According to Nika, the sculpting technique, the meaning of which is to lighten and darken certain areas on the face, will help to correct the nose. To “sculpt” the desired shape, you will need dark and light shades of cream or powder texture. By the way, cream products will last much better and longer.
To make your makeup look as natural as possible, it is important to blend the edges of your beauty products well. Adding natural shadows and highlights will also help to avoid the mask effect. A highlighter will do the job perfectly.
If your nose is uneven
Such a defect occurs due to previous injuries or illnesses. Due to the fact that the shape of the nose in this case is individual, you can only use the general principles of correction.
Apply a dark tone to areas that need to be reduced, and light shades or highlighters to areas that need volume.
Let's say the nose is curved and, when viewed from the front, has a convexity on the right side and a concavity on the left. With such asymmetry, the right side is darkened, as in the case of a “potato” nose. The darkening area is defined where the bulge itself begins and ends.
Other correction methods. Why rhinoplasty is the most reliable method
To correct the nose, surgeons use different surgical techniques depending on the wishes of the client and the result that the patient expects to receive. However, you can find other methods for correcting the tip of the nose on the Internet.
Clamps
In online stores you can find so-called “nose correction clips”. Manufacturers assure that when wearing correctors 2-3 times a day, an effect will be noticeable, comparable to surgical intervention. But, naturally, this is far from the truth. No clamps or other devices from pseudo-specialists are suitable for nose correction. If there is any effect, it will be short-term - for 2-3 weeks, and the correction is insignificant.
Exercises
There is a set of exercises for the face that allows you to adjust its shape. These exercises are useful for maintaining muscle tone, correcting cheekbones and double chin, but they will not correct the shape of cartilage. The effect after systematic exercise lasts for 2 weeks.
Correction with threads
The thread technique is carried out by a specialist with a special needle through micropunctures. Specially designed threads with notches are inserted into the skin of the nose to form a frame. The threads are inserted through small punctures, and the frame keeps it in the desired position. After two days, the doctor removes the ends of the threads and the patient sees the final result, which lasts about 3 years.
Use of hormonal drugs
To correct the tip of the nose, you can also take a course of hormonal medications. First of all, you need to consult an endocrinologist. If there are no contraindications, a hormonal drug can be administered. This procedure is performed to remove excess soft tissue and elevate the tip. For correction, you need to undergo a course of procedures that will last from 2 to 3 weeks. It is worth noting that the drugs provide a temporary effect - from 3 months to 2 years, depending on the drug chosen.
Surgical correction
According to experts, rhinoplasty is the most reliable and effective method of correction. Unlike previous methods, rhinoplasty provides lifelong results. Plastic surgery lasts 1–2 hours under local anesthesia or general anesthesia. Main advantages of the operation:
- all possible correction options (lower or raise the tip, reduce, straighten or narrow the tip of the nose);
- eliminating breathing problems;
- lifelong outcome;
- correction of injuries and birth defects.
Treatment of deviated nasal septum
Deviated nasal septum is treated surgically. The main type of operation that is performed in most cases is septoplasty.
Indications for surgery for deformities of the nasal septum:
- Difficulty in nasal breathing on one or both sides . Surgical intervention is absolutely indicated provided that the difficulty in breathing is caused precisely by a deformation of the nasal septum.
- Chronic rhinitis is inflammation of the nasal mucosa.
- Otitis and eustachitis (inflammation of the middle ear and auditory, or Eustachian, tube), the initial cause of which is a violation of the shape of the nasal septum.
- Inflammation of the paranasal sinuses (sinusitis): sinusitis, ethmoiditis (inflammation of the cells of the ethmoid bone). Surgery is indicated if these complications are caused by a deviated nasal septum.
- Frequent, recurring headaches.
Contraindications to septoplasty for deviated nasal septum:
- Senile age. With age, breathing problems caused by a deviated nasal septum are partially compensated. Therefore, the symptoms of the disease become less pronounced. In older people, atrophy of the nasal mucosa occurs, so the operation is difficult and the risk of complications is high.
- Blood clotting disorder. For example, septoplasty is contraindicated in people with hemophilia.
- Severe diseases of the cardiovascular system.
- Mental illnesses.
- Malignant tumors.
- Severe infections.
- General serious condition of the patient.
- Children and people over 48 years of age can undergo surgery, but the indications for it at this age are narrowed.
How to avoid complications after surgery
To minimize the risk of complications after rhinoseptoplasty, you must strictly adhere to medical recommendations. The rehabilitation period after surgery lasts several months. During this time, the soft tissues grow together and the cartilage is restored. Primary rehabilitation takes 7 days. During this period, hematomas and swelling should subside.
For faster tissue healing, experts recommend using special ointments and creams. The seams are treated daily with an antiseptic. Saline solutions are used to cleanse the nasal cavity. A week after rhinoplasty, the splint and stitches are removed. During this period, mild swelling may persist.
3-4 weeks after surgery, the result becomes more noticeable. The seams become lighter and the shape of the nose is restored. The scarring process takes 8-12 months. After the required time, the scars become light and soft. Small nodules may remain in the affected area, almost invisible to the naked eye.
During the period of primary rehabilitation, the patient should regularly use local medications that help relieve swelling and eliminate hematomas. Various physiotherapeutic procedures accelerate the healing process of damaged soft tissues and lymph outflow.
It is also important to follow a strict diet. On postoperative days, you should avoid sour, spicy and salty foods. It is recommended to completely stop drinking alcohol. You need to visit your doctor at least 2 times a week.
Disorders that occur when the nasal septum is deviated
Difficulty in nasal breathing
Pathological mechanisms that lead to difficulty in nasal breathing when the nasal septum is deviated : 1. Narrowing of the nasal passage on the side of the bulge of the septum . Reducing the volume of space on one side leads to difficulty in the passage of air flow, up to the complete inability to breathe through one nostril.
2. Violation of air dynamics inside the nasal cavity . Normally, during inhalation, the air in the nose rises and passes through the middle and partially upper nasal passage. During exhalation, it is directed into the lower nasal passage. When the nasal septum is deviated, disruption of air flow even through one nasal passage leads to difficulty breathing. Despite the fact that the other two nasal passages on the same side may have normal clearance.
3. Narrowing of the nasal passage and difficulty breathing on the side of the concavity of the deformed nasal septum. Often the symptoms here are even more pronounced than on the side of the convexity. As a result of the expansion of the nasal passage, compensatory hypertrophy (growth) of the nasal concha occurs. Over time, they become so large that they begin to make breathing difficult.
4. Reaction of nerve endings (receptors) of the mucous membrane of the nasal cavity . Normally, the air flow in the nose is uniform. When the nasal septum is deviated, turbulence occurs in it. They irritate sensitive receptors located in the mucous membrane. A reflexive defensive reaction occurs: the vessels of the mucous membrane dilate, swelling occurs, and a large amount of mucus is released.
5. Suction of the wing of the nose to the septum . This is often noted when the septum is deviated in the anterior part. The wing of the nose is constantly tightly adjacent to the septum, as a result, the passage of air is greatly hampered.
Changes in the nasal mucosa
Normally, the mucous membrane of the nasal cavity produces a certain amount of mucus, which humidifies the air and performs protective functions. On the surface of epithelial cells there are cilia. They constantly make movements that remove dust and other small particles from the nose. As a result of turbulence, the air in the nasal cavity constantly hits the mucous membrane in a certain place. Here it thickens, epithelial cells lose cilia. The protective functions and the process of cleansing the mucous membrane from foreign particles and mucus are disrupted. The secreted mucus dries, forming crusts. The mucous membrane of the nasal cavity becomes more vulnerable to pathogens. Rhinitis develops - runny nose, constant nasal congestion.
Oxygen starvation of organs and tissues
The supply of sufficient oxygen to the lungs and blood largely depends on how freely nasal breathing is. When the nasal septum is deviated, gas exchange in the pulmonary alveoli is disrupted. There is a general lack of oxygen in the body.
Mouth breathing
Nasal breathing is the only normal way for humans. When it is disrupted as a result of a deviated nasal septum, mouth breathing is activated. It is less complete in many ways.
Disadvantages of mouth breathing:
- Air that is not humidified or warmed enters the lungs: as a result, gas exchange in the alveoli is not as efficient as with nasal breathing. Less oxygen enters the blood.
- The protective properties of nasal mucus are disabled. The likelihood of developing a respiratory infection increases.
- Mouth breathing can eventually lead to adenoiditis - inflammation of the pharyngeal tonsil.
Nervous disorders
When the nasal septum is deviated, constant irritation of the nasal mucosa occurs. This leads to complications that are reflexive in nature. Reflex disorders due to a deviated nasal septum :
- Bronchial asthma is a type of disease, the main cause of which is neuropsychic imbalance.
- Spasms of the larynx, manifested in the form of short attacks of suffocation.
- Headache.
- Convulsive epileptic seizures.
- Reflex sneezing and coughing .
- Dysmenorrhea in women is a violation of the frequency and duration of menstruation.
- Disorders of the eyes, heart and other organs.
Violations from neighboring organs
- Eustachian tube and middle ear disorders . The nasal cavity passes into the nasopharynx, on the mucous membrane of which there are pharyngeal openings of the auditory, or Eustachian, tubes on the right and left. The Eustachian tube connects the nasopharynx with the middle ear cavity (tympanic cavity, which contains the auditory bones: incus, stapes, malleus ). A chronic inflammatory process as a result of a deviated nasal septum leads to the fact that mucus and infectious agents can enter the auditory tube and the tympanic cavity.
- Inflammation of the paranasal sinuses - sinusitis . A direct connection has been proven between a deviated nasal septum and the development of inflammatory processes in the paranasal sinuses. Such patients often develop sinusitis (inflammation of the mucous membrane of the maxillary, or maxillary sinus) and frontal sinusitis (inflammation of the frontal sinus).
- Inflammation of the tear ducts and lacrimal sac. Tears, which are produced by the lacrimal glands, normally flow into the nasal cavity through the nasolacrimal duct. It can serve as a route for spreading infection.
Types of deviated nasal septum:
- actual curvature of the nasal septum
- crest
- thorn
- a combination of two or three types of curvature
Varieties of the actual curvature of the nasal septum:
- in a vertical or horizontal plane
- in the front or back of the nasal septum
- one-sided and two-sided
- with the capture of the cartilaginous part of the septum (so-called dislocations of the cartilage occur, when it is torn from the bone), the vertical plate of the ethmoid bone (forms the anterior part of the bony nasal septum) or the vomer (forms the posterior part of the nasal septum)
- S-shaped, C-shaped, in relation to the bony crest of the upper jaw.
The development of complications with a deviated nasal septum depends on the severity and type of deformation. Almost every adult has a slight curvature, but it does not lead to breathing problems. There are cases where significant deformations do not prevent normal air flow.
Deviations of the nasal septum in the anterior part occur more often. The opener located behind is less often caught. The rear edge of the opener is almost always exactly vertical. The ridges and spikes are usually located along the upper or lower edge of the opener. They can have different lengths and are directed in different directions. Sometimes they protrude into the mucous membrane on the opposite side. Most often, spines and ridges consist only of bone tissue. Sometimes their apices may be represented by cartilage. But even a slight curvature of the septum in the front part can create air turbulence, which then intensifies and significantly disrupts nasal breathing.
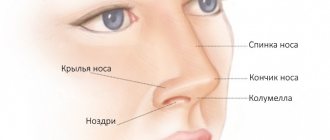
Fig 2
Symptoms of a deviated nasal septum
Complaints that patients with a deviated nasal septum make when visiting a doctor:
- Difficulty in nasal breathing . The symptom can be of varying degrees: from a slight disturbance to a complete inability to breathe through the nose (in this case, the patient breathes through the mouth). However, the absence of this complaint is not a sign that there is also no deviated nasal septum. If the deformation occurs at a young age, the body can compensate for it over time. The patient has no complaints of difficulty in nasal breathing. If the nasal cavity is large, then no difficulties arise either.
- Chronic rhinitis - runny nose . Manifests itself in the form of nasal congestion and constant mucous discharge. Sometimes the patient does not see a doctor for a long time, because he believes that he has frequent colds, and the whole point is a decrease in immunity.
- Allergic reactions . The changes that occur in the nasal cavity as a result of the curvature of the nasal septum are always accompanied over time by a violation of local protective mechanisms and immunity. This manifests itself not only in a decrease in resistance to infections, but also in the appearance of allergic reactions. Allergic rhinitis is a common problem among people with a deviated septum. Chronic rhinitis is a pre-asthma - a condition against which bronchial asthma often develops. The patient complains to the doctor that nasal congestion and discharge occur mainly during contact with some allergen, for example, pollen from certain plants.
- Headache . A spike, ridge, or deviated nasal septum may come into contact with the lining of the nose and put pressure on it. Constant irritation of nerve receptors leads to the development of reflex headaches.
- Dry nose, discomfort and unpleasant sensations during nasal breathing . A symptom that develops as a result of prolonged irritation and inflammation in the nasal cavity.
- Nosebleeds . They are also the result of irritation of the mucous membrane. On the side where there is a bulge on the nasal septum, the mucous membrane is very thin. Even with minor impact it is easily damaged.
- Snoring at night as a result of impaired nasal breathing.
- Increased fatigue, decreased performance, decreased resistance to physical activity . These symptoms are associated with impaired nasal breathing and insufficient oxygen supply to the blood from the lungs.
- Frequent infections that occur with symptoms of acute respiratory infections (runny nose, cough, sneezing), increased body temperature.
- Symptoms of chronic inflammation of the pharynx and larynx : sore throat, dryness and pain, cough.
- Symptoms of inflammation in the middle ear : pain, hearing loss.
- Violation of the shape of the nose . This symptom is characteristic of a deviated nasal septum of traumatic origin.
- In severe cases, the patient and his relatives note periodic convulsive epileptic seizures, blurred vision, heart pain and increased blood pressure, shortness of breath and other symptoms. They can also be associated with deformations of the nasal septum.
- Deterioration of memory, thinking, absent-mindedness . Schoolchildren with a deviated nasal septum experience decreased school performance over time.