- Department of Aesthetic Medicine
Department of Aesthetic Medicine » - Injection cosmetology
Injection cosmetology »
- Services
Services "
- Contour plastic
Contour plastic surgery »
- Tips for correcting the zygomatic region
Correction of the zygomatic region is one of the most popular procedures. To carry it out correctly, you must have in-depth knowledge of facial anatomy, as well as extensive experience in working with a cannula (guide needle).
Two main NOTs that will help you avoid trouble:
1. DO NOT place filler high, that is, in the subcutaneous fat layer, which is located directly under the skin. This is fraught with swelling.
2. DO NOT use a needle. This is fraught with hematoma.
If you follow these two NOTs, half the success has already been achieved. The second half depends on the doctor’s eye, on the ability to use the simplest measuring instruments and make accurate markings of the drug.
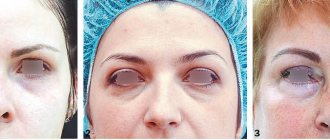
What are tear troughs
The tear trough (nasolacrimal trough) is a small depression that starts from the inner corner of the eye and continues towards the cheek. It is the border between the cheek and the lower eyelid area. The furrow appears over time in all people, but the most important nuance is when it appears.
It is clear that we are not able to cancel the laws of nature, but you can do everything possible to ensure that visible signs of skin aging appear as late as possible. The appearance of tear troughs depends on several factors:
- what you eat,
- how much and what do you drink,
- what kind of physical activity do you do?
- what cosmetic products do you use?
If you add enough fruits and vegetables to your diet, limit the consumption of smoked foods, salt and sugar, consume a sufficient amount of liquid per day (on average 30 grams of liquid per 1 kg of weight), give the body sufficient physical activity, then in the absence of hereditary predisposition, you will never develop a tear trough at 25 or 35 years old.
If, despite all the measures you have taken or due to a hereditary predisposition, you have a noticeable nasolacrimal groove, then it is time to move on to measures to eliminate it. Our doctor's extensive list of tear trough treatments includes surgical procedures and cosmetic procedures.
Why does a nasolacrimal trough occur?
Anatomically, the nasolacrimal groove is the space between two fat pads: infraorbital and medial buccal fat. It is connected to the bone of the infraorbital region by a special muscular septum - the septum. With age or under the influence of stress factors (poor diet, alcohol, smoking, sleep disturbances), the density of muscle fibers decreases, the septal ligaments stretch and lengthen, pulling other tissues with them. A pronounced arched fold forms under the lower eyelid, and the area between the inner edge of the eye and the bridge of the nose darkens due to impaired microcirculation of blood and lymph. Taken together, these changes give the face a tired, haggard expression.
Location of the nasolacrimal groove on the face
The timing of the formation of the nasolacrimal groove is individual: for some it can remain in a sketchy state for years, while for others it can go from slightly noticeable to pronounced in less than six months. Its formation is significantly accelerated by sharp fluctuations in body weight and diseases of the endocrine system. Therefore, if a nasolacrimal groove quickly appears, you should think about visiting not only a cosmetologist, but also a therapist.
Watch the video on how the nasolacrimal trough is corrected in Face&Body
Non-surgical procedures
Non-surgical procedures include cosmetic procedures that do not involve damage to the skin. Perhaps the effect of such procedures is not as pronounced as after surgical operations, but they have much fewer contraindications, possible complications and do not require such a long rehabilitation period. The most common non-surgical methods for eliminating tear troughs are:
- RF lifting . The tightening effect is achieved by increasing skin elasticity under the influence of radio waves. The method is recommended mainly for young patients and brings results that are observed within 1.5 years.
- Ultrasonic lifting . The tightening is carried out by applying ultrasound to the muscle tissue located under the skin. The effect lasts up to 1.5 years.
- Peeling . It is used when there are shallow tear grooves.
In cases where cosmetic procedures do not have a significant effect on the nasolacrimal grooves, you have to turn to plastic surgeons.
We will only inject VOLUMA (JUVEDERM) into the zygomatic area.
Ultra 4, 3, 2 - I never use it in the cheekbone area. Firstly, the structure of Ultra (ULTRA) and Voluma (VOLUMA) preparations differs in their tendency to bind water. ULTRA binds more, and VOLUMA binds less. Therefore, given the close location of the eye socket, it is not good to provoke swelling, especially in our St. Petersburg climate.
Secondly, the injection site (medial compartment) is deep. We must place the drug almost on the periosteum. It’s easy to make a mistake here, because first the superficial fatty tissue is located under the skin, under it lie the zygomatic minor and major muscles and the lower part of the orbital, and then below them is the medial fatty compartment.
A not very experienced doctor can stop at the level of subcutaneous fat and distribute it there. This procedure will not give any effect. There will only be swelling.
Surgical operations
You can eliminate the tear trough with plastic surgery by either filling it or tightening the skin over it. The most popular correction methods are:
- Lipofilling . It involves filling the furrow with transplanted own fat. The most suitable option for those who do not want to change anything about their face other than removing the tear trough. The least traumatic method, the results of treatment last up to three years.
- Blepharoplasty . Plastic surgery for eyelid lift. It has the strongest effect, but is accompanied by a long period of postoperative recovery. The results last up to 10 years.
- Contour plastic . Filling the tear trough with preparations based on hyaluronic acid (fillers). Non-traumatic correction method of short duration (up to 8 months).
- Midface lift . A surgical intervention that corrects many age-related changes in the face, including the removal of tear troughs.
Tear troughs immediately make your face look much older, giving it a tired and sad look. If immediately after their appearance you contact our experienced doctor, then timely and correctly chosen treatment will save you from such a noticeable flaw for a long time.
Be beautiful and healthy!
In the practical aspect of the modern concept of facial rejuvenation, morphometric and aesthetic analysis serves as the most important tool. What parameters of such an assessment should you pay special attention to? Carrying out correction in the upper and middle third of the face – which zones and points are dominant?
Rejuvenation and harmonization of the face require its correction as a single, holistic object with precise definition of the main zones - this is the modern general concept. However, doctors often deviate from this principle, concentrating their efforts on solving individual, sometimes rather insignificant, problems. What is this connected with? The reasons may be different: misunderstanding, ignorance or ignorance of the basics of aesthetic and morphometric analysis, lack of necessary professional skills for correcting certain areas of the face, lack of mastery of certain methods, and sometimes following the patient’s lead. As a result, the cosmetologist is limited to correcting a single aesthetic defect, and the patient cannot even imagine what full-scale effect of facial rejuvenation is possible in his case.
The wishes (and even demands) of our patients, as a rule, do not cover the picture as a whole, but are concentrated on its details, which, in their opinion, spoil the whole thing: “It’s because of these wrinkles around my mouth that I look older, just remove them " In fact, performing some kind of procedure to eliminate one or another aesthetic imperfection, usually considered a sign of facial aging, has nothing to do with the real concept of rejuvenation. For example, correction of nasolabial folds has become a kind of social dominant among other anti-aging procedures. It is surprising that patients who do not have this very conditional defect at all come to cosmetologists to get rid of it. But nasolabial wrinkles when smiling and other facial movements appear even on the face of a baby. In accordance with the general concept of facial rejuvenation, we should not talk about isolated correction of individual aesthetic defects, but about the priority of zones in the complex correction of the entire face.
Morphometry and aesthetic analysis in the applied aspect
To emotionally assess a face along the “young-old” axis, no special analytical thinking is needed; involutional changes can be easily diagnosed by any specialist in aesthetic medicine. And morphological disturbances - what is inharmonious and what is wrong - are also simply determined. However, it is important not only to note them - the professional must explain exactly how and why the violations occurred and be able to eliminate them.
To identify aesthetic and morphological defects of the face, it is enough to determine its height and width as a whole, its upper, middle and lower thirds and the proportional relationship of these parameters and, based on the assessment, understand what violates the correct proportions.
If the face is characterized by a sharp “geometry” rather than smooth transitions from one zone to another, this is also clearly visible (“a smooth transition” here is perhaps the main characteristic). You just need a careful appraising look to notice that there has been a narrowing of the forehead in its lower or upper part, that it is not high enough, there are depressions on it, the temple is deepened, there is no smooth transition from the forehead area to the side of the cheekbone, there is practically no subcutaneous fat layer in the area of the temporal suture or the bony lateral edge of the orbit (this area is skeletonized), there is no gradual (soft) transition from the eyelid area to the anterior convexity of the cheekbone, under the eyes there are depressions that absorb light, the cheekbone has a “mountain-valley” relief, but should be a single smooth one a convexity from the surface of which light is uniformly reflected, etc.
These are the elementary foundations of morphometry and artistic analysis, which at the diagnostic stage allow a modern specialist to determine on the face the point of focus of attention of others (let’s call it the central focus), and, what is extremely important, the dominant zones, evaluate their gradation and joint aesthetic significance and in accordance With this, we can direct the patient’s wishes in the right direction. Only then do real opportunities arise to obtain optimal visual results of facial rejuvenation.
On the face, the center of attraction is, of course, the eyes. Beautiful eyes - almond-shaped, with white sclera, bright irises, black eyelashes and regular canthus. (Correct is when the lateral corner of the eye is higher than the medial one. This position of the canthus ensures a higher position of the lacrimal glands compared to the lacrimal sac and ducts and regulates the physiological outflow of tears under the influence of gravity.)
The eyes, as the central focus of the face, require aesthetic perfection from the areas surrounding them - the lower orbital, zygomatic, temporal and frontal. These zones dominate the perception of the face. Their morphological disorders and involutional changes distract from the beauty and expressiveness of the look, “turning the arrows” towards themselves; they are the ones who primarily age the face.
We will consider aesthetic correction of zones using fillers and their anatomical justification in this material.
Correction of infraorbital grooves and anterior zygomatic zone with gel
Anatomically, the face is divided into two sections - anterior and lateral, the border between which is defined as a line drawn along the medial edge of the masticatory muscle.
The anterior section of the face is more mobile, all facial muscles are concentrated in it, it is responsible for facial expressions, articulation, and food grasping occurs here. In most of this section, the fifth layer of tissue is represented by the mucosa.
The lateral section, on the contrary, is more static. It contains the chewing muscles: the temporal and masseter muscles; SMAS is represented by the superficial fascia - parotid-masseteric and external temporal.
According to this division of the face in the zygomatic zone, the anterior and lateral sections are also distinguished.
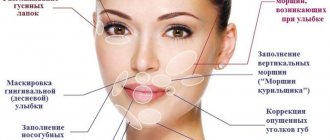
The infraorbital grooves and the anterior zygomatic zone are priority targets for correction. It was from applying uniform light to this area that classic Photoshop and other image-enhancing programs grew. The purpose of the correction is to eliminate the nasolacrimal, nasobuccal and palpebromalar grooves, mask the minimal palpebral and malar hernial sacs, restore the anterior convexity of the cheekbones, and create a smooth transition from the eyelid area to the cheekbone.
The nasobuccal (midbuccal) groove is an area of depression separating the superficial infraorbital compartments (malar hernial sac) and the underlying superficial nasolabial compartment.
To correct the nasobuccal groove with fillers, the drug can be safely administered with a 25G/40 mm cannula. The entry point for the cannula is determined under the zygomatic ligament, but above the septa of the angular vein - on the convexity of the cheekbone along a line roughly drawn through the lateral corner of the eye.
Hyaluronic gels with high viscoelastic properties are preferred, providing long-term results of volumetric correction. If facial tissues rise strongly when smiling and protrude into its anterior plane, then in this case dynamic gels, specially adapted to the natural biomechanics of tissues, elastic under stretching and squeezing, are more suitable.
The injection is performed slowly, supraperiostally, under SMAS.
Deformation of the nasolacrimal groove as an aesthetic defect is expressed in the formation of a depression zone, limited above by the periosteal attachment of the orbicularis oculi muscle, and below by the septa of the angular vein. In this area, the muscle fibers are dense, with good blood supply, there is no surface fat above them, so the muscle is visible through the thin skin tissue.
Correction of the nasolacrimal groove: the cannula is inserted through the same access point as when working with the nasobuccal groove, at an angle of 45 degrees until it touches the periosteum, towards the medial canthus, and then it is positioned parallel to the periosteum.
It is important to take into account that in the vestibule of the orbit the level of the periosteum changes, and in accordance with this it is necessary to change the course of the cannula. The use of a needle in this area is dangerous, since the angular vein, the superior branch of the infraorbital artery, the angular artery (in 30% of patients) and its duplex (in 15% of cases) are localized here.
To ensure maximum aesthetic results when correcting the nasolacrimal groove, it is necessary to smoothly connect the end of the nasolacrimal groove and the beginning of the nasobuccal groove.
The formation of the palpebromalar groove is due to the fact that the outer cheek (zygomatic fat) does not reach the level of the bony edge of the orbit, which causes a difference in tissue level. This zone is conditionally dangerous, so needle work is acceptable here. The needle pierces all tissues slightly at an angle to the periosteum and touches it lightly. The drug is administered as a bolus, in a volume of no more than 0.1 ml per injection. In the presence of palpebral and malar hernial sacs, insertion should be ensured exactly between them (between the bony edge of the orbit and the ligament of the orbicularis oculi muscle) in order to mask their bulging.
This zone is characterized by a low level of tissue hyaluronidase, so here the long-term effect is provided by low-viscosity and low-elastic, well-distributed drugs that do not exert high pressure on the orbicularis oculi muscle.
To create the anterior convexity of the cheekbone as a whole, fillers are injected primarily into the deep medial buccal compartment, easily identified on any face. Its upper border is the zygomatic ligament, the lower is the septa of the angular vein, the lateral border is determined by a line conventionally drawn along the minor zygomatic ligament. Selective increase in the anterior convexity of the cheekbones visually enhances the deepening of the infraorbital grooves, therefore both zones are corrected step by step sequentially and in one procedure.
To reduce pain and ensure patient comfort during the procedure, it is better to choose lidocaine-containing drugs. They are first inserted into the deep medial buccal compartment, and then the nasolacrimal groove is corrected. This ensures maximum anesthesia: lidocaine has time to accumulate in the premaxillary space, where the exit point of the infraorbital branch of the trigeminal nerve is located, which innervates this entire area of the face, and in particular the area of the infraorbital grooves. It is better to first administer lidocaine-containing drugs antegradely, in small portions. Next, the specialist can use any injection technique, since anesthesia has already been achieved.
Gel injections into the anterior zygomatic area are performed sequentially on both sides of the face until optimal correction parameters are achieved.
For successful aesthetic correction, it is necessary to determine the dominant zones and their subordination at the diagnostic stage, and base all cosmetic interventions on aesthetic and morphometric analysis.
Gel correction of the lateral cheekbone
Many patients consider insufficient convexity of the lateral part of the cheekbone to be a significant aesthetic defect.
Anatomically, this section of the cheekbone is partly formed by its body and partly by its temporal process, or the so-called arch. Its superficial fatty compartments are separated by rather weak, vertically oriented connective tissue septa. In this regard, superficial introduction of hyaluronic gels can lead to their displacement into the underlying buccal area. To prevent this displacement and create a sculptural convexity of the lateral cheekbone, the main part of the drug must be injected into the lateral portion of the deep inferior orbital fat (SOOF): its upper border is the suspensory ligament of the orbicularis oculi muscle (ORL), the lower - the zygomatic ligament (ZL), the “roof” "- orbicularis oculi muscle (OOM), "bottom" - periosteum of the zygomatic bone.
The introduction of gels into this anatomical formation allows you to obtain long-term correction results and create a strong lateral vector of the cheekbone.
We insert the cannula from the same point as for correcting the nasobuccal groove and direct it laterally into the above compartment. Further, to ensure a smooth transition from the zygomatic zone to the cheek, correction can be supplemented with superficial administration of the drug.
It should be taken into account that an increase in the convexity of the lateral part of the cheekbone can lead to a visual deepening of the overlying temporal and underlying buccal zones, so at the final stage of correction it is sometimes necessary to ensure smooth transitions between them.
Contour correction of the temporal region
The objectives of correction in the temporal region are to eliminate depressions, mask signs of skeletonization and ensure a visual expansion of the boundaries of the forehead and a smooth transition from the frontal zone to the temple.
The upper border of the temporal zone is the superior temporal septum - a vertically oriented connective tissue running from the temporal suture to the surface of the skin (to simplify understanding, it is better to consider it the temporal suture itself). In front, the temporal region is limited by the lateral bony edge of the orbit (connected by the frontal process of the zygomatic and the zygomatic process of the frontal bones).
The lower border of the temporal zone is represented by the upper edge of the zygomatic arch.
The anatomical posterior border is also the temporal suture, but for contour correction, the aesthetic border of this zone is relevant - the hairline.
Layer anatomy demonstrates 5 traditional layers:
1) skin, 2) subcutaneous fat, 3) superficial temporal fascia, 4) weak areolar vascular tissue (analogous to deep fat), 5) deep temporal fascia.
In this area, it is most easy, safe and effective to inject filler between the superficial and deep temporal fascia using a 25G/40mm cannula from the entry point located in the forehead. We mark the puncture point with the trocar on the frontal bone 1 cm above the eyebrow, above the temporal suture. We insert the cannula supraperiostally, perpendicular to the surface of the forehead, until it touches the periosteum. Then we unfold it parallel to the periosteum, pierce the superior temporal septum and automatically move to the surface of the deep temporal fascia (the cannula slides along the fascia).
To avoid discomfort in the patient while determining the injection level, the puncture site with the trocar should be anesthetized with lidocaine and adrenaline. Here it is also recommended to first use antegrade injection of lidocaine-containing filler, and then, after the onset of anesthesia, the usual retrograde one.
Depending on the severity of the depression, low- or medium-viscoelastic preparations are preferred, ensuring good integration with this delicate area.
Usually, 1 ml of the drug is enough to correct one temporal zone.
It must be remembered that eliminating the depression in the temporal zone can lead to the visual effect of increasing the depressions in the frontal zone, so if necessary, the drug must also be injected into it. The goals and objectives of correction are considered completed if all signs of skeletonization can be masked.
If in other zones the integration of the gel takes an average of 4 weeks, then in the temporal zone it may take longer, during which the surface of the zone looks uneven due to poor distribution of the gel under thin tissues.
Forehead correction
Elimination of depressions and masking of signs of skeletonization in the temporal zone often make morphological and involutional changes in the adjacent frontal zone more noticeable.
Here are the neurovascular bundles: supratrochlear (projected on the perpendicular passing through the medial edge of the iris) and supraorbital (on the midpupillary perpendicular), which emerge from the corresponding supraorbital recesses on the upper edge of the orbit and cross the forehead from bottom to top. It is easy to assume that the septa of these particular neurovascular bundles divide the frontal fat into compartments.
In addition, the forehead correction area is separated from the temporal by the superior temporal septa, which is the lateral border of the temporal compartments.
To create a smooth transition between the interconnected temporal and frontal zones, visually widen the forehead, eliminate depressions and avoid embolism, it is better to administer gels here using large-diameter cannulas.
We choose the entry point for the cannula arbitrarily, next to the depression zone, insert the cannula perpendicular to the surface of the forehead and up to the periosteum, then turn it around and move it parallel to it.
I would like to emphasize that needle insertion is more dangerous. When it is perpendicular to the periosteum, the gel is distributed only within one compartment, so longitudinal administration through the cannula is more preferable.
The forehead area is characterized by significant pain during injection, so it is necessary to use lidocaine-containing preparations.
To obtain the necessary correction parameters, as a rule, gels of medium and low viscosity and elasticity are sufficient.
So, we looked at methods of administering stabilized hyaluronic acid preparations for aesthetic correction of the upper and middle third of the face. In conclusion, I will once again emphasize the most important points.
A person should be assessed as a whole, as a set of structural units - zones. Correcting them in isolation is impractical and incorrect, since improvements achieved in one zone can cause visual deterioration in others adjacent to it. For successful aesthetic correction, it is necessary to determine the dominant zones and their subordination at the diagnostic stage, and base all cosmetic interventions on aesthetic and morphometric analysis.
And we remember the main thing in the new image being created - the smoothness of lines and transitions.
Margarita Egorova, dermatologist, cosmetologist, medical director, Moscow
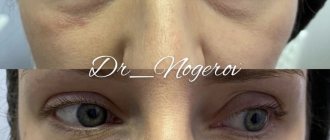
Result after correction of the zygomatic region
Usually the entire procedure takes no more than 20 minutes. But as a result, the effect exceeds all expectations. Because only VOLUMA can resist deformation and flattening under pressure of so many layers of overlying tissues, again, thanks to its structure, which fundamentally distinguishes it from Ultra 2,3,4. The lifting capacity of the drug is so great that the volume lasts up to 4 years.
Swelling never occurs because the drug is properly placed deep. It is possible to reach the medial compartment with Ultra 4, and perhaps this is offered somewhere in training. But I repeat, I never do this, because Ultra 4 is too light and will not withstand the pressure of the tissues, therefore, it will not give good volume.
It is very successful to place Exellens Visage (Aptos) threads after VOLUMA to complete the look. More on this in the section on threads.
If you are really looking for your doctor...
Why is she becoming so visible?
The main reason for the bluish color of the furrow is that the vessels and orbicularis oculi muscle are visible through the skin. Triggers for the formation of this deficiency are age-related or genetic “weight loss” of adipose tissue under the eyes. Because of this, the relief of this area changes, unnecessary shadows are formed, which visually gives the eyes a tired look.
Most often, a pronounced furrow becomes noticeable after 35-40 years.
Wrong lifestyle
Healthy sleep, a well-balanced diet, frequent walks in the fresh air and regular physical activity are key components of a healthy lifestyle.
If you constantly sleep poorly, eat poorly, do not provide your body with adequate rest and spend most of your time indoors, moving little, this can lead to various negative phenomena over time.
First of all, an incorrect lifestyle will affect your health and appearance. Nasolacrimal trenches and bags under the eyes are some of the most common consequences.