo system provides precise control of the temperature of the cooling panels, which allows you to select optimal exposure parameters and provides protection against frostbite. Also, to protect against frostbite, universal propylene glycol gel mats are used, equally suitable for any of the applicators.
Another adjustable parameter is the duration of the procedure, which can be set from 1 to 60 minutes.
With Z Lipo you can treat fat deposits in the following areas:
- stomach;
- sides (“lifebuoy” at the waist);
- upper and lower back;
- hips and knees;
- shoulders (back of the upper arm);
- chest (men only).
Freezefat
The equipment is manufactured by BEKO. Its power is 500 W, so to achieve results you need a long exposure to problem areas (up to 1 hour). But the device has a wide range of temperature conditions. In the settings you can set it to -9 ºС, and there is also a massage function.
Freezefat is equipped with 3 vacuum manipulators, which the doctor uses to treat the waist, riding breeches, knees, inner surface of the arms and thighs. In 4 procedures, the device is able to remove up to 26% of the fat layer. However, it does not work in the neck, face and décolleté area. During the session, the specialist can use 2 hands at the same time, which significantly speeds up the work.
The device is reliable to use and is designed quite simply. It does not require constant scheduled maintenance. The Freezefat procedure does not require expensive consumables.
Combined effect: Z Lipo and Z Wave
A combination of cryolipolysis and shock wave therapy procedures is possible using Z Lipo and Z Wave devices (Zimmer MedizineSysteme, Germany). According to the manufacturers, performing a radial shockwave therapy procedure (Z Wave) immediately after a cryolipolysis procedure (Z Lipo) increases the effectiveness of the latter by 2 times (Fig. 6).
Rice. 6. Comparison of the effectiveness of cryolipolysis and combined effects: cryolipolysis + UVT and cryolipolysis + massage
The Z Wave device generates shock waves using a ballistic electromagnetic mechanism, which is located inside the operating handle and transmits these waves to the tissues through a special tip-impactor, which has a rounded shape and propagates the waves radially (Fig. 7). Thus, shock waves are not focused inside the body, their energy is distributed evenly. The frequency of wave formation is set in the range of 1–22 Hz using a regulator. The pulse (shock) energy can be determined both before and during the generation of pulses - it is adjusted in the range of 60–185 mJ in steps of 10 J. The maximum possible frequency is determined by the selected energy level. The maximum penetration depth of the waves emitted by Z Wave is 35 mm.
Rice. 7. Z Wave device (Zimmer, Germany)
Shock wave exposure immediately after the cryolipolysis procedure increases damage to adipocytes, presumably both due to mechanical damage (oscillations of “lipid ice” damage the cell membrane and organelles of adipocytes) and by activating tissue reperfusion and triggering oxidative stress. A lymphatic drainage effect also occurs, leading to some temporary results from the procedure within a day after its completion. An additional significant advantage of shock wave exposure is the activation of the formation of collagen and elastin, which provides skin tightening. This is especially true in areas where, after reducing the fat layer, sagging and sagging skin may be observed.
A group of scientists led by Dr. G. A. Ferraro studied the effectiveness of the combination of cryolipolysis and shock wave therapy [27] on 50 patients who underwent an average of 3.73 combination therapy procedures with an interval of 15 days between sessions. After the end of the experiment, a significant decrease in the circumference of the thickness of the fat fold in the treated areas was noted (Table 2). At the same time, the decrease in the fat layer was accompanied by a significant decrease in the manifestations of cellulite.
Table 2. Results of the combined use of cryolipolysis and UVT
| Treatment area | Average reduction in circumference (cm) | Average reduction in fat fold thickness (cm) |
| Stomach | 6,86 | 4,50 |
| Hips | 5,78 | 3,60 |
| Hands | 2,75 | 2,10 |
| Buttocks | 5 | 4 |
| Ankles | 2,25 | 1 |
Ls300
The device is made in China. The model has a low power of 450 W, so the procedure lasts up to 1 hour. In this case, the equipment can reduce the temperature to -11 ºС. This effect of cold helps with local lipid deposits, grade 1 obesity and cellulite.
Ls300 is equipped with several attachments: the first applicator is used to treat the abdomen, the second - the back and sides, the third - in the shoulder area. The device is suitable for cryolipolysis on any part of the body, with the exception of the neck, face and décolleté.
The device has touch pressure sensors and an emergency shutdown feature.