Botox shelf life after opening the bottle
In studies of more than 100 patients, 85 ampoules of Botox were used to eliminate age-related facial skin imperfections. The material that remained after the procedures was stored in the refrigerator for a month. After the expiration of the period, examinations were carried out to identify fungi or bacteria in the preparation. As a result of the research, no changes in the composition of the solution were identified, but the experts who conducted the research do not recommend storing the reconstituted botulinum toxin for more than 24 hours. But during the survey, most doctors store Botox for 3 to 7 days, since the effect of action is significantly reduced.
Botox lyophilisate for intramuscular injection solution 100 units fl
Active substance
botulinum toxin type a
pharmachologic effect
Muscle relaxant. The botulinum toxin type A molecule consists of two chains: a heavy chain (with a molecular weight of 100,000 Daltons) and a light chain (with a molecular weight of 50,000 Daltons), connected by a disulfide bond.
The heavy chain has a high affinity for specific receptors localized on the surface of target neurons. The light chain is characterized by Zn2+-dependent protease activity. It is specific for the cytoplasmic regions of the synaptosomal associated protein with a molecular weight of 25,000 Daltons (SNAP-25), which is involved in the processes of exocytosis.
The first stage of action of botulinum toxin type A is the specific binding of the molecule to the presynaptic membrane.
The second stage is the penetration of the bound toxin into the cytoplasm of neurons through endocytosis. Inside the cell, the light chain exhibits Zn2+-dependent protease activity, selectively destroying SNAP-25, which in the third stage leads to blockade of acetylcholine release from the presynaptic terminals of cholinergic neurons.
The end result is prolonged chemodenervation.
Clinically, there is a pronounced relaxation of the muscles into which the injection was made. In denervated muscles, the process of reinnervation occurs due to the formation of lateral processes of nerve endings 12 weeks after injection, which leads to the restoration of muscle contractions. However, the processes are partially effective and subsequently regress while primary neuromuscular transmission is activated.
Indications for Botox
- blepharospasm;
- hemifacial spasm;
- cervical dystonia (spasmodic torticollis);
- focal spasticity of the wrist and hand in patients who have had a stroke;
- paralytic strabismus (strabismus);
- local muscle spasm in cerebral palsy in children aged 2 years and older;
- correction of facial wrinkles.
Dosage regimen
Rules for the preparation and storage of solution for injection
The preparation of the solution for injection and the collection of the solution into the syringe should be carried out on a work surface covered with a paper towel on a polyethylene lining, which makes it possible to quickly remove the spilled drug. Botox restoration is carried out only with 0.9% sodium chloride solution for injection. The injection solution is prepared by piercing the stopper with a sterile needle and introducing the required amount of solvent into the vial. If the solvent is not drawn into the vial under vacuum, the vial is destroyed. Before puncturing, the central part of the rubber stopper must be treated with alcohol. To pierce the cork, use a sterile 23-25 G needle.
The solvent should be carefully introduced into the bottle (see table above), mixing the powder with the solvent with light rotational movements of the bottle. Vigorous shaking of the vial and the formation of foam can lead to denaturation of the drug. The finished solution is a clear, colorless or slightly yellowish liquid without foreign inclusions; slight opalescence may be observed.
Reconstituted Botox® can be stored in the refrigerator at a temperature of 2°-8°C for 24 hours. The prepared solution is administered using an insulin syringe with a non-removable needle. Once reconstituted, the product must be used within 24 hours if stored correctly. Unused solution must be discarded.
The units of action of botulinum toxin in different preparations are not interchangeable. Recommended doses expressed in units of action for Botox differ from those for other botulinum toxin preparations.
No adequate dosing studies have been conducted in elderly patients. The same doses are used as in adults, but the use of the minimum effective dose is recommended.
Botox injections must be performed by a qualified physician who has undergone special training and received permission from the manufacturer. Injections can be performed on an outpatient basis in a treatment room.
The Botox dose and injection points are determined individually for each patient in accordance with the severity and location of muscle hyperactivity. In some cases, electromyography (EMG) is used to more accurately determine the localization of the pathological process.
Treatment of blepharospasm and hemifacial spasm
The Botox solution is injected with a needle measuring 27-30G/0.4-0.3 mm. To treat bilateral blepharospasm, the drug is injected superficially into the upper eyelid into the medial and lateral sections of the orbicularis oculi muscle and into the lower eyelid into the lateral section of the orbicularis oculi muscle. Other points for injection: the pretarsal part of the orbicularis oculi muscle, the eyebrow area and the forehead area (if the spasm that occurs in it affects vision). To prevent the occurrence of ptosis, as a complication of the procedure, it is necessary to avoid administering the drug near the muscle that lifts the upper eyelid. To prevent diplopia, as a complication of the procedure, it is necessary to avoid injecting the drug into the medial part of the lower eyelid.
The initial dose is 1.25-2.5 units of the drug at each injection point. The total initial dose should not exceed 25 units on each side. The effect of the drug appears during the first three days after the procedure and reaches its maximum severity 1-2 weeks after it. The duration of the effect of the drug reaches 3 months, after which the procedure can be repeated.
If the effect of the initial treatment is regarded as insufficient, when the drug is re-administered, the dose can be increased by no more than twice. However, the introduction of more than 5 units of the drug at each injection point is not accompanied by a significant improvement in the clinical effect.
When treating blepharospasm, the total dose of Botox over 12 weeks should not exceed 100 units.
Treatment of patients with hemifacial spasm is carried out in the same way as with unilateral blepharospasm; if necessary, injections of the drug are also carried out into other affected facial muscles. The total dose of Botox for the treatment of hemifacial spasm should be the same as for blepharospasm.
The safety and effectiveness of Botox in the treatment of blepharospasm and hemifacial spasm in children under 12 years of age have not been demonstrated.
Treatment of cervical dystonia (spasmodic torticollis)
The Botox solution is injected with a needle measuring 25-30G/0.5-0.3 mm.
When treating spastic torticollis, the drug solution is injected into the most tense muscles of the neck in a dose of no more than 50 units at each point.
No more than 100 units of the drug is injected into the sternocleidomastoid muscle.
The total dose of the drug during the first procedure should not exceed 200 units.
When treating spastic torticollis, the drug is injected into the sternocleidomastoid muscle on the side opposite to rotation, and into the splenius muscle on the side of rotation.
In cases accompanied by shoulder elevation, the drug should be additionally injected into the trapezius muscle and the levator scapulae muscle on the affected side.
When tilting the head back, the drug is injected into the splenius and trapezius muscles on both sides.
When the head is tilted forward, the drug is injected into the sternocleidomastoid muscles on both sides.
With subsequent administration, the dose of the drug may be adjusted depending on the previous clinical result and observed side effects.
Clinical improvement appears within the first two weeks after injection of the drug. The most pronounced clinical effect is achieved approximately 6 weeks after injection. The duration of the clinical effect reaches an average of 12 weeks, after which, if necessary, treatment can be repeated. Intervals between therapy sessions of less than 10 weeks are not recommended.
In case of complex forms of torticollis or weak effect of treatment, EMG of the neck muscles should be performed to more accurately determine the localization of tense muscles.
The safety and effectiveness of Botox in the treatment of spasmodic torticollis in children under 12 years of age have not been demonstrated.
Treatment of local muscle spasm in cerebral palsy
The Botox solution is injected with a needle measuring 23-26G/0.6-0.45 mm.
When treating spasticity and equinovarus deformity of the foot in children with cerebral palsy, the drug solution is injected into 2 points of each head of the gastrocnemius muscle (medial and lateral). In case of hemiplegia, the drug can be injected into the flexor muscles of the forearm, and when crossing the hips - additionally into the adductor muscles of the thigh. The total dose of the drug for one procedure is determined at the rate of 4-6 units/kg body weight and is distributed evenly between all muscles into which injections are performed. The total dose should not exceed 200 units.
Clinical improvement is evident in the first 7-14 days after injection. The drug is re-administered when the severity of the clinical effect is reduced by half, but not earlier than 3 months after the previous procedure. The dose of the drug is selected in such a way as to achieve at least a 6-month interval between procedures. Orthopedic correction, muscle stretching, and physical therapy can help improve the clinical effect of Botox injections.
Treatment of focal spasticity of the wrist and hand in stroke patients
The Botox solution is injected with a 25G, 27G, or 30G needle into the superficial muscles and a longer needle into the deep muscles.
To establish the localization of the muscles involved in the pathological process, EMG control or nerve fiber stimulation methods can be used. Injecting Botox into several points can help distribute it more evenly in the muscle, which is especially justified when injecting the drug into large muscles.
Selection of the exact dose of the drug and the number of injection points must be carried out individually in accordance with the size, number and location of the muscles involved in the pathological process, the severity of spasticity, the presence of local muscle weakness and the nature of the patient’s response to previous treatment.
Positive changes in muscle tone were noted within 2 weeks after injection, the maximum clinical effect was observed, as a rule, no later than 4-6 weeks.
In cases where the attending physician considers it necessary to re-administer the drug, it can be done after the effect of the drug on muscle tone has decreased. The interval between injections should be at least 12 weeks. Changing the degree and nature of muscle spasticity before re-introducing the drug may require adjusting the Botox dose and identifying new injection points. The minimum effective dose must be used.
In patients with focal spasticity, Botox® is used in combination with a standard treatment regimen. The drug is not intended to be used as a replacement for these treatments.
Treatment of paralytic strabismus (strabismus)
The Botox solution is injected with a 27G needle.
Botox is injected into the muscles of the eyeball under EMG control. To prepare the eye for a Botox injection, it is recommended to instill several drops of a local anesthetic and decongestant into the conjunctival sac a few minutes before the procedure.
For minor deviations of the eyeball, minimal doses of the drug are used; when treating more pronounced deviations, the dose is increased.
Initial doses:
when injected into the muscles that carry out vertical movements of the eyeball (superior and inferior rectus muscles) and with horizontal strabismus, less than 20 prismatic diopters: from 1.25 to 2.5 units for any muscle;
for horizontal strabismus from 20 to 50 prismatic diopters: from 2.5 to 5 units for any muscle;
with abducens nerve (VI nerve) palsy that persists for 1 month or more: from 1.25 to 2.5 units in the medial rectus muscle.
The initial effect is observed 1-2 days after the procedure, increases during the first week, persists for 2-6 weeks and gradually decreases over the same time period. Rare cases of persistence of the effect for more than 6 months have been described.
Approximately half of the patients after the first injection of the drug require repeated administration due to an inadequate clinical response of the muscles to the first procedure or due to mechanical factors: significant deviation or limitation of the mobility of the eyeballs, as well as the inability to stabilize the position of the eyes due to the motor component of binocular fusion (fusion) . It is recommended to examine patients 7-14 days after each injection to assess the effect of the procedure. In patients with incomplete relaxation of the target muscle during subsequent administration, the dose of the drug can be doubled.
Repeated administration of the drug should be carried out only after the clinical effect from the previous procedure has decreased, which is expressed in a stable restoration of the function of the injected and adjacent muscles.
The maximum recommended dose for a single injection into any muscle for the treatment of strabismus is 25 units.
Correction of facial wrinkles
It is not recommended to use Botox for the correction of vertical facial wrinkles between the eyebrows in patients under 18 and over 65 years of age.
Botox solution (100 units/2.5 ml) is injected with a 30G needle.
4 units are injected into 5 injection points: into the musculus corrugator - 2 points on each side, into the musculus procerus - 1 point. The total dose is 20 units.
Before administering the injection, it is necessary to press the thumb and forefinger firmly against the skin below the edge of the orbit to prevent the drug from spreading below this level. When performing an injection, the needle should be directed upward and medially. To reduce the risk of developing ptosis, it is necessary to avoid administering the drug near the levator palpebrae superioris muscle, especially in patients with well-defined levator palpebrae superioris muscle. When injecting the drug into the corrugator musculus, the injection must be made into the central part of the muscle, retreating at least 1 cm above the arch of the eyebrow.
Smoothing of vertical facial wrinkles between the eyebrows occurs, as a rule, within a week after the procedure. The effect lasts up to 4 months.
The interval between procedures should be at least 3 months. If there is no effect from the administration of the drug or a decrease in its severity after repeated injections, other treatment methods should be recommended.
For all indications for use
If the first procedure is ineffective, i.e. In the absence of significant clinical improvement compared to the initial state, 1 month after administration of the drug, it is necessary:
clinical confirmation of the effect of the toxin on the injected muscle(s), which may include an EMG study performed by an experienced specialist in a specialized department;
analysis of the reasons for the ineffectiveness of the procedure, for example, inadequate selection of injection points, insufficient dose, incorrect injection technique, signs of fixed contracture, weakness of antagonist muscles, formation of toxin-neutralizing antibodies;
re-evaluation of the appropriateness of treatment with botulinum toxin type A;
in the absence of any undesirable effects associated with the first administration of the drug, the following conditions must be met during the repeated procedure: dose adjustment taking into account the analysis of the reasons for the ineffectiveness of the previous procedure; EMG control; the interval between procedures should be at least 3 months.
If there is no effect from the administration of the drug or a decrease in its severity after repeated injections, other treatment methods should be recommended.
Before use, consultation with a specialist is required.
The method of administration and dosage regimen of a particular drug depend on its release form and other factors. The optimal dosage regimen is determined by the doctor.
Storage mode, interactions and side effects are indicated in the instructions.
Contraindications for use
Are common
- proven hypersensitivity to any component of the drug;
- inflammatory process at the site of the proposed injection(s);
- acute phase of infectious diseases;
- pregnancy;
- lactation.
For blepharospasm and correction of facial muscles
- pronounced gravitational ptosis of facial tissues;
- pronounced “hernias” in the area of the upper and lower eyelids.
Operating principle
All such drugs are based on the property of the main active ingredient - botulinum toxin - to block the passage of nerve impulses to the muscles.
A few hours after its administration, temporary paralysis occurs and the muscles completely relax. And the skin in the places of creases above them gradually smooths out. The drugs are extremely toxic. Even when used in microdoses, they provoke mild symptoms of poisoning - headache, nausea, decreased vision clarity. In case of an overdose, they intensify many times over and can lead to extremely unpleasant consequences, including anaphylactic shock or cardiac arrest.
Only cosmetologists with medical education and special training work in Botox offices. Additional training is very important, since at such seminars, manufacturer representatives tell all the intricacies of using a particular product. And even among analogues, the rules for calculating the dosage and dilution of drugs can differ quite significantly.
How to dilute Botox with saline solution?
First of all, let us clarify that we are taking a look at how Botox is diluted for informational purposes. Everyone decides for themselves whether to go to a specialist or do the procedure themselves. But we recommend the former, since botulinum toxin is unpredictable, and even experienced doctors do not always know what effect it will have on a particular patient.
Know how to dilute 100 units. Botox is useful for anyone who intends to undergo an anti-aging procedure. This will help you understand the essence of the process and, if necessary, ask a specialist questions of interest.
Botox is sold as a lyophilized mixture. In simple terms, it is a special powder that will be suitable for use only after dilution. Today on the Internet you can find offers to purchase pre-prepared mixtures. However, professional cosmetologists do not buy such compositions because they do not trust them.
The drug is marketed in glass bottles and is a white powder. The container with the product is always accompanied by detailed instructions for dilution, containing not only points with recommendations, but also a table with which the cosmetologist can calculate the number of units required for a particular case.
The accuracy of the calculations is extremely important. An error of just 1 ml can significantly reduce the effectiveness of the resulting solution, or, conversely, lead to an overdose.
Here is a step-by-step algorithm of actions that a professional should follow when preparing a solution for Botox injections:
- The work surface is covered with a sterile cloth. The specialist puts on rubber gloves.
- The protective cap of the bottle is removed.
- The cork is wiped with an antiseptic. Never use alcohol.
- A 10 ml injection syringe is filled with saline solution (the consistency depends on the purpose - from 0.5 ml to 8 ml).
- A puncture is made in the lid through which saline solution is introduced into the container.
- Shake the bottle until a homogeneous mass is obtained.
- The finished product is distributed into small injection syringes.
Important: if the powder does not dissolve and forms lumps, the product should be thrown away as it has spoiled.
How much Botox is needed for different parts of the face?
After diluting the drug, the cosmetologist faces another, no less important, task - calculating the dosage. You can also read the instructions on how to do it. However, in addition to professional recommendations, the doctor must take into account such individual factors as:
- skin condition;
- depth of creases;
- patient's age;
- input frequency;
- dermis thickness, etc.
If the manipulation is done for the first time, it will take more money than will be needed for subsequent administrations. As a rule, one point requires the injection of 1-2 units of the drug. You should also consider which area of the face or body is being treated. Here is a table that will help you determine where to inject how much:
| No. | Zone | Required number of units | Number of insertion points and insertion site |
| 1. | Elimination of eyebrow wrinkles | 8-16 | 4-6 |
| 2. | Outer corners of the eyes | 6-10 | individually |
| 3. | Closer to the inner edge of the eye, above the eyebrow line | 6-10 | individually |
| 4. | Nasalis muscle | 1-2 | 1-2 |
| 5. | Perioral muscles | 1 | under the lower lip - 2, above the upper lip - 4 |
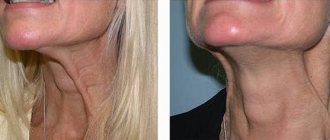
| 6. | Neck | 2 | on both sides of the muscle area, distance between punctures 2 cm |
An optimal scheme is proposed. However, the cosmetologist must decide whether to follow it or make independent decisions. In addition to correctly calculating the number of units and choosing the puncture site, the position of the needle and the depth of its insertion are important. The slightest mistake can lead to unpleasant aesthetic or physical results. So, if a large amount of Botox is injected into the neck area, patients will have difficulty eating and swallowing saliva.
What is a unit
Those who are already familiar with beauty injections know that the cost of the procedure directly depends on the volume of the drug used. And it is calculated in conventional units. This is a universal international designation that allows you to correctly calculate the dosage.
One unit is a dose of type A neurotoxin that, when administered, kills 50% of a population of laboratory mice. Naturally, it is relatively safe for humans. But it is also not enough to get the desired result.
Indications for the use of Botox
- Blepharospasm is an uncontrollable spasm of the orbicularis oculi muscle that provokes persistent contractions of the eyelid.
- Hemifacial spasm - painless periodic spasms of the facial muscles
- Paralytic strabismus
- Spasmodic torticollis - tension in the neck muscles that causes the head to be positioned incorrectly
- Local muscle spasm in adults and children over 2 years of age
- As a cosmetic procedure in the presence of facial wrinkles in the following areas: forehead, bridge of the nose, corners of the eyes, upper lip, neck
Contraindications for the use of Botox
- myasthenic and myasthenic-like syndromes
- tissue infections in the injection area
- concomitant use of aminoglycosides or spectinomycin
- pregnancy
- lactation
- sensitivity to the components of the drug
- generalized movement disorders
- bleeding disorder
- high myopia
Precautionary measures
- The administration of the drug should only be carried out by a qualified physician who has been trained and has permission from the injection manufacturer. If a specialist is unprofessional, there may be negative consequences, such as
- – injuries to important areas and structures (damage to nerves, blood vessels)
- — the possibility of infection if hygiene requirements are not followed
- The substance is administered using a 27-30 gauge needle
- The procedure takes about 15 minutes. After injections, the skin areas are treated with an antiseptic and ice is applied to the injection sites
- After administration of the drug, it is recommended to remain in an upright position for up to 4 hours.
- During the day after administration of the drug, you should
- do not strain the treated muscles
- avoid bending over and lifting heavy objects
- do not massage the injection areas
- don't drink alcohol
Composition of drugs
Both drugs contain water-soluble protein Albumin (Albuminum humanum) and sodium chloride.
Difference between Botox and Botulax:
- production technology;
- cleaning level;
- auxiliary components;
- dosage;
- price.
Let's look at each tool in more detail.
…
Botox
A classic anti-aging product with botulinum toxin, it has long been successfully used in cosmetology and medicine. Produced by the American company Allergan. World famous, well studied. The effect lasts up to 6-8 months.
Compound:
- purified class A botulinum toxin to suppress muscle impulses and relax muscles;
- Albumin is a protein for tissue repair;
- sodium chloride is a solvent for the ingredients of the drug.
Storage method: at temperatures from -3o to -17o.
…
Botulax
Manufactured by the South Korean company Hugel Inc. The effect lasts up to 4-6 months.
A relaxing antipsychotic with a good effect on facial muscles. The basis of the composition is highly concentrated protein botulinum toxin A. For stabilization, auxiliary ingredients are present. Injections are carried out slowly - foaming may occur if injected quickly.
Compound:
- Category A protein neurotoxin;
- simple water-soluble proteins in whey;
- sodium chloride 0.9%.
The prepared solution is stored for no more than a day at temperatures up to +7o.
Description of the procedure
Stages of botulinum therapy:
- Before injections, the face is thoroughly cleansed of dirt, sebum, and makeup.
- Application of anesthetic gel to relieve pain.
- The drug is prepared in accordance with the intended dosage regimen. The required number of units is calculated depending on the segment of the face in which the injection is given.
- Administration of injections according to the scheme.
- Compress for the prevention of edema and hematomas.
- Recommendations for skin care.
The procedure takes 20-45 minutes, upon completion the client quickly returns to normal life. After 3-5 hours, visible results are already visible. All that remains is to observe the changes and follow all the specialist’s recommendations.
Summing up
The opinion of experts is categorical. Even if you know exactly how to dilute Botox and calculate its dosage, you should never give beauty injections at home yourself. It’s better to find an experienced cosmetologist and trust him with your face - this way the risk of side effects is much lower.
Professionals also know other secrets of using Botox. For example, when in contact with alcohol, its effectiveness decreases sharply. Therefore, injection sites are wiped with antiseptics that do not contain it. As you can see, in such a simple procedure at first glance, there are a lot of nuances. And therefore the price for it in good salons is quite high. But they also guarantee results.
A few words about the Botox procedure
Cosmetologists have been successfully using botulinum toxin, which can prolong youth, for more than 30 years. Its main function is muscle relaxation. As soon as the facial muscles relax, facial wrinkles are smoothed out. Women look 5-10 years younger without effort or serious discomfort.
The word “Botox” has long become a household word. The main drug with a popular name has a lot of analogues. The most common are:
- Xeomin;
- Dysport.
Each product has its own instructions for dilution and use. The most important thing is the ability to correctly dilute 100 units (units) of the drug with saline solution.
Anyone can buy Botox and its analogues if they wish. Many women believe that they can do without a certified specialist. To avoid making mistakes, you need to carefully study the instructions and strictly follow the recommendations of professionals.